* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Marketing Concept
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
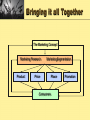
Basic Marketing Concepts Chapter 2 Section 2.1 – The Marketing Concept The Marketing Concept • Businesses must satisfy customers’ needs and wants in order to make a profit. • Competition forces businesses to embrace this idea. – They must have the right goods and services at the right time, at the right price, and at the right place for purchase. Customers vs. Consumers • Part of fulfilling a person’s needs is determining if they are a customer or a consumer. – Customer are the ones who buy a product (good or service). – Consumers are those people who actually use the product. • Ex: You parents buy you new shoes, but you are the one who wears them. You are the consumer and your parents are the customer. • Note: Make sure to keep in mind that for certain businesses a person is not the customer, but rather other businesses are. Nike sells primarily to department stores not to individual consumers. What is a Market? • All customers who share common needs and wants, and who have the ability and willingness to buy the product, are considered a market. – Market can also be a companies percentage of total sales in their industry. Ex: Nike sales 48% of all cross trainers in the U.S. • So how do we determine what customers share common needs and have the ability to purchase? Target Marketing • Focusing all marketing decisions on a very specific group of people you want to reach. – The more information you have on this group the easier it is to make marketing decisions • Businesses will frequently create what they call a customer profile, which is a breakdown of the characteristics of the target market. (age, income, ethnic background, geography) The Marketing Mix • The Marketing Mix is comprised of 4 strategies. These strategies should be carefully planned and considered before selling your product. • Also know as the Four P’s – – – – Product Strategies Place Strategies Promotion Strategies Price Strategies • It’s important that your product (good/service) fits the target market you’ve selected. Product Strategies • Includes what product to make, how to package it, what brand name to use and what image to project. – Ex: As CEO of Widgets Inc. I decided there is a need for extra large widgets, I decide the best name for them would be Ginormous Widegets, and they should come in packs of 14. Place Strategies • Determine how and where a product will be distributed. – Ex: As CEO of Widget Inc. I decide to have warehouses in 3 major U.S. cities and to operate M-Sa 9-6pm. I am also providing shipping to most areas in the U.S. only. Price Strategies • Price strategies should reflect what customers are willing and able to pay. – Ex: Through research I found that most companies need around 10-12 widgets at a time. The packages of 14 Widget Inc. sells fulfill that need. I also have determined that a price of $239.99 per pack allows me to cover my cost and make a reasonable profit. Promotion Strategies • Deals with how potential customers will be told about the new product, what the message will be, when and where it will be delivered, and with what inducements to buy. –Ex: Widget Inc. spends a great deal of money advertising in business journals, employing salespeople, creating informational documents, and creating and dispersing radio/TV advertisements. They also send out press releases, take time to give interviews, and support a little league team in each city they have a warehouse. Bringing it all Together The Marketing Concept Marketing Research Product Marketing Segmentation Price Consumers Place Promotion