* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Populations Evolve
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
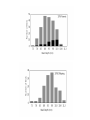
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
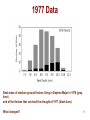
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Evolution Website: http://evolution.berkeley.edu/ Evolution is the explanation of many facts of life FACTS: Life has change through time • Extinction is common • Species exist today that did not exist before Today’s species share many features • Similar DNA and proteins • Same genetic code SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION: Descent with modification (theory of evolution) Independent lines of evidence to support it: Misconceptions about Evolution Biology professor interviewed in Colbert Report Evolution is NOT in conflict with any religion Evolution, as science, looks for natural explanations to natural phenomena Darwin’s Finches 2:30min -4:40 4 Peter and Rosemary Grant • Scientists Peter and Rosemary Grant have studied many of these species for the past thirty years. – Spend months at a time on the islands – Often know every finch on an island • They focused on one species: medium ground finch 6:00min-7:50 • Let’s look at some of their data. 5 Graph showing the distribution of beak depths for medium ground finches in Year 1 (1976) Population size 641 finches Number of finches with a specific beak depth 6 1. What is the most common beak depth of the finches living in Daphne Major in 1976? ______________ Write answers on part 2 of evolution handout 7 2. What is the range of beak depths in this group of medium ground finches? ________________ 8 A Change in the Weather • In a normal year, 130mm of rain would fall. • In 1976, 137mm of rain fell. • In 1977 The total rainfall for the entire year: 24mm. How did this affect the island? Min 7:50-8:15 9 3. What do you think a graph of population size would look like for year before the drought to the year after the drought? B: A: Time C: Time D: Time Time Where all the finches equally affected? Min 8:15-9:20 10 1977 Data Beak sizes of medium ground finches living in Daphne Major in 1976 (gray bars) and of the finches that survived the drought of 1977 (black bars). What changed? 11 4. Approximately what percentage of birds with the most common beak depth in 1976 survived the drought? 12 1978 Offspring 13 5. What is the most common beak depth of the finches living in Daphne Major in 1978? ______________ 14 6. Did the finch population evolve from 1976 to 1978? A: Yes B: No C: Maybe D: I don’t know 16 Microevolution: descent with modification within a population POPULATION is a group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area 1st generation What has been modified? the individual? 2nd generation Proportion of the phenotypes in the population has changed over time These phenotypes have a genetic basis Microevolution can also be defined as the the change in the proportion (frequency) of alleles over time What was the cause for the change in the population? Mechanism: Natural selection Organisms best suited to the environment have the most resources for survival and reproduction And pass their successful traits to offspring. What was the cause for the change in this population? Mechanism: Genetic drift Changes in the gene pool of a small population due to chance event. Two Types of Genetic Drift Bottle neck Effect: Genetic drift resulting from a drastic reduction in population size Bottle neck effect Founder effect Founder Effect: Genetic drift due to colonization by a limited number of individuals from a parent population. Some colonies show high frequency of certain inherited disorders Examples: British colony on Tristan da Cunha has higher incidence of retinitis pigmentosa Dutch colony on South Africa has higher incidence of Huntington's disease What type of genetic drift is this? Species that have been endangered and rebound show low genetic diversity Hundreds of thousands of Elephant seals once inhabited the Pacific Ocean. The Northern population were slaughtered in the 1800s for their blubber By 1892, only 50 to 100 individuals were left. 1900 the Mexican and US government decided to protect them Today, there are approximately 160,000 northern elephant seals. The Northern population of elephant seals is less genetically diverse than the Southern Population. What type of genetic drift is this? Why is this not considered natural selection? What was the cause for the change in this population? Mechanism: Gene flow The loss or gain of alleles in a population due to the migration of fertile individuals or gametes between populations What was the cause for the change in this population? Mechanism: Mutation A rare change in the DNA of a gene introducing a new allele The Hardy-Weinberg principle or equilibrium can be used to test whether a population is evolving Condition that need to be met for a population to be in H-W equilibirum The Hardy-Weinberg principle or equilibrium p = proportion (frequency) of the dominant allele in the population q = proportion (frequency) of the recessive allele in the population p2 = proportion (frequency) of homozygous dominant individuals q2 = proportion (frequency) of homozygous recessive individuals 2pq = proportion (frequency) of heterozygous individuals Population genetics handout Work in groups of 4: one pair does simulation 1: population in equilibrium simulation 2: population under a negative selection pressure the other pair does simulation 1 and simulation 3: population with a heterozygous advantage exchange data from simulation 2 and 3 between pairs Fill out handout, except for question 7 at the end of handout Applications of Hardy-Weinberg principle: The Hardy-Weinberg equation is often used to test whether evolution is occurring in a population. Public health scientists use the Hardy-Weinberg equation to estimate how many people carry alleles (are heterozygous) for certain inherited diseases. Complete the set of H-W problems from your evolution handout (part 3) Natural Selection: a closer look This type of trait is said to be an adaptation Types of Natural Selection depending on which phenotype is being favored Directional selection: shifts the frequency curve in one direction. It happens when the environment changes or a population migrates to a new habitat Disruptive selection: conditions favor individuals on both extremes. Stabilizing selection: Acts against extreme phenotypes and favors intermediate ones 7. Which type of selection was observed on the Darwin finches? A. B. C. D. Directional Disruptive Stabilizing I am not sure Misconceptions about Natural Selection: “Natural Selection gives a species what it needs” When the environment changes, a population can survive or die out, depending on the variation present before the change. Natural selection is more of an editing process than a creating process Misconception: “Natural Selection is a random process” A population of organisms experiences random mutations but selection is non-random (one specific mutation is selected) Natural Selection results a population better adapted to the environment (at least momentary) What happened to the finches after the drought? Min 9:20-11:20 Misconception: “Natural selection is the survival of the strongest and fastest” More important than surviving is reproducing FITTNESS: The contribution an individual makes to the next generation, relative to the contributions of other individuals. Natural selection does not act only on the traits that allow for survival of the individual but also on the traits that increase ability to find a mate and reproduce 8. Which statement describes the swallow with the greatest evolutionary fitness? A. A finch that lives to be 3 years old and has four offspring, two of which survive to reproduce themselves B. A finch that lives to be 5 years old and has five offspring, one of which survives to reproduce C. A finch that lives to be 2 years old and has four offspring, all of which survive to reproduce themselves D. A finch that lives to be 7 years old and has three offspring, all of which survive to reproduce E. All are equally fit Some traits are selected for even if they are a burden to health or survival of the individual Because they increase the fitness of the individual Sexual selection: natural selection for mating success due to mate choice or male competition Misconception: “Natural selection will produced perfectly engineered organisms” Natural selection is THE SURVIVAL OF THE FIT ENOUGH Reasons why there are not faster cheetah: Variation not present not possible Trade-offs Misconception: Natural Selection should eliminate bad genes • Bad genes might not really reduce fitness Example: Huntington’s disease • Bad genes might be maintained by heterozygote advantage Example: Sickle cell disease Natural Selection is happening today Pesticides become less effective with each spraying Antibiotics become less effective with successive uses Artificial Selection: Humans (instead of nature) select for which individuals in the population reproduce (those with the desired phenotype)