* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plate tectonics - mfischerscience
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
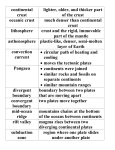
PLATE TECTONICS or: Why Earth Farts CHAPTERS 1 & 17 How old is the Earth? • Recall that Earth is 4.6 billion years old. • Earth has changed a lot in that time. • http://www.wwnorton.com/college/ geo/egeo/flash/2_1.swf What is continental drift? • Earth’s continents had once been joined in a single landmass. • The continents drifted to their present locations. • http://www.wwnorton.com/college/ geo/egeo/flash/2_1.swf What is the • Early observations of drifting evidence for continents • Starting in the 1500’s, people continental noticed that the continents had drift? matching coastlines. • Alfred Wegener came up with the first real theory of continental drift in 1912. He proposed: • The idea of Pangaea, a single landmass. • That the continents began to split apart 200 million years ago (MYA). • That continents slowly moved to their present positions. • Rock formations • Rocks from far apart lands are made of similar material and are similar ages. • This is because mountains and other rock formations split apart. • Ex. Similar rocks in the Appalachian Mountains in the U.S. and in Greenland & Europe. • Fossils • Fossils from related plants & animals were found far apart. • This is because animals living on joined land masses died, and their fossils spread apart over time. • These animals could NOT have swam such long distances. • Ex. Kannemeyerid, Labyrinthodont, & Glossopteris • Climatic patterns • Coal deposits were found in Antarctica. • Coal forms in ancient swamps, and Antarctica used to be nearer to the equator, which made it a swampy habitat. • Glacial deposits were found in Africa, India, Australia, & South America. • This is because these continents used to be closer to the poles. • There are no present glaciers there. What is sea floor spreading? • Seafloor spreading is the idea that new ocean crust is formed at ocean ridges and destroyed at deep-sea trenches. • This involves continuous movement of magma, like a conveyer belt. What is the • Underwater topography • Sonar showed that the sea floor is evidence for not flat. seafloor • Underwater mountain ranges and spreading? deep-sea trenches were discovered and were made through seafloor spreading. • Earthquakes and volcanoes occur there. • Ocean rocks & sediments • Rocks on the sea floor are NOT all the same age. • Rocks near ridges were younger because new magma formed them. • Rocks near trenches were older because they were pushed away from ridges and toward trenches. • Sediments on the sea floor are not as thick as expected. • Sediments get thicker as they get farther away from ridges because they accumulate over time. • Paleomagnetism: study of the earth’s magnetic record • Iron is in basalt, the rock that makes oceanic crust. • Iron orients parallel to earth’s magnetic field as it cools. • So, the seafloor shows a record of magnetic reversals. • A magnetic reversal is a change in Earth’s magnetic field. • There are parallel stripes of magnetic material on either side of a ridge. • This shows that new rock was coming from the ridges. What is the theory of plate tectonics? • Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle (lithosphere) are broken into moving plates. • There are 12 major plates and several smaller ones. • Plate boundaries are the places where tectonic plates meet. What are the • Divergent boundaries • Two plates are moving APART types of • New crust forms there plate • Most form ridges on the sea floor boundaries? • On continents they form rift valleys Rift Valley in Africa Mid Ocean Ridge in the Atlantic Ocean • Convergent boundaries • Two plates are coming TOGETHER • Old crust is destroyed there at a subduction zone • Can be classified as: • Oceanic-oceanic: form trenches & island arcs • Oceanic-continental: form trenches & volcanic mountains • Continental-continental: form folded mountains • Oceanic crust sinks below continental crust because it is more dense. Aleutian Islands Marianas Trench Cascade Mountain Range & Mt. Saint Helens in Washington State Himalayas • Transform boundaries • Two plates SLIDE PAST each other • Crust is deformed there • These boundaries form faults San Andreas Fault in California What causes plate tectonics? • The mantle is made of magma, which is mostly liquid. • Plate tectonics is caused by mantle convection. • Hot magma moves up, and when it cools it moves down. • This is because hot magma is less dense (floats) and cool magma is more dense (sinks). • This creates currents. • The currents cause the plates on top to move. http://education.sdsc.edu/optipu ter/flash/convection.htm