* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHYSICAL FITNESS AND CARDIOVASCULAR ENDURANCE
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
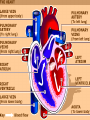
PHYSICAL FITNESS AND CARDIOVASCULAR ENDURANCE LESSON #2 WHAT IS FITNESS? • PHYSICAL FITNESS DEFINITON: – Ability of the whole body (muscles, skeleton, heart & other body parts) to do work together efficiently – Do the most work with the least amount of effort • 2 CATEGORIES – HEALTH RELATED FITNESS – SKILL RELATED FITNESS CARDIOVASCULAR TRAINING • F.I.T.T. FORMULA – FREQUENCY – INTENSITY – TIME/DURATION – TYPE FREQUENCY • How often to exercise • Minimum – 3 X’s weekly • Maximum – 4-5 X’s weekly INTENSITY • How hard to exercise • Minimum – heart rate above the lower limit of your training range • Maximum – heart rate below the upper limit of training range TYPE • The kind of exercise you choose to participate in • Minimum – low impact exercise – walking • Maximum – high impact exercise - running TARGET HEART RATE • Exercise within your target heart rate to get maximum benefits of exercise • Maintain range for at least 15-30 continuous minutes • Maximum heart rate = 220 – age – Fastest your heart can beat without collapse • Target heart rate range = 70-85% of maximum heart rate Factors Affecting Heart Rate • Sex: adult females average 5 – 10 beats per minute more than men due to supporting more body fat • Size: Extra body fat causes the heart to work harder • Temperature: A rise in body temperature will raise the heart rate eg. Hot tub, desert • Ingesting food: It takes extra energy to digest a meal • Posture: The more prone, the lower the heart rate. THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM YouTube - How the Body Works Inside the Heart.url Heart Terminology • Cardio - the heart – about the size of a fist • The Heart – a hollow organ containing 4 chambers • Septum – wall which divides the heart cavity into a “right heart” & a “left heart” • Right Atrium/Left Atrium – holding tanks for the blood • Right Ventricle/Left Ventricle – acts as a pump • Vascular – systems of blood vessels • Veins – bring blood back to the heart • Arteries – take blood from the heart to the needy muscles & organs