* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Training
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Residual-current device wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
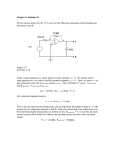
Principles of Electrical Safety Franklin L. Scamman Electricity - What Is It? Flow of electrons along a conductor Current (I) Ampere (A) 18 1 A = 1 coulomb/sec = 6.242 x 10 electrons/sec Think FLOW (Cardiac output) Voltage (E) Volt (V) 1 V = 1 joule/coulomb Potential energy with each charge Think PRESSURE Resistance (R) Ohm (W) 1 W = 1 volt/ampere Opposition to flow Think RESISTANCE Ohm’s Law E = IR or R = E/I R = MAP-CVP/CO Power (P) Watt (W) 1 W = 1 joule/sec Work done per unit time P = EI= I2R Energy Kinetic – One-half mass X velocity squared Potential – – – – Watt Hours Joules Car battery – 12 volts times amp hours AA battery – about 2.2 amp hours Electrical Circuit 120 V 0.5 AMP “HOT” FLOW OF ELECTRONS - POLE (CATHODE) 60 WATT BULB + POLE (ANODE) 0 V 0.5 AMP “NEUTRAL” Capacitance Ability of a charge to induce a equal but opposite charge in nearby conductors Capacitor - POLE ----------+++++++ + POLE Induction Ability of a magnetic field to induce current in a wire The wire must cross the lines of flux of the magnetic field All energized circuits are surrounded by a magnetic field With AC circuits, the field constantly expands and collapses, producing a moving magnetic field Transformer Uses principle of induction Functions in AC circuits only Magnetic field from primary winding induces current in secondary winding No physical contact between the two windings Transformer VOLTAGE SOURCE IRON CORE PRIMARY WINDING SECONDARY WINDING Grounded Power Common household electrical supply Supplied through “hot” and “neutral” lines Neutral connected to earth ground both at source and end user Earth ground provides an easy reservoir for excess electrical charge Grounded Power HOT 120 volts Power Suppily NEUTRAL 0 volts GROUND Isolated Power Isolated power - requires isolation transformer Lacks connection to earth ground Requires line isolation monitor to detect faults (short circuits) Originally installed to reduce explosions/fires from anesthetics Isolated Power ISOLATION TRANSFORMER HOT 120 volts Power Suppily NEUTRAL 0 volts GROUND No connection between circuit and ground Advantages of Isolated Power Reduced spark hazard Reduced possibility of electrocution Short circuits do not shut off power Line Isolation Monitor Monitors isolation of circuit from ground Alarms when a “first fault” occurs Threshold for alarms 2 or 5 mA LIM Function Connects isolated circuit directly to ground and measures potential current flow Alternates connecting each lead of the isolated circuit to ground Contains high resistance to prevent appreciable current flow LIM Circuit ISOLATION TRANSFORMER BLOOD WARMER LIM First Fault ISOLATION TRANSFORMER BLOOD WARMER LIM Response to LIM Alarms Find device that has excess leakage current Unplug devices one at a time LIM may alarm without a specific first fault Leakage Current All electrical appliances/monitors have leakage current Leakage current arises principally from capacitance coupling in appliances The ground wire is critical for detecting leakage current Leakage current is additive in a circuit Maximum leakage for each device 100 µA Leakage to Ground ISOLATION TRANSFORMER BLOOD WARMER LIM Physiology of Electrical Current Nerve excitation Muscle contraction Ventricular fibrillation Threshold of Perception Let Go Current Factors In Fibrillation Location of current flow Duration of current flow Density of current flow Alternating verses direct current Frequency of AC current Fibrillation Current vs. Weight Current necessary to achieve fibrillation Fibrillation Potential 0 100 200 300 400 Frequency (Hz) 500 Effect of Current Intensity (amps) 0.001 0.005 0.010-0.020 0.050 0.1 to 2 6 or more 1 second application Threshold of perception; tingling Maximum “ harmless” current intensity Skeletal muscle spasm; unable to let go Pain; mechanical injury; possible unsciousness; transient spastic interruption of respirations Ventricular fibrillation Sustained myocardial contraction followed by normal sinus rhythm; temporary respiratory paralysis; possible thermal injury if contact area is small In Vivo Resistance Electrical contact Dry skin Resistance (ohms) 100,000 Moist skin 1000 Electrode Paste 500 Implanted cardiac electrode 10 Macroshock Application of current to the exterior of the body Fibrillation threshold around 100 mA (0.1 A) for a 1 second application to dry skin Isolated power system provides protection against macroshock (2-5 mA limit) Macroshock How We Get Electrocuted Isolated Power Circuit Microshock Application of current directly to the heart Route for current flow may be a pacemaker lead or a saline filled CVP/PA catheter Fibrillation threshold about 50 µA (2x103 less than macroshock) Isolated power system does not protect against microshock Microshock Ground Fault Interrupter (GFI) Required in wet locations Monitors outflow and return of current in a circuit Disconnects circuit if a flow imbalance occurs Can detect 5 mA differences and disconnect the circuit in milliseconds GFI Electrical Surgical Unit Burns Electrical Surgical Unit Burns History of Electrical Safety History of Electrical Safety History of Electrical Safety History of Electrical Safety