* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Investigation of a Chicken Wing Purpose The purpose of this
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
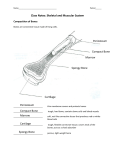
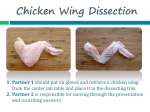
Name: _______________________________ Investigation of a Chicken Wing Purpose The purpose of this lab is to observe the interaction of muscle and bone using a chicken wing as a model. After completing this investigation, you should be able to demonstrate the function of flexors and extensors, describe the tendons and ligaments, explain the difference between cartilage and bone, and show how muscles and bones fit together. Materials One raw chicken wing Pen or pencil Lab questions Scissors/scalpel Rubbing alcohol Procedure Part A: Skin 1. Flex the chicken wing and observe the skin. Note how it stretches. What material enables the skin to stretch instead of crack? __________ ____________ 2. What function do you think is served by the bumps on the skin? ______________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. These bumps are similar to what structures in human skin? __________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Cut through the skin layer as shown in Figure 1. Be careful to avoid cutting the muscle tissue underneath the skin. 5. Peel the skin off the wing. You will not be able to get all the skin off; remove as much as possible. If you are unable to peel the skin, dip the wing in a beaker of alcohol. This will make it easier to remove the entire skin layer. 6. What type of tissue holds the skin to the muscle? _______________ _________________ 7. As you remove the skin, you’ll notice how greasy it seems. What skin part causes this greasiness? _____________________________________ Part B: Muscle There are three types of muscle: striated (skeletal), cardiac, and smooth. Striated muscle is voluntary muscle; these are the muscles you can move at will. Smooth muscle is involuntary; you have no control over its movement. Organs such as the stomach and the intestines are made up of this type of muscle. Cardiac muscle is striated involuntary muscle that makes up the heart. 8. Which type of muscle do you find in the chicken wing? _______________________ 9. Is this voluntary or involuntary? _____________________________ 10. Pull on the various muscles in the middle, or forelimb, of the wing. Describe the resulting bone movement. _______________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Find an opposing pair of muscles on the wing. Draw a picture showing the opposing muscles and where they attach to the bone. 12. Remove one entire bundle of muscle, including one of the tendons. Tendons are white, cord-like endings of muscle made of strong connective tissue. Cut the tendon from the bone as close as possible to where it attaches to the bone, away from the end of the muscle. Draw a picture of the muscle and tendon, and draw an arrow pointing to the end of the muscle that was attached to the bone. Part C: Bone 13. Remove all the muscle from the upper limb, forelimb, and wingtip. Examine the bones. 14. Name the human bone most like the upper limb bone of the chicken wing (Figure 3). ____________________________________ 15. Name the two human bones most like the forelimb bones of the chicken wing. ____________________________ ____________________________________ 16. How many joints are there between the upper limb and the forelimb? ________________ 17. What do we call the tissue that holds the bones together at the joints? ______________________ 18. What color is this connective tissue at the joints? _________________________ 19. Is the cartilage different from the bone in color or to the touch? Describe. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Conclusion Could the muscles function if they were not attached to the bone? Explain. Answer Key 1. What material enables the skin to stretch instead of crack? 2. What function do you think is served by the bumps on the skin? They hold each feather. Muscles in them can contract to life the feathers, creating air pockets, so the bird can keep warm. 3. These bumps are similar to what structures in human skin? Hair follicles 6. What type of tissue holds the skin to the muscle? Connective tissue 7. What skin part causes this greasiness? The fat 8. Which type of muscle do you find in the chicken wing? Skeletal muscle 9. Is this voluntary or involuntary? voluntary 10. Pull on the various muscles in the middle, or forelimb, of the wing. Describe the resulting bone movement. When you pull on a muscle, it pulls on one of the bones that it is attached. 11. Find an opposing pair of muscles on the wing. Draw a picture showing the opposing muscles and where they attach to the bone. See drawing 12. Draw a picture of the muscle and tendon, and draw an arrow pointing to the end of the muscle that was attached to the bone. See drawing 14. Name the human bone most like the upper limb bone of the chicken wing (Figure 3). humerus 15. Name the two human bones most like the forelimb bones of the chicken wing. Radius, ulna 16. How many joints are there between the upper limb and the forelimb? one 17. What do we call the tissue that holds the bones together at the joints? tendons 18. What color is this connective tissue at the joints? White 19. Is the cartilage different from the bone in color or to the touch? Describe. Cartilage is bright white and smooth. Conclusion - Bones and muscles cannot work without each other. Muscles need attachment points on the bones so they can pull the bones. If muscles were not attached to bones, neither could move.