* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characteristics - Net Start Class
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
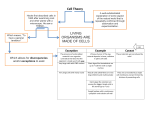
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Name:KEY 7th Grade Cumulative Review Science Process Skills 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. A triple beam balance is used to measure the mass of an object. A graduated cylinder is used to measure liquid volume. The independent or manipulated variable is placed on the x-axis of the graph. A variable is something that changes during an experiment. Constants or controlled factors are all factors that are NOT allowed to change during the experiment. The experimental group is the group(s) that is being tested with the independent variable. The basic unit of measure for mass is the gram. The basic unit of measure for liquid volume is the liter. A hypothesis is a possible explanation for a set of observations or answer to a scientific question. Use the graph above to answer question 10-14 What information is found on the x-axis? Average wind speed (independent or manipulated variable.) 12.What units are used to measure the information on the x-axis? Kilometers per hour 13.What are the interval values on the x-axis? 4 14.What information is found on the y-axis? Monthly energy output (dependent or responding)variable) 11. 15.What units are used to measure the information on the y-axis? Kilowatt hours 16.What are the interval values on the y-axis? 20 Use the following scenario to answer questions 17 – 26. Anita heated 4 beakers of water to boiling. Each beaker contained 100 ml of water with a certain amount of salt dissolved in it. The results of her experiment are listed in the table below. Beaker A B C D Mass of salt dissolved (g) 0 3 6 9 Boiling temperature (oC) 99 102 105 ? 17.If everything remains the same, what will be the boiling temperature of the solution in beaker D? 108 (+3) 18.What is an appropriate title for the data table? Effect of salt on boiling temperature of water 19.Write a problem for this experiment. Will the amount of salt added to water affect the boiling temperature? 20.List the constants in this experiment. Amount of water, type of water, type of salt, beakers, thermometers, heat source, environmental conditions etc 21.What is the manipulated (independent) variable? Amount of salt 22.What is the responding (dependent) variable? Boiling temperatures 23.Write a hypothesis for this experiment. If the amount of salt is increased, then the boiling temperature will also increase. 24.What is the control group in Anita’s experiment? Beaker A – no salt 25.What are the experimental groups in this experiment? Beaker B, C, D (3-6-9 g of salt) 26.What information is found on the x-axis? Amount of salt (independent variable) 27.What information is found on the y-axis? Boiling temperature (dependent variable) Chemistry 1. An atom is the smallest part of an element. It is made up of three small particles: protons, which are in the nucleus and have a positive charge - - neutrons, which are also in the nucleus and have no charge - - and electrons which orbit around the nucleus and have a negative charge. 2. A characteristic that can only be observed when a substance changes into another substance (during a chemical reaction) is a chemical property. 3. The modern periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. Elements are arranged into 18 columns (that go up and down) and 7 rows (that go side to side.) The columns are called groups or families and the rows are called periods. 4. Tarnishing, rusting, and wood burning are all examples of chemical changes. 5. Compounds are composed of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio, and are represented by a chemical symbol. 6. An element’s atomic number tells how many protons are in the nucleus of an atom of that element. 7. Elements that are dull, brittle, good insulators, not ductile, have low density and low boiling points, and are often gases at room temperature are nonmetals. 8. There are four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. When matter changes from one state to another (like when an ice cube melts) it is always a physical change. 9. An element is represented by a chemical symbol and cannot be broken down into any other substance. (hint: there are over 100 and they are all on the Periodic Table.) 10.The metalloids are located along the zig zag line that divides the periodic table. The nonmetals are to the right of the zig zag line and the metals are to the left of the zig zag line. 11.During a chemical reaction (change) new materials are produced that are different from the starting materials. The starting materials are called the reactants and the new substances produced are called the products. 12.Elements in the same group or family have similar properties or characteristics. 13.Production of a gas (bubbles), change in temperature, formation of a precipitate (a solid), or a color change are all possible evidence that a chemical change has taken place and a new substance has formed. 14. Mixtures are composed of two or more substances in the same place that are not chemically combined. 