* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Post-test review - Plain Local Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
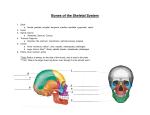
Anatomy review Define anatomy, physiology, homeostasis, metabolism, anatomical position Describe superior, inferior, medial, lateral, anterior, posterior, superficial, deep, distal, proximal Organization– atom, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism Planes – saggital, transverse, frontal/coronal Cavities – dorsal, ventral, thoracic, abdominopelvic, cranial, spinal Describe the roles water and oxygen play in the human body Define enzyme Define selectively permeable, osmosis, filtration, differentiation Explain how diffusion aids in the exchange of gases within the body Distinguish between anabolism and catabolism Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic respiration Describe the four main types of tissues using general functions and characteristics Name and describe the four types of membranes Name the five structures of the integumentary system and their functions Explain the role of the integumentary system in body temperature regulation What are the five sections of vertebrae? What is the purpose of the vertebral column? What is an articulation? What connects bone to bone? Explain the functions of bone. Describe epiphysis, diaphysis, periosteum, articular cartilage What are osteocytes? Full skeleton Bones to know… mandible, vertebrae, clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpals(as a group), metacarpals, phalanges, sternum, ribs, ilium, femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals (as a group), metatarsals, phalanges (for lab also hyoid) Describe the three types of muscle tissue Explain the functions of skeletal muscle Distinguish between tendon, ligament, aponeuroses, fascia Explain the Sliding Filament Theory Describe the effects of exercise on muscles Muscle man Muscles to know… Frontalis, Sternocleidomastoid, Trapezius, Biceps brachii, Triceps brachii, Pectoralis major, Rectus abdominis, External obliques, Latissimus dorsi, Quadriceps, Hamstring , Gluteus maximus, Gastrocnemius, Tibialis anterior (for lab also Masseter and Deltoid) What is the purpose of the nervous system? What are the 2 main divisions of the nervous system? What are nerve cells called? How is the brain protected? (3 things) Where do you find CSF? Brain diagram – locate: cerebrum, corpus callosum, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, cerebellum… function of corpus callosum and cerebellum, 3 parts of brain stem Endocrine system – as a group, endocrine glands secrete hormones that regulate metabolism The major glands are pituitary (in the brain), thyroid (in the neck), adrenal (on top of the kidneys), and pancreas Erythrocytes, Leukocytes, Thrombocytes – other name, function What is hematopoiesis? What is plasma? what’s in it? What is coagulation? What are the possible ABO blood types? Who is the universal donor? universal recipient? Where is the heart located? What is the major difference between the right and left side? Describe systemic and cardiopulmonary circulation. Arteries – carry _______ blood, ______ the heart. Veins – carry _____ blood, _____ the heart. Capillaries – are the smallest ______, have _____ walls, which allow for? Heart diagram – 4 chambers, 4 valves, vena cavas, aorta, pulmonary arteries/veins Blood flow through the heart Lymphatic system – it transports excess fluid to the bloodstream, absorbs fats, and protects against disease-causing agents The major structures are the lymph nodes (filters harmful particles from fluid and produce lymphocytes), thymus, and spleen (filters foreign particles and damaged red blood cells from the blood) The pathway of respiration What does the epiglottis do? Explain gas exchange between the alveoli and capillaries. Bones to know… mandible, vertebrae, clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpals(as a group), metacarpals, phalanges, sternum, ribs, ilium, femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals (as a group), metatarsals, phalanges (for lab also hyoid) Muscles to know… Frontalis, Sternocleidomastoid, Trapezius, Biceps brachii, Triceps brachii, Pectoralis major, Rectus abdominis, External obliques, Latissimus dorsi, Quadriceps, Hamstring , Gluteus maximus, Gastrocnemius, Tibialis anterior (for lab also Masseter and Deltoid) Organs to know… Brain, eye, ear, liver, stomach, kidney, heart, lung, pancreas, urinary bladder, small intestine, large intestine, appendix, gall bladder, spleen, skin