Title Superficial brachial artery continuing as the common
... superficial brachial artery in the upper part of the brachium became the deep brachial artery or the common interosseous artery in the cubital fossa, whereas the deep brachial artery in the upper part of the brachium became the superficial brachial artery in the lower part of the brachium and divide ...
... superficial brachial artery in the upper part of the brachium became the deep brachial artery or the common interosseous artery in the cubital fossa, whereas the deep brachial artery in the upper part of the brachium became the superficial brachial artery in the lower part of the brachium and divide ...
reference bone set: vertebrae
... inferior nasal concha is the largest. It is a separate bone that joints with the maxilla. The smaller middle nasal concha (just above the inferior concha) and the smallest superior nasal concha (barely visible just above and posterior to the middle concha) are parts of the ethmoid. Right Nasal bone ...
... inferior nasal concha is the largest. It is a separate bone that joints with the maxilla. The smaller middle nasal concha (just above the inferior concha) and the smallest superior nasal concha (barely visible just above and posterior to the middle concha) are parts of the ethmoid. Right Nasal bone ...
Document
... Visceral Serosa “covering the external surface of the organs within the [ventral] cavity” ...
... Visceral Serosa “covering the external surface of the organs within the [ventral] cavity” ...
PDF - SAS Publishers
... 7. Vichare NA; Anomalous muscle belly of the flexor digitorum superficialis. The Journal of Bone and ...
... 7. Vichare NA; Anomalous muscle belly of the flexor digitorum superficialis. The Journal of Bone and ...
The Language of Anatomy - Holly H. Nash
... If an incision cuts the heart into right and left parts, the section is a 15 section; but if the heart is cut so that superior and inferior portions result, the section is a 16 section. You are told to cut a dissection animal along two planes so that both kidneys are observable in each section. The ...
... If an incision cuts the heart into right and left parts, the section is a 15 section; but if the heart is cut so that superior and inferior portions result, the section is a 16 section. You are told to cut a dissection animal along two planes so that both kidneys are observable in each section. The ...
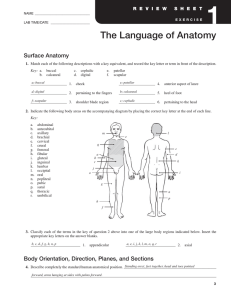
Surface Anatomy
... Standing erect, feet together, head and toes pointed 4. Describe completely the standard human anatomical position. _________________________________________________ forward, arms hanging at sides with palms forward. ...
... Standing erect, feet together, head and toes pointed 4. Describe completely the standard human anatomical position. _________________________________________________ forward, arms hanging at sides with palms forward. ...
Unusual high-origin of the pronator teres muscle from a Struthers
... Struthers ligament is a remnant of the tendon of the vestigial muscle, the latissimo-condyloideus, which is found in some climbing animals and also provide a large muscular attachment for the PT [2]. In lower mammals, the osseo-fibrous tunnel formed by the humerus, supracondylar process and the Stru ...
... Struthers ligament is a remnant of the tendon of the vestigial muscle, the latissimo-condyloideus, which is found in some climbing animals and also provide a large muscular attachment for the PT [2]. In lower mammals, the osseo-fibrous tunnel formed by the humerus, supracondylar process and the Stru ...
Teacher`s Guide For - Wisconsin Media Lab
... of course, we have already looked at some of the main arm muscles. Tendons, Ligaments and Fascia We know that we can isolate both bones and muscles in the lab, but somehow in the body they must get connected. What is the glue that ties the skeletal and muscular systems together into a movable functi ...
... of course, we have already looked at some of the main arm muscles. Tendons, Ligaments and Fascia We know that we can isolate both bones and muscles in the lab, but somehow in the body they must get connected. What is the glue that ties the skeletal and muscular systems together into a movable functi ...
Sample
... 1.1 The lowest living level of organization in the body is the chemical (molecular) level. 1.2 Homeostasis is the maintenance of a relative steady internal environment. 2.1 Anatomical position places the body in a reference position to standardize the location and descriptions of structures. 2.2 The ...
