* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit: Ecology
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of the San Francisco Estuary wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Ecological economics wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
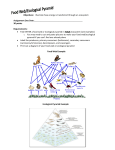
Unit: Ecology Chapter 34 Be able to…. Describe the 5 levels of ecological study: Biosphere, (biome) Ecosystem, Community , Population and Individual Organism Compare and Contrast biotic and abiotic and be able to give examples. Identify the main terrestrial biomes and aquatic ecosystems. KEY TERMS: Ecology Biotic factor Abiotic factor Population Community Ecosystem Biosphere Habitat Microclimate The main terrestrial biomes (identify them and know major characteristics) Tropical rain forest Savanna Desert Chaparral Temperate grassland Temperate deciduous forest Coniferous forest Tundra Permafrost The main aquatic ecosystems (identify them and know major characteristics) Ponds and Lakes Streams and Rivers Estuaries Ocean Intertidal Neritic Oceanic Coral reefs Deep-sea vents Photic zone Phytoplankton Aphotic zone Benthic zone Estuary Pelagic zone Zooplankton Hydrothermal vent Chapter 35 Be able to…. Explain how scientists define a population Explain how density is calculated Describe several methods scientists use to measure population density and their limitations. Relate limiting factors to carrying capacity Compare and contrast Density-dependent factors and Density-independent factors Explain how a countries age structure affects its population growth Identify causes and results of interspecific competition. Identify adaptations because of predator prey relationships Compare and contrast symbiotic relationships. Identify pos. and neg. effects of ecological disturbances. Compare and contrast primary and secondary ecological succession Relate human activity to effects in species diversity KEY TERMS: Population Density Exponential growth Limiting factor Carrying capacity Density-dependent factors Density-independent factors Age structure Interspecific competition Competition exclusion Niche Predation Symbiotic relationship Parasitism Mutualism Commensalisms Ecological succession Primary succession Secondary succession Introduced species Chapter 36 Bea able to…. Contrast the flow of energy and chemicals through an ecosystem Explain how trophic levels relate to food chains and food webs. Relate ecosystem productivity to biomass Identify the information in the three types of ecological pyramids Describe the flow of chemicals in the ecosystem: Carbon, Nitrogen and Water Examine how human activity impacts the flow of energy and chemicals in an ecosystem Identify things that can be done that can limit the impact humans have on their environment KEY TERMS Producer Consumer Decomposer Trophic levels Food chain Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer Detritus Food web Biomass Primary productivity Energy pyramid Biomass pyramid Pyramid of numbers Nitrogen fixation Nitrification Transpiration Deforestation Greenhouse effect Global warming Eutrophication Acid rain Pollution Biological magnification ozone TEST SCHEDULED—OCTOBER 13th (TUESDAY)