* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Physiology Notes
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
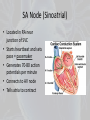
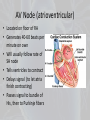
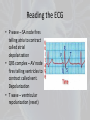
HEART PHYSIOLOGY Physiology of Circulation • Indicators of efficiency of a person’s circulatory system can be obtained by taking arterial pulse and blood pressure measurements. • These, along with respiratory rate and body temperature, are called vital signs. Heart Work • Heart pumps the body’s 6 L of blood over 1,000 times a day = 6,000 L of blood in a day • Atria contract (Luppa), then ventricles contract (Duppa) = Luppa Duppa • Atria contracts 60 beats/min • Ventricles contract 20-40 beats/min • Heart Rate - the number of beats per minute Arterial Pulse • The alternating expansion and recoil of an artery that occurs with each beat of the left ventricle creates a pressure wave – a pulse – that travels through the entire aterial system • Normally, the pulse rate equals the heart rate • It averages 70-76 bpm • Affected by activity, posture, and emotions Heart Rate • Palpated at one of several arterial locations close to surface • Same spots used to stop hemorrhage, called pressure points • Radial • Carotid • Brachial • Popliteal • Posterior tibial • Dorsalis pedis • Facial • Temporal • Use two fingers to palpate – not thumb • Coordinated by electrical pacemaker within heart The Electricity of the Heart • Heart contains two special batteries called nodes • Made of specialized cardiac tissue that can generate electricity – mixture of nervous and muscle tissue Intrinsic Conduction System • Nodal System – sets basic rhythm of heart • Forces contraction rate of 75 beats/min so heart beats as coordinated unit • Two nodes: • Sinoatrial node (SA Node) • Atrioventricular node (AV Node) • AV Bundle of His – bundle of fibers between atria and ventricles • Purkinje fibers – spread within muscle of ventricle walls SA Node (Sinoatrial) • Located in RA near junction of SVC • Starts heartbeat and sets pace = pacemaker • Generates 70-80 action potentials per minute • Connects to AV node • Tells atria to contract AV Node (atrioventricular) • Located on floor of RA • Generates 40-60 beats per minute on own • Will usually follow rate of SA node • Tells ventricles to contract • Delays signal (to let atria finish contracting) • Passes signal to bundle of His, then to Purkinje fibers Control of Heart Rate • Cardioinhibitory Center • ANS– parasympathetic • Normal everyday activity • Vagus nerve releases Ach to slow heart • Acts like a break • Decreases heart rate • Cardioacceleratory Center • ANS – Sympathetic • Fight or Flight response • Cardiac nerve releases norepinephrine or epinephrine • Increases heart rate Electrocardiogram • Also known as ECG • Way to measure SA and AV nodes • Attach electrodes to skin (moves thru water) • Helps us know rhythm and strength of contractions Reading the ECG • P wave – SA node fires telling atria to contract called atrial depolarization • QRS complex – AV node fires telling ventricles to contract called vent. Depolarization • T wave – ventricular repolarization (reset) Bradycardia • Slow heart rate • Usually below 60 • Sign of large ventricle or athletic • Also can mean death is near • Characteristics on ECG? Tachycardia • Means fast heart rate usually over 100 • Can mean small ventricle or exercising • Death can result around 220 or higher • Characteristics on ECG? Ventricular fibrillation • Bad News! • Heart has uncoordinated contractions • Cannot effectively move blood • ECG characteristics? • Will use a defibrillator Atrial flutter • Atrium is contracting quickly • Many atrial contractions per ventricle contract. • Why would this be Bad? • ECG characteristics? Cardiac Output • Cardiac Output (CO) is the amount of blood pumped out by each side of the heart in 1 min • It is the product of heart rate (HR) and the stroke volume (SV) • Stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped out by a ventricle with each heart beat • CO = HR X SV • CO = HR (75 beats/min) X SV (70 ml/beat) • CO = 5,250 ml/min (average adult human) Regulation • Starling’s law of the heart – critical factor of controlling stroke volume is how much the cardiac cells are stretched before they contract • More stretch = more contraction • Venous return – amount of blood entering the heart and distending its ventricles • Anything that increases volume/speed of venous return also increases stroke volume and strength of contraction • Example: a slow heartbeat allows more time for ventricles to fill Blood Pressure • Blood pressure is the pressure the blood exerts against the inner walls of the vessels • Force that keeps blood circulating evenly • Flows along a pressure gradient (high to low) from large arteries to small arterioles Factors affecting B.P. • BP = CO X PR where PR = Peripheral Resistance • Peripheral Resistance – amount of friction the blood encounters in blood vessels • Vasoconstriction – narrowing of blood vessels. • Effect on BP? • Increase in BP. When would this occur? • Baroreceptors – e.g. when lying down • Vasodilation – dilating of blood vessels. • Effect on BP? Decrease BP • During fight or flight Factors affecting B.P. 1. Neural factors: ANS – vasodilation/vasoconstriction 2. Renal factors: kidneys – when BP high, kidneys allow more blood to leave body in urine 3. Temp – cold = vasoconstriction, warm = vasodilating 4. Chemicals – nicotine leads to vasoconstriction, alcohol leads to vasodilation 5. Diet – low salt helps prevent hypertension