* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson Title:
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
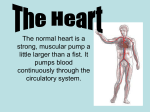
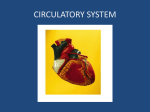
Lesson Title: Layout of the Heart Unit Title: Circulatory System Lesson Purpose/Goal: Explain the key terms and components of the circulatory system. Teacher Name: Jones Time: 45 min Instructional Objectives: (Students…) 1. Define the circulatory system and its functions. 2. Explain the layout of the heart. 3. TEKS: 130.7.c (8)(B) TAKS: LifeKnowledge Precept: (If Applicable) Materials/Supplies Needed: Projector/PPT with heart diagram Notes Page Question Slips Answer Slips Circulatory System Quiz 1 References: IMS Modern Livestock and Poultry Global Contextual Set: (1. Where we have been; 2. Where we are going & why; 3. What we are doing today; 4. How learners should conduct themselves) 1. We just finished up our reproduction unit. 2. Now, we are going to explore even more into the anatomy of livestock, So we can be well rounded in the industry. 3. Today is going to start our section over the circulatory system. 4. So be ready to take notes, move around, and have fun learning. Focus/Interest Approach/Anticipatory Set: (Captures attention and focuses students’ thinking through physical/cognitive engagement. Principle – Experience before label.) We had chicken fingers for lunch, right? What do fried foods do to your body on the inside? Well they might make gain a little weight, but what is that thing called when your arm is unmovable, your body begins to ache, and your heart stops. Heart attack. All of that food begins to clog your arteries and furthermore hurts your heart. And our arteries and heart are part of our circulatory system. Lesson Content: Objective 1: (Define the circulatory system and its functions.) (Include all content, activities, directions, scripting, etc. below. Use as much space as needed) So guys if we were going to list all the components of the circulatory system, what would some of those be? - Heart, Veins, Capillaries, Arteries, Lymph Vessels, Lymph Glands Teaching Method: Teacher Led Discussion Notes: List on the board And overall all, who can tell us what all of these components work together to accomplish? - Supply the body tissues with nourishment and collect waste materials. What we will do now is list all the functions of the circulatory system. - Distribution of nutrients - Transport + Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide - Remove Waste Materials Let students say them, if they don’t know ask probing questions. - Distribute Secretions of endocrine glands - Prevent Excessive Bleeding - Prevent Infection - Regulate body temperature On a scale on 1-10 how important do you all think our circulatory system is? Checking for Understanding: Are there any questions at this time? Contextual Bridge: Well now we will actually get into the key terms and layout of the system. Objective 2: (Explain the layout of the heart.) (Include all content, activities, directions, scripting, etc. below. Use as much space as needed) Heart: is located near the center of the thoracic cavity b/t the lungs and is contained in the pericardial sac. It is a funnel shaped, hollow, muscular organ that is responsible for pumping blood to all parts of the body. Teaching Method: Lecture PPT Notes: Pericardial Sac: Supports heart and contains some fluid for lubrication. At the base of the heart, it is supported by large arteries and veins. The heart wall is made up of three layers. - Epicardium: outer layer; inner layer of epicardial sac - Endocardium: inner layer; consists of endothelial cells, whish line the heart, covers the valves, and lines the blood vessels. - Myocardium: Middle layer; composed of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is involuntary meaning we donnot control it. In mammals the heart is divided into a right and left side which is then divided into an atrium and ventricle. With this being said, the heart is said to have four chambers; right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle. Atrioventricular valves: separate the atrium and ventricle on each side of the heart AV valves have flaps of tissues called leaflets or cusps, which open and close To ensure that blood only flows in one direction and doesn’t backflow into the Atriums. - Tricuspid valve: on right side of heart; has 3 leaflets. - Bicuspid valve: on left side of the heart; has two leaflets Pulmonary & Aortic Valve: Prevent blood from back flowing into their respective ventricles. - Pulmonary valve: located b/t right ventricle and pulmonary artery. - Aortic valve: located b/t the left ventricle and aortic artery. Sinoatrial Node: group of cells that control the beat of the heart by sending out electrical signals to make it pump. Checking for Understanding: What terms would you like for me to go over again? What questions do you have? Contextual Bridge: Well we have listed the functions, we have gone over the terms, now it is time to get some practice with these concepts. Guided Practice: (Group oriented and teacher supported. Include all activities, directions, and description below.) (Using the slips of questions and answers in SM’s). On this stack of cutout slips of paper, I have placed different questions covering the concepts we have talked about today. And on this stack, I have placed the answers to the questions of that stack. One half of the room is going to get the questions while the other half of the room is going to get the answers. Once everyone has a slip of paper, you may begin to move about the room and find either the answer to your question, or the question to your answer. What questions do you have? When you all find your partners, we will then go over your individual questions and answers. Contextual Bridge: Does anyone have any questions about the terms, components, and functions of the circulatory system? Independent Practice: (Individualized and independent activity occurring in the classroom. Include all activities, directions, and description below.) Very good guys. I am passing out a quiz that you need to complete and hand to me as you are walking out the door today. The is an independent activity. Closure - Global Contextual Set: (1. Where we have been; 2. Where we are going & why; 3. What we will do next; 4. How learners should conduct themselves or what supplies are needed next.) 1. Well today we have covered the functions, components, and layout of the heart and furthermore the circulatory system. 