* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metal carbonyl - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
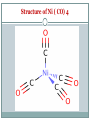
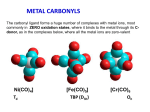
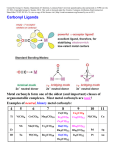
Metal Carbonyls CARBON ATOM OF CO HAS LONE PAIR OF ELECTRONS WHICH CAN BE DONATED TO TRANSITION METAL TO FORM COMPLEX COMPOUND CALLED METAL CARBONYLS. Metal carbonyls are complex compound of transition metals with CO. The number of CO molecules which get chemically bonded to a metal through coordination bonds vary with nature of the metal. Example: Number of CO molecules bonded o nickel carbonyl, Ni(CO) 4 is 4, while in chromium carbonyl Cr(CO)6 it is 6 Carbonyls are formed readily with transition metals since they have vacant d-orbitals which can accept the donated electron pairs. The number of coordination bonds that can be formed in this manner depend largely on the number of vacant orbitals. Generally the number of ligands attached to such that the metal atom appears to possess the same number of electrons as that noble gas. For example: Ni (atomic no.= 28) Metal-ligand bond formed by donating one lone pair from CO Ni, so four CO donate 8 electrons & all arising electrons on the central metal atom is 36. 36 no. of Kr. This number is called Effective Atomic Number (EAN). EAN = Atomic no.( Z) of metal atom- oxidation state + 2 x C.N. [ Fe ( CN) 6 ] 4- = 26-2+ 2 x 6 = 36 Structure of Ni ( CO) 4 Since the energy of 3d and 4s electrons are not so very much different, the 4s electrons can easily go to fill the 3d orbitals, vacating thereby the 4s orbitals Some other carbonyl compounds are Fe(CO)5, V(CO)6, Cr(CO)6, Mo(CO)6. These are mononuclear carbonyls since there is only one metal in them. A large number of polynuclear carbonyls which contain more than one metal atom are also known. Common examples are Co2( CO)8, Mn(CO)10, Fe2(CO)9, Fe3(CO)12, etc PROPERTIES OF METAL CARBONYLS Solid at room temperature and pressure. Mononuclear carbonyls are volatile as well as toxic. Colorless or light in color BONDING IN METAL CARBONYLS Molecular Orbital Theory In metal carbonyls initial overlap takes place between the filled bonding (sigma) orbital of CO with a vacant d-orbital on the metal atom resulting n sigma bond which is actually coordinate bond (M CO). Thus carbon monoxide CO acts as a ligand with C atom as the donor atom. The next overlap is between filled d-orbital on the metal atom with anti bonding orbital of carbon monoxide( back bonding) resulting in additional pi bond. Thus M to C bond in metal carbonyl consist of weak sigma bond and M C and M C pi bond which result due to back bonding. The back bonding between metal and C create a synergic effect which stabilize the M C bond