* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download General Body and Directional Terms
Lymphatic system wikipedia , lookup
Circulating tumor cell wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Body snatching wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Body Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Murder for body parts wikipedia , lookup
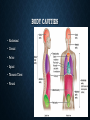
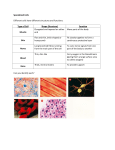
GENERAL BODY AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS BRANCHES OF SCIENCE THAT STUDY THE HUMAN BODY • Anatomy • Biology • Embryology • Histology • Pathology • Physiology THE BODY IN GENERAL • Cells are the basic unit of life • Cells of similar function join together to form tissue • Groups of tissue join together to form organs • Groups of organs work together to perform a complex functionbody system • Trillions of cells vary in size and shape according to their function • Specialized cells are responsible for growth, secretions, excretions, nutrition, reproduction • Mechanical, chemical and nervous stimulation activate the cells CELLS • Epithelial • Fat • Muscle • Nerve TISSUE • Connective • Main types • Bone • Cartilage • Dense fibrous • Loose • Adipose • Epithelial • Muscle • Nerve ORGANS • When two or more kinds of tissue work together, you have an organ • Although they act as units, they do not function alone • Several organs combine to form a body system • Each system has a special function BODY SYSTEMS • Cardiovascular • Reproductive • Digestive or GI • Respiratory • Endocrine • Sensory • Integumentary • Nervous • Lymphatic • Urinary • Musculoskeletal BODY CAVITIES • Abdominal • Cranial • Pelvic • Spinal • Thoracic/Chest • Pleural ROOTS OF STRUCTURES Root What it means Example term Cyt/o Cell Cytology Epitheli/o Epithelium Epithelioma Fibr/o Fibrous Fibrosis Hist/o Tissue Histologist Lip/o Fat Liposuction Myo Muscle Myositis Neur/o Nerve Neuropathy Organ/o Organ Organomegaly Viscer/o Internal organs Viscera What it means STRUCTURAL SUFFIXES Suffix What it means Example term -cyte Cell Erythrocyte -gen Agent that causes Carcinogen -genic Producing Carcinogenic -oma Tumor or swelling Myoma -osis Abnormal condition Cytosis -pathy Disease Neuropathy -plasm Growth or formation Neoplasm -sarcoma Malignant tumor Myosarcoma What it means DIRECTIONAL TERMS • Used to pinpoint or specifically locate an area on the body • Anatomical position • Anatomical plane • Frontal/Coronal • Mid-sagittal • Sagittal DIRECTIONAL TERMS (CONT.) • Ventral • Lateral • Dorsal • Medial • Cephalad • Distal • Caudal • Proximal • Superior/Inferior • Ipsilateral • Mediolateral ROOT WORDS Root word What it means Anter/o Front Caud/o Tail or downward Cephal/o Head or upward Dist/o Away from (distant) the point of orgin Dors/o Back Infer/o Below Later/o Side Medi/o Middle Poster/o Back or behind Proxim/o Near to (proximity) the point of origin Super/o Above Ventr/o Front or belly REGIONS OF THE BODY • Anatomical divisions of the abdomen • Diagnose abd. Problems with greater accuracy • Hypochondriac • Epigastric • Lumbar • Umbilical • Inguinal/Iliac • Hypogastric QUADRANTS • RUQ • LUQ • RLQ • LLQ DIVISIONS OF THE BACK Division Abbreviation Location Cervical C Neck region, there are seven cervical vertebrae (C1-C7) Thoracic T or D (D=dorsal) Chest region; there are 12 thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12), each attached to a rib Lumbar L Loin or flank region (between ribs and hip bone), there are five lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5) Sacral D Five bones (S1-S5), fused to form the sacrum Coccygeal (none) Coccyx (tailbone) composed of four fused pieces Region Auricular Axillary Buccal Clavicular Infraorbital Infrascapular Lumbar Mammary Mental Orbital Pubic Sacral Sternal Submental Supraclavicular Where it is