* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanisms of common and important adverse drug reactions
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
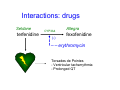
Mechanisms of common and important adverse drug reactions Jack W. Strandhoy, Ph.D. Drug Safety Pharmacovigilance • Paracelsus: “All substances are poisons…dose differentiates” • Toxicology – adverse effects of chemicals, incl drugs, on living organisms. ↑doses. • Pharmacovigilance – concerns detection, assessment, understanding, prevention of adverse events with medicines in nl doses • Adverse Drug Reactions – noxious and unintended; at normal therapeutic doses – Affect 2 million / yr in US; 100,000 deaths / yr Idiosyncratic Adverse Drug Reactions (or Effects) Mechanism-dependent toxicities Genetic influences Interactions: drugs, foods Mechanism-dependent toxicities • exaggerated effects • ion disturbances • cardiovascular problems Mechanism-dependent toxicities • An exaggeration of the expected pharmacological effect • Hyperkalemia – ACEI, ARB, K-sparing diuretics; complicated by ↓renal fx, acidosis, diabetes … • Cardiovascular risks – – COX-2 inhibitors (rofecoxib) – ↑ stroke and MI – Immediate release Ca blockers - ↓↓BP • HTN, proteinuria – cediranib for cancer. VEGF-R tyr kinase inhibitor. Titrate to dose • Bleeding, coughing, GI ulcers, infection risk, CNS effects … Interactions • drugs (Rx, OTC, herbal) • foods (vitamins, suppl) Interactions: drugs Seldane terfenidine CYP3A4 (-) Allegra fexofenidine erythromycin Torsades de Pointes - Ventricular tacharrythmia - Prolonged QT Interactions: drugs • Interaction occurs esp. in patients with altered KCNE2 gene for IK r potassium channel that is important for repolarization • ↑QT also by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Interactions: drugs Tylenol Sinus Congestion & Pain Daytime Tamoxifen ? Tylenol Allergy Multi-Symptom CYP2D6 chlorpheniramine • also 2D6↓ antidepressants like fluoxetine Interactions: foods • Grapefruit juice – irreversibly inhibits CYP3A4 on GI mucosa – Consequence is ↑drug absorption – Cyclosporine, some statins • Ca+2, GI transit time may ↓ absorption of some drugs – Tetracyclines, ciprofloxacin Genetic Influences • • • • metabolism Disposition, PK receptors transporters Effect, PD HLA haplotypes Env Health Perspect Genetics in ADRs metabolism: deficiency • Clopidogrel (Plavix) - ↓platelet P2Y12 receptor binding of ADP • Prodrug, activated by CYP2C19 • Loss of function = 2C19*2 allele – Greater risk of thrombi, MI, stroke • PPIs may also ↓2C19 (esp.omeprazole) but ↓ risk of GI bleeding (esp. pantoprazole) – Ray et al., Ann Int Med (2010) Genetics in ADRs metabolism: surplus • Azathioprine, 6-MP detoxified by thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) • Genetic ↓ TPMT → toxicity, pancytopenia • Kits available for genotyping TPMT • Dose adjustments in pts can be life-saving Genetics in ADRs metabolism, receptors • Warfarin (Coumadin) – anticoagulant antagonist of vit. K • Wide variability in dosing, to effect measured by INR • Pharmacogenomic variability in CYP2C9 and VKORC1 [receptor] Genetics in ADRs transporters • Pravastatin, simvastatin – myopathy risk ↑ with variant of organic anion transporter polypeptide (OATP), SLC01B1 – More severe rhabdomyolysis may also be linked but is very rare • P-glycoprotein variant ↑digoxin bioavailability; p-gp also site of drug interactions Genetics in ADRs HLA haplotypes • Carbamazepine (Tegretol) – used for seizures, trigeminal neuralgia, etc. – HLA B*1502 associated with propensity for severe toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome – Mechanism unknown • Aspirin hypersensitivity – associated with HLAs and altered AA metabolism to leucotrienes – HLA DPB1*0301; HLA DB1*0609 Opportunities for teaching drug safety in the curriculum • Explaining ADRs and drug interactions illustrates PK/PD mechanisms of drugs • Vigilance in drug safety improves clinical observational skills • Predictive modeling of ADRs requires laboratory skills and sagacity • Population-based data supports EBM, regulatory and cost-saving decisions • Learners will better identify, predict, report, model and prevent ADRs Pre-clinical Mechanisms Education Reporting ADRs Clinical Observations