2. We are gaining a greater understanding of the anatomy of livestock for various future endeavors. 3. Tomorrow we will dig deeper into the circulatory system. 4. So be ready to participate, and have fun learning. Extension Activity: (Optional) Assessment: (What formal method will be utilized to measure students’ knowledge/learning?) Students will be tested over the objectives at the end of the unit. (*Note: All supplemental materials including but not limited to handouts, visuals, worksheets, etc. required for the lesson is to be included on the following pages. Each should be separated by a page break.) 1. Circulatory System is comprised of: 2. Functions of the circulatory system include: 3. The heart is responsible for: 4. The heart is located: 5. The pericardial sac is responsible for: 6. The three layers that make up the heart wall are: 7. The Epicadium is which layer of the heart wall: 8. The Endocardium is which layer of the heart wall: 9. The Myocardium is which layer of the heart wall: 10. The heart is comprised of this type of muscle: 11. The cardiac muscle is involuntary which means: 12. Each side of the heart is divided into these two things: 13. The four chambers of the heart are: 14. The atrioventricular valves separate what two things: 15. The tricuspid valve is on which side of the heart: 16. The bicuspid valve is on which side of the heart: 17. The pulmonary valve and aortic valve prevent: 18. The sinoatrial node is a group of cells that control what: Heart, veins, capillaries, arteries, lymph vessels, and lymph glands. Distribute nutrients, transport/exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Pumping blood to all parts of the body. Near the center of the thoracic cavity. Supporting the heart and lubrication. The Epicardium, Endocardium, and Myocardium. Cardiac Muscle You do not control it. The atrium and ventricle. The Right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle. Separates the atrium and ventricle on each side of the heart. Right Side Left Side Prevent blood from back-flowing into their respective ventricles. Control the beat of the heart by sending electrical signals. The ____________________ system is comprised of the heart, veins, capillaries, arteries, lymph vessels, and lymph glands, which work together to _____________ the body tissues with ____________________ and ______________ ___________ material. _________________ of the circulatory system: Distribute _________________ Transport and exchange _____________ and _____________ ______________ Remove ___________ materials Distribute ___________________ of endocrine glands Prevent excessive ________________ Prevent _________________ Regulate body ____________________ ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE HEART The ___________ is a funnel-shaped hollow, muscular organ that is responsible for pumping blood to all parts of the body. The heart is located near the center of the ________________ cavity between the lungs and is contained in the pericardial sac. The ____________________ sac supports the heart and contains some fluid for lubrication. The broad end, or base, of the heart is supported by large ________________ and ___________. The pointed end, or __________, of the heart is directed toward the abdomen. The heart __________ is made up of three layers: ___________________ - outer layer of heart wall, which is also the inner layer of the epicardial sac; ____________________ - inner layer that consists of endothelial cells, which line the heart, cover the heart valves, and line the blood vessels; and ___________________ - middle layer composed of cardiac muscle. The ______________ muscle is an ____________________, striated muscle with fibers that intertwine. In mammals and birds, the heart is divided into a ___________ and __________ side and each side is divided into an _____________ and _________________. Therefore, the heart has __________ ________________ (right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle). The __________________________ ___________ (AV valves) separate the atrium and ventricle on each side of the heart. The AV valves have flaps of tissues, called leaflets or ___________, which open and close to ensure that the blood flows only in one direction and does not backflow into the atriums. The AV valve on the right side of the heart is called the _________________ valve because it has three leaflets (cusps). The AV valve on the left side of the heart is called the ________________ valve (or mitral valve) because it has two leaflets. The _________________ valve and the _____________ valve prevent blood from back-flowing into their respective ___________________. The _________________ ___________ is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. The _____________ ___________ is located between the left ventricle and the aortic artery. A group of cells called the ___________________ __________ (SA node) control the beat of the heart by sending out ___________________ signals to make the heart pump. Circulatory System Quiz 1 1. T / F The circulatory system functions in the transport and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. 2. T / F The heart is made up of five layers. 3. T / F The pericardial sac supports the heart and contains lubrication. 4. T / F Cardiac muscle is voluntary muscle. 5. T / F The Myocardium is the outer layer of the heart. 6. T / F The heart is divided up into four compartments.