* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Savoyard crusade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
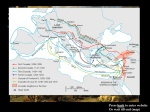
The Crusades took place in Europe around the end of the Eleventh century. The Byzantine Empire controlled by Emperor Alexius I was losing territory from invading Turkish peoples. In the year 1095 Alexius asked Pope Urban II for troops to help him defend his territory and recapture the “Holy Land” from Muslim control. This brought on a tremendous amount of people determined to fight for the Christian cause. From this beginning, six extensively tragic Crusades were started. The First Crusade ranged from the year 1096 through 1099. Four armies were formed from Western European regions and were set to depart for Byzantium. These armies left havoc in their wake, slaughtering Jewish, murdering innocent families, and destroying towns and villages. The first few sections of these armies were crushed pathetically by Turkish armies. After regrouping and swearing their alliances wholly to Alexius, the Crusaders captured the cities of Anatolia, Antioch, and finally Jerusalem. The Crusaders slaughtered hundreds of men, women, and children along their victorious entrance to the Holy City. The Second Crusade began when the Muslims created their own holy war against the Christians (known as Jihad). In the year 1147 the Crusade was led by King Louis VII of France and King Conrad III of Germany. An army of 50,000 Crusaders was defeated in Damascus by combined Muslim forces, decisively ending the Second Crusade. The Third Crusade ranged from the years 1189 to 1192. The city of Cairo, Egypt was captured by Muslim forces and eventually went on to reclaim the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem. Christian forces retaliated, and ultimately a peace treaty was signed between leaders to reestablish the Kingdom of Jerusalem, which ended the Third Crusade. The Fourth through the Sixth Crusade can be summed up easily. These conflicts lasted from the years 1198 through 1229. Power Struggles between Europe and the Byzantine Empire created havoc and ended up sacking Emperor Alexius in favor of, Alexius IV (his nephew). The new emperor attempted to convert religious affiliations with the Church of Rome, and was as a result strangled to death and had his palace looted, ending the Fourth Crusade. The remainder of the 13th century saw the rest of the Crusades aimed not so much against Muslim forces in the Holy Land, but focusing instead on combating any and all enemies (everyone who was not a Christian) of the Christian Faith. Essentially the Crusades were just a big long drawn out fight for Jerusalem and the “Holy Land”. Mainly, the fights were between the Muslim faith and the Christian faith, and were inspired by petty differences between leaders and belief systems. Countless numbers of people were inspired to become Crusaders and fight for their beliefs, some achieved victories, while others humiliating defeat, and in all instances was a large loss of life. Major outcomes from this time in history were the formation of new states and territories, the destruction and re-forming of priceless palaces and artifacts, and the major separations and prejudices between the Muslim and Christian faiths which we still see in our present day society. Key Terms: Serfs -agricultural workers that belong to the manor Manors -self-sufficient farming estates Piety- dutifulness in religion Holy Land- the area of Palestine held spiritually important to Christians, Muslims, and Jews Hierarchy- a ruling body of clergy organized into ranks Crusades- a series of holy wars to drive the Muslims out of Palestine Sacrament- one of the church's ceremonies in which you obtain grace from God Saladin- most famous Muslim leader of the 1100's, who defeated the armies of the 2nd crusades Richard the Lion hearted- the King of England who left to join the crusade, leaving others to rule in his place Reconquista-beginning in the 11th Century, a military campaign to drive the Muslims out of Spain Byzantine Empire-Eastern Roman empire that began when Constantine moved the capital out of Rome to Byzantium (Constantinople) Holy Roman Empire- a loose federation of mostly German states and principalities headed by the emperor, lasting from 962-1806 Lesson Plan Resources · http://westernreservepublicmedia.org/middleages/images/middleages.pdf · http://dnet01.ode.state.oh.us/ims.itemdetails/lessondetail.aspx?id=0907f84c805313db · http://www.tes.co.uk/article.aspx?storyCode=6257990 · http://www.lessonplanet.com/article/history/the-crusades · http://sheg.stanford.edu/first-crusade Technology Resources · http://www.history.com/topics/crusades · http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/the_crusades.htm · http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/crus/hd_crus.htm · http://history-world.org/crusades.htm http://gbgm-umc.org/umw/bible/crusades.stm