* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Terrestrial planets
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
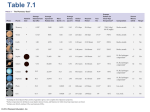
The Solar System © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. An Inventory of the Solar System Now known: Solar system has 166 moons, one star, eight planets (added Uranus and Neptune), eight asteroids, and more than 100 Kuiper belt objects more than 300 km in diameter (smaller asteroids, comets, and meteoroids) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. An Inventory of the Solar System More than 400 extrasolar planets have been found Understanding planetary formation in our own solar system helps understand its formation as well as formation of other systems © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. The Overall Layout of the Solar System All orbits but Mercury’s are close to the same plane © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. The Overall Layout of the Solar System Because the planet’s orbits are close to being in a plane, it is possible for them to appear in a straight line as viewed from Earth. This photograph was taken in April 2002. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Terrestrial and Jovian Planets In this picture of the eight planets and the Sun, the differences between the four terrestrial and four jovian planets are clear. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Terrestrial and Jovian Planets Turn to your neighbor an list all the differences you see between the Terrestrial and Jovian planets. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Terrestrial and Jovian Planets Terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Terrestrial planets are small and rocky, close to the Sun, rotate slowly, have weak magnetic fields, few moons, and no rings Jovian planets are large and gaseous, far from the Sun, rotate quickly, have strong magnetic fields, many moons, and rings © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Terrestrial Differences among the terrestrial planets: • All have atmospheres, but they are very different; surface conditions vary as well • Only Earth has oxygen in its atmosphere and liquid water on its surface • Earth and Mars spin at about the same rate; Mercury is much slower, Venus is slow and retrograde • Only Earth and Mars have moons • Only Earth and Mercury have magnetic fields © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Interplanetary Matter Asteroids and meteoroids have rocky composition; asteroids are bigger Asteroid Eros is 34 km long © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Interplanetary Matter Comets are icy, with some rocky parts Comet Hale-Bopp © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Interplanetary Matter Pluto, once classified as one of the major planets, is the closest large Kuiper belt object to the Sun © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Turn to your neighbor Discuss your theory of how the solar system formed. Why do you think that? What characteristics of the solar system might your theory address? © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. How Did the Solar System Form? Solar system properties show it has a high degree of order 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Each planet is relatively isolated in space The orbits of the planets are nearly circular All planets but Mercury lie in the same plane Rotational direction around the sun is the same direction as the sun rotates Planets are differentiated between terrestrial and Jovian Asteroids are very old The Kuiper belt is asteroid-sized icy bodies The oort cloud comets are icy fragments that do not orbit on the plane of the ecliptic © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction: Cloud of gas and dust contracts due to gravity; conservation of angular momentum means it spins faster and faster as it contracts © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Aug. 24, 2006 Demotion of Pluto “Plutoed” -meaning to demote or devalue someone Dr. Mike Brown and Neil Degrase Tyson to “blame” © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Eris is at fault • Found large asteroids by 1851 (including Ceres) between Mars and Jupiter • Pluto not in the asteroid belt but in the Kuiper belt • Then we discovered Eris, which is in the Kuiper belt • However Eris is classified Pluto would be classified (both have large inclinations) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 2006 IAU meeting Planet Criteria 1. Must orbit the sun 2. Enough gravity to shape itself into a sphere 3. Big enough to clear its neighborhood around its orbit © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Dwarf planet criteria 1-2 are the same 3. Not cleared its neighborhood around its orbit 4. Not a moon © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Plutoid criteria Same criteria as dwarf planet except 5. Must orbit beyond Neptune Known Plutoids: Pluto, Haumea, Makemake,Eris “Pluto Heard ME” © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.