* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stress: The Constant Challenge
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Self-blame (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Effects of stress on memory wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Social stress wikipedia , lookup
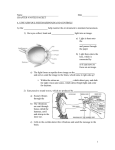
Stress: The Constant Challenge Chapter 2 Stress * What is Stress? * Two Situations – Physical response to stress – Emotional responses to stress Concepts in Stress * Stressor * Stress response * Stress * Homeostasis * Eustress * Distress Physical Responses to Stress * Actions of the Nervous System – Autonomic Nervous System • Sympathetic System – Fight or Flight response – Influences in modern day life • Parasympathetic System – Return to Homeostasis – Actions of the Endocrine system • Hormones Endocrine System * Function of the Amygdala * Hypothalamus – Corticotropin releasing factor, CRF * Pituitary gland – ACTH * Adrenal gland – Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cortisol Effects of Adrenaline on the Body * Hearing and Vision * Lungs * Heart * Liver * Sweat glands * Pain receptors * Muscles * Digestive system The Fight or Flight Reaction in Modern Life * Today’s stressors elicit a physical response regardless of the treat. Emotional & Behavioral Responses to Stress * Effective responses to stress: – Talking, Laughing, Exercise and Time Management * Ineffective responses to stress: – Overeating, procrastination, frustration Responses to Stress * Somatic Nervous System – Manages conscious actions * Personality and Stress – Type A, B and C – Hardy Personality * Cultural background * Gender * Past Experiences General Adaptation Syndrome (G.A.S.) * Alarm – Fight or Flight * Resistance * Exhaustion * Allostatic load Alarm Phase Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI) * The study of …. * Complex network of nerve and chemical connections between the nervous system, endocrine system and the immune system. Links Between Stress and Specific Health Conditions * Cardiovascular Disease * Weakened Immune System * Psychological Problems * Other health problems – Digestive disorders – Headaches – Insomnia – Injuries Common Sources of Stress * Life changes * Daily hassles * College * Job * Interpersonal * Social * Environmental * Internal Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) * Cognitive, emotional and behavioral reactions to trauma – Signs – Positive steps to help cope Techniques for Managing Stress * Social Support * Communication * Exercise * Nutrition * Sleep Techniques for Managing Stress * Time Management – Say “NO” to procrastination – Say “YES” to: Setting priorities Schedule Realistic Goals Visualization Techniques for Managing Stress * Cognitive Techniques – Think and Act constructively – Take control – Problem solve – Modify the experiences – Stay positive Relaxation Techniques * Deep Breathing * Progressive Relaxation * Visualization * Meditation * Yoga * T’ai chi ch’uan * Music * Biofeedback Counterproductive Coping Strategies * Tobacco use * Alcohol * Other drugs * Binge eating Personal Plan for Managing Stress * Identify the Stressor * Designing your Plan – Personal contract * Getting Help Behavioral Change Strategy * Systematic Desensitization – Phase I – Phase II – Phase III – Success Rehearsal