... 1.1 The lowest living level of organization in the body is the chemical (molecular) level. 1.2 Homeostasis is the maintenance of a relative steady internal environment. 2.1 Anatomical position places the body in a reference position to standardize the location and descriptions of structures. 2.2 The ...
Sample
... 1.1 The lowest living level of organization in the body is the chemical (molecular) level. 1.2 Homeostasis is the maintenance of a relative steady internal environment. 2.1 Anatomical position places the body in a reference position to standardize the location and descriptions of structures. 2.2 The ...
... 1.1 The lowest living level of organization in the body is the chemical (molecular) level. 1.2 Homeostasis is the maintenance of a relative steady internal environment. 2.1 Anatomical position places the body in a reference position to standardize the location and descriptions of structures. 2.2 The ...
PDF sample
... study of structures as they appear on the surface of crosssectional or longitudinal sections through a cadaver). ...
... study of structures as they appear on the surface of crosssectional or longitudinal sections through a cadaver). ...
The Skeleton
... • Consists of the clavicle and the scapula • Pectoral girdles do not quite encircle the body completely – The medial ends of the clavicles articulate with the manubrium and first rib – Laterally – the ends of the clavicles join the scapulae – Scapulae do not join each other or the axial skelet ...
... • Consists of the clavicle and the scapula • Pectoral girdles do not quite encircle the body completely – The medial ends of the clavicles articulate with the manubrium and first rib – Laterally – the ends of the clavicles join the scapulae – Scapulae do not join each other or the axial skelet ...
CHAPTER 1 STUDY GUIDE
... 15. The mouth, or buccal cavity, and its extension, which stretches through the body inside the digestive system, is not listed as an internal body cavity. Why is this so? It is not a body cavity because it has an opening at the mouth as well as an opening at the end (anus). Body cavities do not ope ...
... 15. The mouth, or buccal cavity, and its extension, which stretches through the body inside the digestive system, is not listed as an internal body cavity. Why is this so? It is not a body cavity because it has an opening at the mouth as well as an opening at the end (anus). Body cavities do not ope ...
Instructor`s Guide The Human Body: How It Works THE SKELETAL
... synergist muscle: A muscle that aids the agonist muscle in movement. synovial joint: Joints connected via a fluid-filled sac-like pad (e.g., knee joints). Synovial joints are more movable than fibrous or cartilaginous joints, and are the most common type in the human body. Synovial joints are classi ...
... synergist muscle: A muscle that aids the agonist muscle in movement. synovial joint: Joints connected via a fluid-filled sac-like pad (e.g., knee joints). Synovial joints are more movable than fibrous or cartilaginous joints, and are the most common type in the human body. Synovial joints are classi ...
Body Organization
... The person is standing up straight The palms face anteriorly The knees, elbow, and neck are straight (not bent) The toes point anteriorly, but the fingers point inferiorly Once the body is in this position (or imagined to be in this position,) the positional terms can be used correctly. Right or ...
... The person is standing up straight The palms face anteriorly The knees, elbow, and neck are straight (not bent) The toes point anteriorly, but the fingers point inferiorly Once the body is in this position (or imagined to be in this position,) the positional terms can be used correctly. Right or ...
1.3 PowerPoint
... Write the following words on your bellwork sheet. You’ll have till 11:45 to define them. There will be a QUIZ THIS FRIDAY, which will include the words from Monday. YOU MAY PICK YOUR OWN SEATS ...
... Write the following words on your bellwork sheet. You’ll have till 11:45 to define them. There will be a QUIZ THIS FRIDAY, which will include the words from Monday. YOU MAY PICK YOUR OWN SEATS ...
human anatomy 101
... (left & right lungs) cavities Abdominopelvic cavity- consists of the abdominal (stomach, spleen, ...
... (left & right lungs) cavities Abdominopelvic cavity- consists of the abdominal (stomach, spleen, ...
Knee Anatomy - Indiana University
... Ernest F. Talarico, Jr., Ph.D. Associate Director of Medical Education Associate Professor and Course Director, Human Gross Anatomy & Embryology Coordinator, Anatomical Education Program Indiana University School of Medicine-Northwest ...
