* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standard EPS Shell Presentation
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
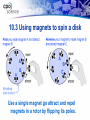
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
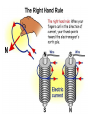
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
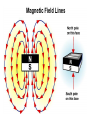
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup