* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concepts of Modern Physics Presentations
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Supersymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Matrix mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum potential wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chaos wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum logic wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
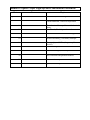
SPH4U: Concepts of Modern Physics Presentations Guidelines: You will choose a topic in modern physics from the list below. Each topic is a basic concept or idea in modern physics (related to quantum mechanics, general relativity, particle physics, or theories of everything) You will be allotted 10 minutes to present a summary of your topic, highlighting the significance of the main concepts related to your topic, and you will then field questions from the class. You may use the chalkboard or the projector (powerpoint, youtube, other animations) to aid in your presentation, but this is not mandatory. You will then post your summary on the Modern Physics class wiki: rosedalemodernphysics.wikispaces.com You will be assessed based on the clarity and accuracy of your presentation, and on how well you answer questions and stimulate discussion. Presentations will be given at the beginning of Thursday and Friday classes. Modern Physics Topic Sign-up and Presentation Schedule Date Name September 12 Topic JJ Thomson, Plum Pudding Model Ernest Rutherford, Gold Leaf Experiment 26 Photoelectric effect – problems with classical theory Max Planck, Planck’s postulate and constant October 2 Niels Bohr – atomic model with energy levels 18 10 Werner Heisenberg, Uncertainty Principle 16 Photography and CCDs (charge coupled devices) Louis De Broglie, matter waves 24 November 6 Erwin Schrodinger, Wave Equation 20 Wave functions and quantum numbers 28 Electron microscopes December 4 Quantum tunneling Date Name January 8 Topic Scanning tunnelling microscopes 16 Radioactivity and radiocarbon dating 22 Wolfgang Pauli, Pauli Exclusion Principle Bosons and Fermions 30 Quarks February 6 Transistors and microelectronics 12 Lasers – basic principles and applications 20 Richard Feynman, Quantum Electrodynamics (QED) Schrodinger’s Cat, Quantum mechanics and the nature of reality Quantum entanglement 26 March 6 26 Aprils 2 10 Quantum computing General Relativity – basic ideas 16 Arthur Eddington, Experimental Evidence for General Relativity Paul Dirac, matter and anti-matter 24 The Standard Model 30 The Steady State Theory The Big Bang Theory May 8 String Theory Dark Energy 14 Higgs Boson – recent developments Topics List: 1. Photoelectric effect – energy quantization 2. Light as a particle (photons), Planck’s constant 3. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle 4. Photography and CCDs 5. De Broglie’s matter waves 6. Schrodinger’s wave equation 7. Electron microscopes 8. Wave functions, quantum numbers 9. Quantum tunneling 10. Scanning tunnelling microscopes 11. The Standard Model 12. Radioactivity and radiocarbon dating 13. Pauli Exclusion Principle 14. Bosons and fermions 15. Transistors and microelectronics 16. Lasers – basic principles 17. Niels Bohr, atomic model 18. Schrodinger’s cat 19. Richard Feynman, Quantum Electrodynamics (QED) 20. Quantum computing 21. Experimental Evidence of General Relativity (Arthur Eddington) 22. Paul Dirac and anti-particles 23. Steady State vs. Big Bang 24. Ernest Rutherford, Gold Leaf Experiment 25. Large Hadron Collider (LHC) and the Higgs Boson