* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Review - Issaquah Connect
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
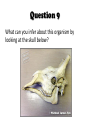
Evolution Review Talk about old school! Question 1 Imagine that you are Charles Darwin and you are trying to convince people that your theory of natural selection really does explain how animals change over time. Use what you learned about Galapagos finches, giant tortoises and/or iguanas during your voyage to help support your claim. Answer 1 • Darwin’s theory of natural selection explains that individuals that are most fit for their environment are most likely to survive and pass their beneficial mutations to the next generation. • Darwin was able to see slight differences in beak shape between finches from different islands, which related to the food available where each species lived. • The marine and land iguanas have a lot of similarities, but marine iguanas have learned to eat seaweed instead of land plants, have a special way of shooting excess salt from their nose, and blend in with the black rocks near the water. • Tortoises have different shell shapes depending on the island they are from. Like the finches, this is based on their food sources. Question 2 Your brother thinks that the largest and fastest individual of a species is most fit to survive. Explain why you agree or disagree. Answer 2 • In this case, fitness does not imply big muscles and the ability to play sports! • An animal that is fit for it’s environment has traits that will help it survive. This might mean that it can run fast, eat from tall trees, camouflage, fly, etc… It all depends on where it lives and what it needs to survive! Question 3 Some whales have been found with a few rear leg bones that seem random and are unattached to the rest of their skeletons. Explain why you think this happens. Answer 3 • Whales have evolved from land mammals, so they could still be carriers of the back leg gene. Maybe it’s just recessive now instead of dominant! • It could also be caused by new mutations in the DNA. Question 4 Your grandma thinks that the theory of evolution can't be possible because she has never seen a monkey turn into a human. How could you convince her otherwise? Use evidence to support your claim! Answer 4 • First of all, monkeys have tails so you’re not a monkey and neither was your great, great, great, great, great, etc… grandma because she didn’t have a tail either. • No primate (monkeys and apes, for example) will ever turn into a human, especially not overnight. Evolution of one species takes thousands, if not millions, of years. These small genetic changes happen over many, many generations. • We do share a common ancestor with other modern day great apes and our DNA is about 97% the same as a chimpanzee! However, we are still human and they are not. • Since we are different species, human and chimpanzees can’t breed even with such similar DNA. Sorry, no monkey men as offspring! Question 5 Explain how a species can get more genetic variation and give a specific example of the results. Why is it important to have variation? Answer 5 • Genetic variation comes from the many mutations within a species. • The most common examples are size and coloration. • It is important to have genetic variation to prevent genetic deformities and massive deaths caused by disease or environmental change. Question 6 Using the stratigraphic column below, what can the rock layers and their contents help you infer about this evidence? Answer 6 • These rock layers contain fossils – preserved evidence of living things. • According to the Law of Superposition, which states that rock layers at the bottom of a stratigraphic column are oldest and younger layers are above, fossil 5 is oldest and 2 is youngest. • This area was most likely under water in the past. • Fossils 1 and 4 lived at about the same time. Question 7 Compare these two pictures and explain whether or not you think these species share a common ancestor. Why or why not? Answer 7 • Most likely yes. • Many dinosaur species evolved into modern day birds over the last 65 million years. Some laid eggs, had similar pelvic bones to birds, almost hollow bones, babies with feathers, made nests, were warm blooded, etc… • These two species both have large three-toed feet, a crest on their heads, somewhat beaklike mouths, walk with a similar stance, etc… Question 8 Looking at the following image, which species is more closely related to birds, the Acrocanthosaurus or the Tyranasaurus? Be ready to defend your decision! Answer 8 • Acrocanthosaurus because it is closer to birds on the evolutionary tree. • All three species share the same common ancestor, Tetanurae. Question 9 What can you infer about this organism by looking at the skull below? Answer 9 • It is a giraffe, but you could not know that for sure just by looking at the picture. That would be an inference, not an observation. • It had horns. • It had monocular vision (eyes on the side of its head) so it was probably not a predator. • The bones are not fully fused together so it was probably young when it died. • It had flat teeth that are good for grinding, so it probably ate plants. • It had a large nasal cavity (nose hole) so it may have needed lots of oxygen in each breath.