* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Land Beneath Our Feet (Geology) Vocabulary
Survey
Document related concepts
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
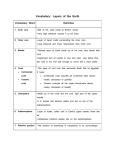
The Land Beneath Our Feet (Geology) Vocabulary Word/Term Definition Density The amount of mass in a given space; mass per unit volume Inner Core Innermost layer of the Earth; solid nickel and iron Outer Core Liquid layer of the Earth made out of nickel and iron; lies between the inner core and the mantle Mantle The layer of material between Earth's crust and core; extremely hot; mostly solid but with becomes liquid as you get nearer the outer core Asthenosphere Upper part of the mantle Lithosphere A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and crust Crust The layer of rock that forms Earth's outer surface; made of basalt and granite; both oceanic and continental Continental Drift The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth's surface Tectonic Plate A rigid layer of Earth's crust that is believed to drift slowly Pangaea The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today's continents Plate Tectonics The theory that pieces of earth's lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle Primary Waves A type of seismic wave that compresses and expands the ground Secondary Waves A type of seismic wave that moves the ground up and down or side to side Surface Waves A type of seismic wave that forms when a P wave and S wave reach Earth's surface Earthquake The shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface Volcano A weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface Igneous Rock A rock formed from cooled magma Metamorphic Rock type of rock that forms when rock is exposed to high temperature and pressure Sedimentary Rock Type of rock that forms from layers of sediment compacted and cemented together Rock Cycle The never-ending cycle in which one rock type changes into another rock type Soil Mixture of minerals, water, air, and decayed organic matter Soil Profile/ Horizons Different types of soil, each with its own set of characteristics Particle Size The general dimensions of the particles or mineral grains in a rock or sediment pH Measures the acidity of a solution. A pH of 7 is neutral; smaller numbers are more acidic and larger numbers are more alkaline Soil The top layer of Earth's surface containing weathered rocks and minerals and organic material Erosion The transport of weathered materials by water, wind, ice, or gravity Weathering The chemical or physical breakdown of rocks, soils or minerals at Earth's surface Conservation Plowing Technique where farmers plow with the curve of the land instead of in straight rows Contour Plowing Plowing along the contour of the land(hill) to minimize soil erosion Crop Rotation System of rotating crops Stewardship A person whose responsibility is to take care of something