* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download V NL - UiO
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
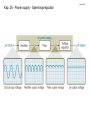
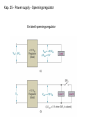
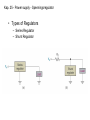
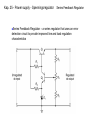
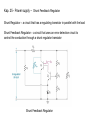
Lindem 2009 Kap. 25 - Power supply - Spenningsregulator Kap. 25 - Power supply - Spenningsregulator En ideell spenningsregulator Kap. 25 - Power supply - Spenningsregulator Vout line regulation Vin Vout = the change in output voltage (usually in microvolts or millivolts) Vin = the change in input voltage (usually in volts) VNL VFL Vout load regulation I L I L VNL = the no-load output voltage (i.e., the output VFL I L voltage when the load is open) = the full-load output voltage (i.e., the load current demand is at its maximum value) = the change in load current demand Kap. 25 - Power supply - Spenningsregulator • Types of Regulators – Series Regulator – Shunt Regulator Kap. 25 - Power supply - Spenningsregulator • Series Regulators – circuits that have one or more devices placed in series with the load – Pass-Transistor Regulator – a circuit that uses a series transistor to regulate load voltage A decrease in VL causes VBE to increase, which increases conduction through the pass transistor and a relatively constant load voltage is maintained Kap. 25 - Power supply - Spenningsregulator Problem: As input voltage or load current increases, the zener diode must dissipate a relatively high amount of power – reduced by using a Darlington pass-transistor regulator VL VZ 2 VBE Kap. 25 - Power supply - Spenningsregulator – Series Feedback Regulator a series regulator that uses an error detection circuit to provide improved line and load regulation characteristics Kap. 25 - Power supply - Spenningsregulator Series Feedback Regulator Feedback Regulator – a series regulator that uses an error detection circuit to provide improved line and load regulation characteristics Series Kap. 25 - Power supply – Spenningsregulator m / sikring I E max VBE Q3 RS Kap. 25 - Power supply – Shunt Feedback Regulator Shunt Regulator – a circuit that has a regulating transistor in parallel with the load Shunt Feedback Regulator – a circuit that uses an error detection circuit to control the conduction through a shunt regulator transistor Shunt Feedback Regulator Kap. 25 - Power supply – Linear IC Voltage Regulators – a device that is used to hold the output voltage from a dc power supply relatively constant over a specified range of line and load variations Basically Four Types Fixed-Positive – provide a specific positive voltage Fixed-Negative – provide a specific negative voltage Adjustable – can be adjusted within a specified range of values Dual-Tracking – provides equal positive and negative output voltages Kap. 25 - Power supply – Linear IC Voltage Regulators Adjustable Regulators – Example LM317 Kap. 25 - Power supply – Switching Regulators Regulator Operation – when the control circuit senses a change in the output voltage, it sends a signal to the switch driver Switching The power switch is constantly driven back and forth between saturation and cutoff Average voltage at the emitter of the power switch Vave Ton Vin Ton Toff END
















![Regulated Power Supply [ppt]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001086228_1-9a7fc8aab7a3192d0e202a8163eee145-150x150.png)