15. Valence electrons are the electrons farthest from the nucleus that are most loosely held and are involved in chemical bonding. 16.Chopping, grinding, melting or dissolving a material causes a physical change, and does not change the material into a new substance. 17.Elements that are malleable (can be pounded into shapes), ductile (can be drawn out into wires), have high luster (they’re shiny), are good conductors of heat and electricity, have high densities and high boiling points, and are almost all solids at room temperature are metals. 18.When chemicals combine to form compounds electrons get transferred or shared. If the electrons get transferred from one element to another an ionic bond forms. If the electrons are shared by two elements a covalent bond forms. 19.The most reactive metals are in family 1 (alkali metals( and the most reactive non metals are in family 17 (halogens) 20.A characteristic that can be observed without changing the substance into something else is a physical property. Earth Science 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The energy in waves comes from wind that blows across the water’s surface. The mixture of sediment that a glacier deposits directly on the surface is called till. Abrasion is the wearing away of rock by grinding action. Dust on furniture is an example of deposition. Some plants produce acid that result in chemical weathering. Deposition is the process in which sediment is laid down. Erosion is the process by which natural forces move weathered rock and soil from one place to another. 8. The material moved by erosion is sediment. 9. Mass movement is any one of several processes that move sediment downhill. 10. Moving water is the major agent of erosion that has shaped Earth’s land surface. 11. A glacier is any large mass of ice that moves slowly over land. 12. A river’s slope, volume of flow, and the shape of its streambed affect how fast the river flows and how much sediment it can erode. 13. Mudflow is a type of mass movement that most likely follows a heavy rain on a mountain. 14.Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth’s surface. 15.Roots of trees and other plants enter cracks in rocks. As the roots grow, they force the cracks farther apart. This is a form of mechanical weathering. 16. A tributary is a stream that flows into a larger river. 17. Earth spinning on its axis is called rotation. 18. The movement of one object around another is called revolution. 19. The tilt of Earth’s axis as Earth revolves around the sun causes seasons. 20. The different shapes of the moon that we see from Earth are called phases. 21. When the moon’s shadow hits Earth or Earth’s shadow hits the moon, an eclipse occurs. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Ecology A deer eats only plants, it is a primary (first level) consumer. In an energy pyramid, the first or lowest (producer) level has the most available energy. Vultures feed on the bodies of dead organism, they are scavengers. The specific environment of the ecosystem in which an organism lives is its habitat. How much energy is transferred from one level to the next higher level in a food web? 10% The diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web is called an energy pyramid. Complete the questions based on the food web: Use the food web to answer these questions. 1. What are the producers? 2. Name two organisms that are herbivores. 3. Name one organism that is a carnivore. 4. What would happen to the snake population if the hawk were removed? Image: http://weedeco.msu.montana.edu/class/LRES443/Lectures/Lecture20/FoodWeb.JPG 8. Succession is the series of changes that occur after a disturbance in an existing ecosystem. 9. The first species to populate an area where primary succession is taking place are called a pioneer species. 10.Plants growing on a new island formed by the eruption of an undersea volcano are examples of pioneer species. 11.Adaptations allow organisms to survive and reproduce in their environment. 12.A producer ( An autotroph) is an organism that can make its own food 13.Organisms that capture energy from sunlight through photosynthesis are called producers (autotrophs) 14.Why does secondary succession occur more quickly than primary succession? Soil already exists Label each as photosynthesis, respiration or both: 17.Oxygen is taken in and used to help generate energy. Respiration 18.Carbon dioxide molecules are joined together to make glucose. Photosynthesis 19.Light energy is required for this process. Photosynthesis 20.This process occurs in plant cells. Photosynthesis and Respiration 21.Occurs in heterotrophs. Respiration 22.Occurs in autotrophs Photosynthesis and Respiration 23.How do cilia function to move materials? Hair like structures beat in unison Physics 1. A force is a push or a pull and is measured in Newtons using a spring scale. In diagrams, forces are often represented with arrows. The head of the arrow shows the direction of the force. A thicker or longer arrow has a greater force than a shorter or thinner arrow. 2. Simple Machines are devices that can make work easier, but they can’t make less work. They make work easier by 1.) multiplying force 2.) multiplying distance or just 3.) changing the direction in which you exert force. 3. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. To have it the object must be moving. 4. Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion. It is determined by the mass of the object. It causes you to move forward if you’re riding in a car that stops suddenly. 5. The force you exert on a machine is called the input force. The force exerted by the machine is called the output force. 6. A wheel and axle is a simple machine made of 2 circular objects fastened together and that rotate about a common axis. The larger circular object is the wheel and the smaller circular object is the axle The Mechanical Advantage is calculated by dividing the radius of the wheel by the radius of the axle. 7. Potential energy is stored energy. It can be gravitational, elastic, chemical, or due to build up of pressure. 8. When forces acting on the same object are going in the same direction they combine by addition and when forces acting on the same object are going in opposite directions they combine by subtraction. 9. Newton’s Second Law is stated mathematically. Force = mass x acceleration. Put that formula into the magic triangle. 10.An inclined plane is a flat slanted surface (like a ramp.) It’s a simple machine that allows you to exert less input force, but you have to exert it over a longer distance. The Mechanical Advantage is equal to the length of the incline divided by the height of the incline. 11.When a ball is thrown the two forces that cause it to slow down and fall are gravity and friction. 12.A lever is a rigid bar that is free to pivot around a fixed point called a fulcrum. There are three types. In First class the fulcrum is in the middle. In Second class the output force is in the middle. In Third class the input force is in the middle. The Mechanical Advantage is equal to the effort arm divided by the resistance arm (effort arm = distance from fulcrum to input force - - resistance arm = distance from fulcrum to output force.) 13.Gravitational potential energy is based on height. The higher the object is the more GPE is has. 14.Equal forces acting on an object in opposite directions are called balanced forces. The net force is zero and the object does not move 15.To do work on an object, the object must move some distance in the direction you applied the force. The formula for work is force x distance (N x m.) Newton times meter is the SI unit, and is also called a joule. Put the formula into the “Magic Triangle.” 16.A wedge is a simple machine that is thick at one end and tapers to a thin edge at the other end. Since it is really just a moving inclined plane the Mechanical Advantage is equal to the length of the incline divided by the height of the incline. 17.A swinging pendulum is an example of kinetic energy continuously being changed to potential energy and back again. At the top of the swing it has maximum potential energy and at the bottom of the swing it has maximum kinetic energy. 18.Newton’s First Law states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion at a constant velocity will continue moving at constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. It’s also called the Law of Inertia. 19.Mechanical advantage is the ratio of the output force to the input force. (MA=OF/IF) If the mechanical advantage is greater than one – the machine is multiplying force If the mechanical advantage is less than one – the machine is multiplying distance If the Mechanical Advantage is equal to one the machine is just changing the direction of the force. 20.When unbalanced forces are acting on an object the object will move in the direction of the net force which is the overall force on an object after all forces on it are added. 21.A pulley is a simple machine consisting of a grooved wheel with a rope, chain, or cable wrapped around it. It’s fixed if it is attached to a structure. It’s moveable if it is attached to the object being moved. The mechanical advantage is equal to the number of weight bearing ropes. Life Science: Cells 1. The structure of the plant cell whose main function is to support and protect is the cell wall. 2. The organelle that can be compared to the powerhouse of the cell (it is where the energy is released) is the mitochondria. 3. The Cell Theory states that all organisms are made of cells that came from preexisting cells which are the basic unit of life. 4. The cell part that functions like a water storage tank is the vacuole. 5. Three structures present in plant cells but NOT in animal cells are the cell walls and chloroplast. 6. The part of the plant cell that is responsible for food production is the chloroplast. 7. The organelle in which cellular respiration takes place is the mitochondria. 8. The organelle that is centrally located in the cell and controls the cell activities is the nucleus. 9. Structures in the cytoplasm that have a specific job are called organelles. 10.The endoplasmic reticulum is the folded membrane that moves materials around the cell. 11.All cells have some common structures and functions. 12.Eukaryotic cells have many chromosomes with linear DNA compared to prokaryotic cells that have one (a single) circular DNA. 13.Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler than Eukaryotic cells. 14.A cell that contains no membrane bound organelles is Prokaryotic. 15.Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. 16.The process in which plants convert the sun’s energy into chemical energy is known as photosynthesis. 17.Cellular respiration is the process in which cells break down simple food molecules such as glucose and release the energy they contain. 18.The cell membrane forms the outer boundary of the cell and controls what enters and leaves. 19.Write the equation for photosynthesis. 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Life Science: Kingdoms 1. An organism that lacks a true nucleus is classified as a prokaryotic. 2. Offspring that are identical to the parent is a product of asexual reproduction. 3. Organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and many other organelles are called eukaryotic. 4. An organism that cannot make its own food is heterotrophic. 5. The process that involves two parents whose genetic material is combined to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents, is called sexual reproduction. 6. An organism that consists of many cells is called multicellular. 7. A student wrote this description of a cell after looking at it under a microscope. a. The cell has a cell wall and many organelles, including: mitochondria, a nucleus, a vacuole, and several chloroplasts. The student is most likely describing a plant. 8. A cell that has a cell wall, but not chloroplasts is most likely describing a fungal. 9. An organism that makes its own food is called autotrophic. 10.Algae have chloroplasts and can make their own food, they are autotrophic. Bread molds do not have chloroplasts and cannot make their own food, they are heterotrophic. 11.An organism that is eukaryotic, multicellular, and heterotrophic could be classified as a(n) animal. 12.An organism that consists of a single cell is unicellular. 13.A bird and a frog are similar because they are in the animal kingdom and have body systems. 14.A unicellular organism reproduces and its offspring are identical to the parent. This is considered asexual reproduction 15.A flowering plant and a hawk are classified in different kingdom(s) and different species. Life Science: Body Systems 1. A tube from the ovary where the egg travels to get to the uterus (RE: this is where fertilization takes place!) Oviduct or fallopian tube 2. What two body systems does the pharynx belong? Respiratory and Digestive 3. The stomach contains hydrochloric acid (enzymes of gastric juices that destroys pathogens. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. The liver produces bile What type of blood cell carries oxygen to the body cells? Red blood cell Epiglottis is the small flap of tissue that seals off the trachea during swallowing. What structure causes air to move into and out of a person's lungs? Diaphragm muscle Peristalsis: wavelike contractions that move food Digestion that physically changes food is called mechanical digestion. 10.Which chamber of the heart pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs? Right ventricle 11.The tiny part of the brain that links the nervous system and endocrine system. Hypothalamus 12.How does the oxygen in the alveoli get to the body cells? Diffusion Identify the system to which the following organs belong: 13.Circulatory: Heart, blood, and vessels: provides oxygen and food to tissues and removes wastes. 14.Digestive: Mouth, esophagus, stomach, SI, LI, liver, pancreas: Uses enzymes to break down food into its building blocks and transport it to the blood stream, then removes the wastes. 15.Nervous: Brain, spinal cord, nerves: Control system of the body. Works with other systems to maintain homeostasis. 16.Endocrine: pituitary, ovaries, testis, adrenal glands, and thyroid: Produces hormones that circulate in the blood stream and tell other systems what to do. 17.Reproductive: Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina (females) testis, seminiferous tubules, vas deferens, penis (males): Meiosis produces gametes in ovaries and testis. The remainder of the system either delivers them, or protects a developing fetus until birth. 18.Integumentary: Skin, hair, nails: Protection from infection, temperature control 19.Skeletal: Bones, ligaments, cartilage: Support and protection of organs. Provides an attachment for muscles. 20.Respiratory: Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, and alveoli: Brings O2 to circulatory system and removes CO2. 21.Muscular: Muscles: Uses bones as simple machines to exert force on the body to create movement. 22.Excretory: Kidney, ureter, bladder, and urethra: Takes nitrogenous waste from the blood stream for removal from the body. 23.Immune: White blood cells (lymphocytes including T-cells and B-cells which make antibodies), lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils: Fights infection. 24. theses cells belong to the Nervous system Complete the chart Characteristics Male Female 25. sperm 26.egg or ova 27. testes 28. ovary 29. testosterone 30.estrogen Sex Cell Organ Hormone produced