* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT1 THE ECOSYSTEMS A ) DEFINITIONS : ECOLOGY
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
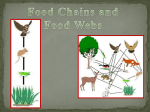
UNIT1 THE ECOSYSTEMS A ) DEFINITIONS : ECOLOGY, BIOSPHERE, ECOYSTEMS WHAT IS THE BIOSPHERE? THE BIOSPHERE CONSISTS OF ALL THE ECOSYSTEMS OF THE PLANET WHAT IS ECOLOGY? ECOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF ECOSYSTEMS WHAT IS AN ECOSYSTEM? An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving, physical components of the environment WHAT IS BIOCOENOSIS? BIOCOENOSIS IS all the organisms living together in a specific biotope WHAT IS BIOTOPE? BOITOPE ARE THE PHISICAL CONDITIONS OF AN ECOSYSTEM LIKE TEMPERATURE, HUMIDITY, COMPOSITION OF WATER OF SOIL, ETC.. ECOSYSTEM= BIOCOENOSIS + BITOPE + RELATIONSHIPS WHAT IS A HABITAT? A habitat is part of the biotope inhabited by a particular species of organism B) TAKE NOTES: ABIOTIC FACTORS THE ABIOTIC FACTORS ARE THE SAME AS THE BIOTOPE OF AN ECOSYSTEM THE MOST IMPORTANT ONES ARE LIGHT: It is the source of energy for plants to sustain photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process of producing food from light, carbon dioxide water and minerals. The result of photosynthesis is oxygen and food. TEMPERATURE: Living things must get adapted to the temperature of the enviroment. So that there are homeothermal animals like mammals and poikilotherm animals like reptiles (homeothermal: having constant and relatively high body temperature ) (poikilotherm: is a plant or animal whose internal temperature varies ) HUMIDITY:All living things need water to live in order to perform the three vital functions. They have many ways of retaining water in their bodies C) RELATIONS AMONG LIVING THINGS. CLASSIFICATION INTRAESPECIFIC RELATIONSHIPS. Relationships among living things of the same kind of spieces competition intraespecific relationships: Relationships among the same kind of species that compete with each other cooperation intraespecific relationships:Relationships among the same kind of species where they profit overall. Family: Relationships among the same kind of spieces where they look after their new born. Society: Relationships among the same kind of spieces where there are different castes. Colony: Relationships among the same kind of spieces where different individuals have a common body with specialized functions. INTERESPECIFIC RELATIONSHIPS. Relationships among living things of different spieces Competition:Relationships among different kind of species that compete with each other Parasitism: Relationships among different kind of spieces that Mutualism: Relationships among different kind of spieces that take advantage from each other. Commensalism: Relationships among different kind of spieces where one kind of spice profits and the other one is placid. Symbiosis: Relationships among different kind of spieces where must live together o cohabit. Predation: Relationships among different kind of spieces where one gets fed from the other. D)MATTER AND ENERGY IN ECOSYSTEMS The trophic structure of an ecosysten are all the trofic relationships which we can find in it, which means, all the trophic chains or trophic webs with different trophic levels. Trophic Chain: http://www.field-studies-council.org/urbaneco/images/011-food-chain.jpg Trophic Web: http://image.tutorvista.com/content/ecosystem/food-web-grassland-ecosystem.jpeg Trophic Level: A trophic level is the position that an organism occupies in the trophic chain. Producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, and tertiary consumer are examples of trophic levels. Producer: A producer is at the beginning of the trophic (or food) chain. Producers are plants and vegetables. Grass is an example of a producer. Primary Consumer: A primary consumer is the next link in the food chain. Primary consumers are herbivores, so they eat plants. Grasshoppers and mice are examples of primary consumers. Secondary Consumer: A secondary consumer eats primary consumers. For example, rabiits, snakes, and shrews are secondary consumers. Tertiary Consumer: A tertiary consumer is an animal that eats the primary and secondary consumers. Owls and hawks are examples of tertiary consumers. Dialogues: What does a ________________ eat? A _______________ eats _____________. What does a primary consumer eat? A primary consumer eats a producer. What does a grasshopper eat? A grasshopper eats grass. What does a ________________ feed? A _______________ feeds _____________. What does a producer feed? A producer feeds a primary consumer. What does grass feed? Grass feeds a mouse. E) ENERGY FLOW IN ECOSYSTEMS ALL THE ENERGY OF THE ECOSYSTEMS COMES FROM THE SUN. EACH TROPHIC LEVEL GETS 10 PERCENT OF ENERGY FROM THE PREVIOUS LEVEL. SO THE COMPLETE THE SQUEME KILOGRAMES OF MATTER SUN → GRASS → GRASSHOPPER → 678 Kg(8%) → Kg(7%)→ SPIDER → Kg(6%) → SPARROW → EAGLE Kg(4%) → Kg F) MATTER CYCLES COPY THIS SQUEME CARBON DIOXIDE IS A BYPRODUCT OF COMBUSTION FROM FOSSIL FUELS AND RESPIRATION OF LIVING THINGS BIOMATTER IS IS A BYPRODUCT OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS FROM CARBON DIOXIDE FOSSIL FUELS ARE BYPRODUCTS OF THE DESCOMPOSITION FROM LIVING THINGS ANSWER THESE QUESTIONS How is ____________ produced?___________ is/are produced by____________ Where does/do _________ came from?__________ come/comes from ______________