* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Italian Renaissance - Manasquan Public Schools
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance painting wikipedia , lookup
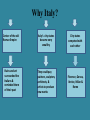
The Italian Renaissance Renaissance rebirth Italian Renaissance rebirth of ancient Greek and Roman worlds Characteristics Secular Urban Society (City-States) Age or Recovery New view of human ability and worth Why Italy? Center of the old Roman Empire Ruins and art surrounded the Italians & reminded them of their past Italy’s city-states became very wealthy City-states competed with each other They could pay painters, sculptors, architects, & artists to produce new works Florence, Genoa, Venice, Milan & Rome Origins of the Renaissance European trade with Asia increased during the 1300’s Italian merchants organized much of the trade Trade cities in Italy grew wealthy The competed to create works that would increase the prestige of their cities Venice Genoa Milan Italian City States - Not yet the nation of Italy Each Each Italian citystate had its own wealthy ruler The Medici family They were the greatest bankers in Florence – Making Florence the banking center of Italy They became Patrons of the Arts Lorenzo Medici represented the Renaissance Ideal – some called Him the Renaissance man Leonard da Vinci – The true Renaissance man –painter, artist, sculptor, humanist, scientist , philosopher, architect, engineer and more Niccolo Machiavelli – The Prince “The End Justifies the Mean” – Rule like a lion to keep peace and stabilize power Italian Renaissance Humanism Stressed man was center of the universe –Man had dignity and value Humanism-intellectual movement based on the classics Each individual finds the truth for himself One can enjoy life and still be good Christians Encouraged human achievement Study-grammar, rhetoric, poetry, philosophy & the Humanities Goal-Create complete citizens Vernacular Literature – written in common language Petrarch – “Father of Humanism” – recovered works of Greek and Roman writers Artistic Renaissance in Italy Rome center of Renaissance art in the 1500’s Masters –Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Raphael Fresco – water color on fresh plaster Law of Perspective Leonardo da Vinci Study of Human anatomy Creation of Adam Michelangelo Last Judgement PIETA Comparison between Renaissance in Northern Europe and Italy NORTHERN EUROPE Did not study the classics as much Art emphasized everyday life in greater detail Artists supported by royalty and nobility Linked with religion although studies of religion led to questioning of church practices ITALY Heavy emphasis on reading the classics Art depicted every day life, but not as detailed Artists supported by wealthy merchant class Not as much emphasis on religious issues humanism very important The Printing Press Johannes Gutenberg was a German goldsmith and printer Guttenberg 1st to develop moveable type Allowed for mass production of books Guttenberg was the key figure in spreading the Renaissance His invention of moveable type is considered the most important invention in history Impact of the printing press Much easier to publish books Increased literacy 1450-1500-20 million books printed covering 35,000 topics Vernacular Literature Written in common language Dante, Chaucer, Shakespeare Contributions of the Renaissance Invention of the Gutenberg Press The banking industry Exploration, colonization of world Expansion of trade Humanism, individual is center of universe Reintroduction of Greek & Roman knowledge and philosophy Gateway to modern art forms Expansion of Greek and Roman architecture & sculpture Increased scientific knowledge, and desire to know more