* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
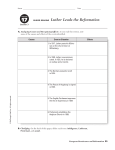
Download Chapter 5 Study Guide—Renaissance and Reformation
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Art in the Protestant Reformation and Counter-Reformation wikipedia , lookup
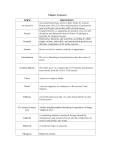
Chapter 5 Study Guide—Renaissance and Reformation 1. Edict of Worms—(1521) Charles V (Holy Roman Emperor) made Luther an outlaw in the empire and forced him into hiding 2. Predestination—idea of John Calvin that God had decided the destiny of salvation at birth, contradicted Luther’s belief in faith alone as means of salvation 3. The Prince—written by Machiavelli, written about how to get and keep political power, first book to encourage readers to abandon morality as a basis for ruling 4. Council of Trent—meetings held by leaders of Catholic Church to discuss problems, reaffirmed traditional Catholic teachings in opposition to Protestantism 5. Leonardo da Vinci—perfect example of the “Renaissance Man,” was a painter, sculptor, inventor, and mathematician. Best known for Mona Lisa and The Last Supper paintings 6. Christine de Pizan—wrote The Book of the City of Ladies written in defense of women, said women deserved same educational opportunities as men 7. Massaccio—most known for his beautifully painted frescoes 8. Christian Humanism—believed people must read the bible to achieve salvation and not be dependent on the Church 9. Peace of Augsburg—officially accepted the division of Christianity in Germany (Catholics and Protestants) 10. Castiglione—wrote The Book of the Courtier which described the characteristics of the perfect Renaissance noble, was followed for centuries 11. The Divine Comedy—written by Dante, is about a soul’s imaginary journey through hell, purgatory, and heaven (or paradise) 12. The Canterbury Tales—written by Geoffrey Chaucer in the English vernacular that laid the basis for our modern English language. Story follows pilgrims of all classes on a pilgrimage 13. Ninety-Five Theses—published by Martin Luther in 1517, it attacked the sale of indulgences 14. van Eyck—was the first to use oil paint showing greater color and detail 15. “Bloody Mary”—Queen Mary of England called this because she had protestants rounded up and executed by burning them at the stake, moving England back towards Catholicism 16. Dowry—the amount of money paid by a bride’s family to the groom’s family prior to a wedding 17. Indulgence—is an excuse from all of part of the punishment for sin, idea attacked by Martin Luther 18. Petrarch—is considered the father of Italian Renaissance Humanism 19. Erasmus—was the first to criticize the Church and sales of indulgences, never made an effort of break away from the Church. He “laid the egg that Luther hatched.” 20. The Consistory—established by John Calvin to enforce moral discipline in Geneva Switzerland after the death of Zwingli . Essay Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Reformation/Martin Luther/Indulgences/95 Theses Role of Henry VIII in changing religion in England. Luther vs Erasmus in the Reformation Renaissance Man/Define and give examples Compare/contrast ideas of Luther and Erasmus Define and describe the Reformation and Protestantism Catholic Response to the Reformation/Council of Trent Define/describe the Renaissance