* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Renaissance
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
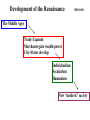
The Renaissance “The Rebirth of Europe” 1300-1600 Middle Ages 500 – 1200 CE Collapse of Roman Empire marks start of Middle Ages Key Outcomes of Middle Ages: • • • • Leads to eventual formation of 47 new countries Roman Catholic Church gains extreme power Begins a period of “cultural” decline (arts, literature, etc…) Judeo-Christian thought spreads in Europe Social Hierarchy (of Middle Ages) Feudalism Peasant-Noble-Priest Life in the Middle Ages • Medieval Man had 3 primary concerns Eternal salvation Protection from enemies Food and shelter Black Death 1347-1352 • Bubonic plague killed 1/3rd of Europe’s population – 25 million people died in 5 years! • Medieval Society never recovered from the effect black plague: – Labor shortages developed => Workers demanded higher wages => Peasant revolts occurred throughout Europe – People openly questioned the church: Why did God let this happen? “people ate lunch with their friends and dinner with their ancestors” Renaissance Begins • When: • Meaning: “rebirth” (in terms of art & learning) • Began in ITALY & spread north throughout Europe • Why Italy: 1300 - 1600 – Thriving cities meant more trade – France and England locked in the 100-years war. (1337-1453) – Classical heritage of Greece and Rome Italy Changes • Trade expands – most of Europe was rural – Italy had more cities due to trade – Banking system rapidly developed • Wealthy merchant class developed – Many became patron of the arts (example: Medici) • Growth of cities meant “new ideas” spread quickly 3 Themes of Renaissance Individualism Secularism Humanism “Never again would western men be so occupied with the nature of the next world that they would be unattentive to the nature of this one” Society developed a: 1) Interest in classical culture 2) Curiosity about the world 3) Belief in Human Potential Development of the Renaissance 1300-1600 The Middle Ages Trade Expands Merchants gain wealth/power City-States develop Individualism Secularism Humanism New “modern” society The Northern Renaissance • Late 1400’s Northern Europe recovered from plague & Hundred Years’ War • Italy was ruled by city-states • England & France ruled by strong monarchs • Renaissance ideas began to spread north to England, France, Germany & Flanders Monarchs & the Renaissance • Northern Kings supported artists during Renaissance • War in Italy caused artists & writers to flee to northern Europe • Northern Renaissance developed its own unique style The Printing Press Changes the World • Gutenberg invented the printing press 1440 – The Bible was the first book printed [1455] – By 1500 presses in 250 cities printed 9-10 million books • End result: – New ideas spread more quickly than ever before – Writing in vernacular languages increase Analyze this Cartoon Renaissance Italy Key Historical changes: • • • • • Social: Economic: • Cultural: • Religious: • • Political: • Increased city living Increased Trade & Banking New focus on art & literature Less focus on “afterlife” Merchant class gained power