* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standard EPS Shell Presentation
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
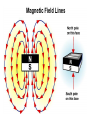
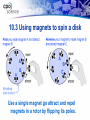
Integrated Science Unit 3, Chapter 10 Unit Three: Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 10 Magnets and Motors 10.1 Permanent Magnets 10.2 Electromagnets 10.3 Electric Motors and Generators Chapter 10 Learning Goals Describe the properties of a permanent magnet. Describe the forces that magnets exert on other. Explain why materials like iron and steel are attracted to magnets. Explain why a compass points north. Build an electromagnet. Analyze how electric current affects the strength of the magnetic field in an electromagnet. List three ways that the strength of an electromagnet can be increased. Compare permanent magnets and electromagnets. List several applications of electromagnets. Explain electromagnetic induction. Describe how electric motors and generators work. Chapter 10 Vocabulary Terms electromagnet electromagnetic induction generator magnet magnetic magnetic field intensity magnetic force permanent magnetic south pole 10.1 Permanent Magnets Key Question: What effects do permanent magnets have? *Read text section 10.1 AFTER Investigation 10.1 10.1 What is a magnet? A permanent magnet is a material that keeps its magnetic properties even when it is NOT close to other magnets. 10.1 Properties of Magnets Magnets have two opposite poles. — north — south Magnets exert forces on each other. The forces depend on the alignment of the poles. 10.2 Electromagnets Key Question: Can electric current create a magnet? *Read text section 10.2 AFTER Investigation 10.2 10.2 Applications of electromagnets mag-lev train toaster doorbell 10.3 Electric Motors and Generators Key Question: How does an electric motor or generator work? *Read text section 10.3 AFTER Investigation 10.3 10.3 Using magnets to spin a disk Use a single magnet go attract and repel magnets in a rotor by flipping its poles. 10.3 Generating Electricity A power plant generator contains a turbine that turns magnets inside loops of wire to generate electricity.