... Ernest F. Talarico, Jr., Ph.D. Associate Director of Medical Education Associate Professor and Course Director, Human Gross Anatomy & Embryology Coordinator, Anatomical Education Program Indiana University School of Medicine-Northwest ...
Human Anatomy * Class Notes Skeletal System
... Cartilage provides a smooth surface for bones to glide across and bend and is more slippery than ice You will find cartilage in your knee, nose, and elbow - and is located between bones Breakdown in cartilage causes bone to rub against bone, this can be painful and can also lead towards arthritis Yo ...
... Cartilage provides a smooth surface for bones to glide across and bend and is more slippery than ice You will find cartilage in your knee, nose, and elbow - and is located between bones Breakdown in cartilage causes bone to rub against bone, this can be painful and can also lead towards arthritis Yo ...
DE Science Elementary “5
... Reality: There are three types of muscle: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal which account for over 600 muscles found throughout the entire body. ...
... Reality: There are three types of muscle: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal which account for over 600 muscles found throughout the entire body. ...
Fractures, Sprain and Strains
... Bones are rigid organs that form the skeletal system. They function to move, support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce blood cells both red and white. The also store minerals. Because bones come in a variety of shapes and have a complex internal and external structure, they are li ...
... Bones are rigid organs that form the skeletal system. They function to move, support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce blood cells both red and white. The also store minerals. Because bones come in a variety of shapes and have a complex internal and external structure, they are li ...
skeletal system
... appearance is different from the other spinal vertebrae. The atlas is a ring of bone made up of two lateral masses joined at the front and back by the anterior arch and the posterior arch. Axis (C2) The Axis is the second cervical vertebra or C2. It is a blunt tooth–like process that projects upward ...
... appearance is different from the other spinal vertebrae. The atlas is a ring of bone made up of two lateral masses joined at the front and back by the anterior arch and the posterior arch. Axis (C2) The Axis is the second cervical vertebra or C2. It is a blunt tooth–like process that projects upward ...
Name: Investigation of a Chicken Wing Purpose The purpose of this
... 1. What material enables the skin to stretch instead of crack? 2. What function do you think is served by the bumps on the skin? They hold each feather. Muscles in them can contract to life the feathers, creating air pockets, so the bird can keep warm. 3. These bumps are similar to what structures i ...
... 1. What material enables the skin to stretch instead of crack? 2. What function do you think is served by the bumps on the skin? They hold each feather. Muscles in them can contract to life the feathers, creating air pockets, so the bird can keep warm. 3. These bumps are similar to what structures i ...
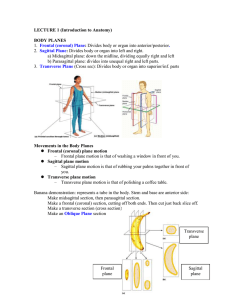
Anatomical Planes
... • Body is standing, the feet together, the arms to the side, and the head and eyes and palms of the hands facing forwards. • Used for the purpose of description ...
... • Body is standing, the feet together, the arms to the side, and the head and eyes and palms of the hands facing forwards. • Used for the purpose of description ...
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The shoulder joint also known as the glenohumeral joint, is the major joint of the shoulder, but can more broadly include the acromioclavicular joint. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, the head sitting in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint.There are two kinds of cartilage in the joint. The first type is the white hyaline cartilage on the ends of the bones (called articular cartilage) which allows the bones to glide and move on each other. When this type of cartilage starts to wear out (a process called arthritis), the joint becomes painful and stiff. The glenoid labrum is the second kind of cartilage in the shoulder which is distinctly different from the articular cartilage. This cartilage is more fibrous or rigid than the cartilage on the ends of the ball and socket. Also, this cartilage is also found only around the socket where it is attached.The shoulder must be mobile enough for the wide range actions of the arms and hands, but also stable enough to allow for actions such as lifting, pushing and pulling. The compromise between mobility and stability results in a large number of shoulder problems not faced by other joints such as the hip.