* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mineral Resources
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Ore genesis wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
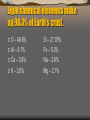
Mineral Resources Economic and environmental considerations Eight chemical elements make up 98.3% of Earth’s crust. O – 46.6% Al – 8.1% Ca – 3.6% K – 2.6% Si – 27.78% Fe – 5.0% Na – 2.8% Mg – 2.1% Other elements comprise 1.7% of Earth’s Crust Many of these are important to industry Examples: Ni, Ti, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, U, Pt, Au, Ag, etc. Distribution of these elements in not uniform across the Earth. Many rocks contain none of these elements or only trace quantities. Other areas may have one or more of these elements in abundance. Ore If one or more chemical elements occur in sufficient abundance that they may be mined for a profit, then the rock is termed an ORE. Ore today, not tomorrow. Designation as an ore depends on The degree of concentration of the mineral The current market price of the mineral The cost of production Why do ore deposits occur where they do? Why are they not found everywhere? The location of an ore deposit depends on The geologic history of an area The specific process by which the minerals became concentrated How do ores become concentrated? Ores may become concentrated by processes that are: Chemical Physical Biological Processes of ore concentration are related to formation of rocks. Rocks are grouped in three major families, based upon their processes of formation. Igneous Rocks Sedimentary Rocks Metamorphic Rocks Three Families of Rock Igneous Rocks – form by the cooling and crystallization of magma (melted rock). Sedimentary Rocks – form by deposition and consolidation of sediments (e.g., sand, mud, etc.) or by evaporation of water and crystallization of dissolved materials. Metamorphic Rocks – form by the action of heat and pressure on some other rock. Ore Concentration by Igneous Processes Magmatic segregation – crystals sink in magma and concentrate near bottom of magma chamber Hydrothermal enrichment – water, superheated by magma, dissolves minerals Dissolved minerals move with water to a new location and are then precipitated to form ore. Hydrothermal Enrichment Pegmatites – “veins” in continental rocks Common form of gold enrichment Exhalites – Submarine vents of hot, mineral-rich water “Black Smoker Chimneys” Associated with mid-ocean ridges “Black Smokers” Sulfide Mine in Exhalite Deposit Ore Concentration by Sedimentary Processes Placers Concentration by density and current action Residuum Enrichment by chemical weathering – Other minerals are removed leaving ore Ore Concentration by Metamorphic Processes During metamorphism, heat and pressure alter pre-existing rock If water is present, process is more efficient and related to hydrothermal processes Metamorphism occurs deep within mountain systems as they form Plate Tectonic Connections Hydrothermal enrichment associated with volcanic activity at convergent and divergent margins Placer and Residuum enrichments occur on stable continental platforms (plate interior) Metamorphic enrichment occurs at convergent margins in mountain systems Economic Implications Ores are not found everywhere Some ores are richer than others Ore distribution is a function of geology Ore distribution is not equal across the world Some nations are rich in mineral resources Other nations have few mineral resources No nation is self sufficient in mineral resources Environmental Considerations Mining leaves holes in the ground Mining adds unusual quantities of sediment to rivers and streams Mining exposes minerals to interaction with surface and groundwater, which may contaminate them Mine waste may be unstable - landslides Smelting may pollute air and water We all make choices. Industrialized societies depend on mineral resources Environmental problems must be considered in extracting wealth from the Earth Its not Good (environment) vs. Evil (industry) It’s a compromise, of which, we must make the best