* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt - EC - Unit 7 - Linear Power Supply
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
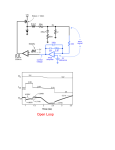
Unit 7 Linear Power Supplies, Switched Mode Power Supply Learning Objectives: Linear Power Supplies: 14.1 Constituents of Linear Power Supply 14.2 Designing Mains Transformer 14.6 Linear IC Voltage Regulators 14.7 Regulated Power Supply Parameters Switched Mode Power Supplies: 15.1 Switched Mode Power Supplies 15.6 Connecting Power Converters in Series 15.7 Connecting Power Converters in Parallel 14.1 Constituents Linear Power Supply: • • • • Stepdown transformer Rectifier Filter (C, LC) Regulator (ICs LM78XX, LM79XX, LM321) 14.2 Designing Mains Transformer: 1. To avoid magnetic saturation – core cross section area, Ac Ac = √P / 5.6 where P=power required in Watts 2. t / W ratio = stack thickness (t) -------------------------------- = 1.1 to 1.5 Width of central limb (W) … 3. Turns per volt = 108 ----------------------4.44 x f x Ac x B Where f=frequency=50 or 60 Hz B=flux density=50000 lines / square inch (gauss) 4. Turns ratio (Ns / Np), n =Vp / Vs = Ns / Np 5. Primary current = P ------------------------------------Efficiency x Primary Voltage … 6. Secondary current = Primary Current ----------------------n where n is turns ratio 14.1 Numerical Example: 14.6 Linear IC Regulators: Features: • PCB mountable • Precision • Best voltage & current regulation • Wide range of output voltages • Protection inbuilt: current limit & thermal shutdown Three terminal regulators: Boosting current delivery capability: 14.7 Regulated Power Supply Parameters: Load regulation: Change in regulated output voltage as the load current varies. VNL – VFL % load regulation = --------------- X 100 VFL Line regulation: is defined in terms of variation of regulated output voltage for a specified change in line (input AC) voltage. Eg. For input voltage variation, say 170 V to 220V, output voltage 10V, varies ±1% has lineregulation (1+1) = ---------- x 100 10 = 0.2 % Output Impedance: In Thevenin’s equivalent circuit of RPS, output impedance comes in series with load resistance. It determines load regulation of the power supply. Ripple rejection factor: 15.1 Switched Mode Power Supplies: power supply Linear 1. 2. 3. 4. Stepped down, Rectified, Filtered, Regulated Loss Costly Switched 1. The unregulated DC is chopped at a high frequency (using transistor / MOSFET / IGBT) 2. The chopped waveform is then rectified and filtered to get the desired DC voltage. 15.5 Switching Regulator: 1. Buck regulator – step down 2. Boost regulator – step up 3. Buck-boost regulator – both step down / up 15.6 Connecting Power Converters in Series: • Can be connected in series, provided specifications allow for the series connections. • It is possible that the output of one converter affects the output loop of another. • Output voltage should not exceed breakdown voltage of the devices. 15.6 Connecting Power Converters in parallel: • Again, if specification allow the connection, then they can be connected in parallel.