* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Structure and Isotopes
Einsteinium wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Isotope analysis wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
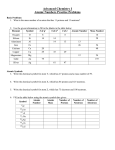
Atomic Structure and Isotopes August 15, 2013 Atomic Structure (Chapter 4) An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. The ancient Greek philosopher Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. Aug 152:30 PM Democritus's ideas lasted until the late 1700s when John Dalton proposed Dalton’s Atomic Theory: > All elements are composed of atoms. > Atoms of the same elements are the same. > Atoms of different elements can combine together to make compounds. > Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Aug 152:30 PM 1 Atomic Structure and Isotopes August 15, 2013 There have been many models of the atom since Dalton introduced his atomic theory. 1. Dalton's Theory The "Billiard Ball" Model Aug 152:30 PM 2. Thomson’s Theory– The “Raisin Bun” Model Aug 152:30 PM 2 Atomic Structure and Isotopes August 15, 2013 3. Rutherford’s Theory – “beehive” or “nuclear” model. Aug 152:30 PM Bohr Theory – The ‘Planet’ Model Bohr stated that the nucleus contains both protons and neutrons with electrons in fixed energy levels around the nucleus. Aug 152:30 PM 3 Atomic Structure and Isotopes August 15, 2013 The Structure of the Nuclear Atom Subatomic Particles • Electrons (e) are negatively charged subatomic particles that surround the nucleus of the atom. • Protons (p+) are positively charged subatomic particles and are found within the nucleus of an atom. • Neutrons (n0) are subatomic particles with no charge (neutral). They are found within the nucleus of an atoms. Aug 152:30 PM Aug 152:30 PM 4 Atomic Structure and Isotopes August 15, 2013 Distinguishing Among Atoms Atomic Number Each element in the periodic table has a unique atomic number. The atomic number corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus. For an element, the number of electrons will equal the number of protons. Atomic Number (Number of protons and electrons) Aug 152:30 PM Mass Number The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Mass Number = protons + neutrons Not found on the periodic table! Aug 152:30 PM 5 Atomic Structure and Isotopes August 15, 2013 Aug 152:30 PM Isotopes Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. Therefore, isotopes of the same element will have different mass numbers. Aug 152:30 PM 6 Atomic Structure and Isotopes August 15, 2013 Special notation is used to distinguish between different isotopes: 12 13 6 6 C Carbon12 C Carbon13 Aug 152:30 PM Atomic Mass The atomic mass is the weighted average mass of the atom’s naturally occurring isotopes. It is not the mass number! Atomic Mass Aug 152:30 PM 7 Atomic Structure and Isotopes August 15, 2013 Aug 152:30 PM Fill in the following table: Element Name Number e Number of p+ Number of n0 Shorthand Carbon12 25 25 Chlorine35 14 16 50 24 Cr Aug 152:30 PM 8