* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction_to_Horticulture_2
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
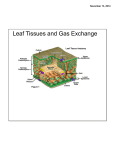
Introduction to Horticulture Plants Parts A World Without Plants Find a Partner On your note card Identify why plants are so important to the world Provide Examples Parts of a Plant Leaves Stems Roots Flowers Fruits or Seeds Leaves The FOOD FACTORY Produces all the food required by the plant or animals Leaf Structure Petiole – leaf stalk Blade – flat, large part of leaf Midrib – large center vein Veins – structural framework Margin – edge of leaves (assists in ID) Leaves Internally – Epidermis – single layer of cells that is the skin of the leaf – protect leaf from excessive moisture loss Guard Cells – open and close a small pore on the underside of the leaf (stoma) Allows leaf to breath and transpire Transpire – give off moisture and exchange gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) Leaves Transpiration is the evaporation of water through plant leaves and stems through the stomata (necessary for survival) Transpiration slows when adequate water is unavailable (plant will begin to wilt) If wilting continues into the evening, the plant needs more water to prevent damage Extreme Drought – stomata close and photosynthesis slows or stops Leaves Transpiration Cools the Plant Maintains the flow of nutrients and manufactured food from root to top Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light Energy = Glucose + Oxygen 672 Kilocalories of Light – (1 molecule of glucose and 6 molecules of oxygen) Carbon Dioxide enters through the Stoma Food made in the Leaves travels DOWN through the stem to the roots Food is used by plant or stored in the stem or root in the form of sugar, starch, or protein Respiration Respire – 24 hours a day Respiration – plant consumes oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide (just like us and animals) Roots, Stems, and Leaves all use oxygen As they grow they use oxygen and give off carbon dioxide BUT – they produce more oxygen through photosynthesis than they consume BIG DIFFERENCE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Respiration Photosynthesis 1. Food Used Food Made Sun’s Energy Used 2. Energy Released Carbon Dioxide Used 3. Carbon Dioxide Given Off Oxygen Given Off 4. Oxygen Used Produces Sugar & 5. Produces Carbon Dioxide Starch & H2O Requires Light 6. Goes on All Day and Night Chlorophyll must be 7. Carried on in All Cells Present Stems TWO 1. Main Functions Movement of Materials Water and Minerals (Roots – Up) [Xylem] Manufactured Food (Leaves – Down) [Phloem] 2. Support of the Leaves and Reproductive Structures Flowers, and Fruits or Seeds (Reproductive Structures) Stems ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE Potato (Modified Stem) – USED FOR FOOD Asparagus – USED FOR FOOD And Trees Several Others – trunks – USED FOR BUILDING MATERIALS Roots Anchor and hold plant Upright Absorb water and minerals from the soil Store large quantities of plant food Propagate or Reproduce some plants (First Three are Essential to All Plants) Roots Contains Xylem – Water and Minerals Up Phloem – Manufactured Food Down Root Hairs – absorb moisture and minerals Important for Cash Crops Carrots, Fibrous Beets, Radishes, Sweet Potatoes vs. Tap Monocot Fibrous vs. Dicot are easier to transplant Flower Fruit Seed The Beauty of a Flower is necessary to Attract Insects When visited: Fertilize Seed) Fruits by pollination (Beginning of Fruit & and Seeds are Attractive so: Birds and Animals will eat, collect, and spread them Flower Complete Male and Female Parts – Can pollinate themselves Contain: Sepals, Petals, Stamens, and Pistil Incomplete Male – OR – Female Parts Contain: Sepals, Petals, Stamens (Male) Pistil (Female) Exit Slip With Partner Back of Note Card 3 Things you Now Know, that you Didn’t Know when you walked in.