Keystone2011poster
... The sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of rRNA molecules demonstrated that all organisms could be placed on a single tree of life. Highly conserved, homologous 16S rRNA genes' presence in all organismal lineages makes them the only universal marker that has been adopted by biologist. Unfortunately ...
... The sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of rRNA molecules demonstrated that all organisms could be placed on a single tree of life. Highly conserved, homologous 16S rRNA genes' presence in all organismal lineages makes them the only universal marker that has been adopted by biologist. Unfortunately ...
Phylogenetic relationships among iguanian lizards using alternative
... mixture model that employs a reversible-jump algorithm to estimate the number of rate matrices that best explains the data. This method chooses the appropriate number of independent rate matrices using Bayes factors during the MCMC procedure. By default, BayesPhylogenies assigns uniform priors on a ...
... mixture model that employs a reversible-jump algorithm to estimate the number of rate matrices that best explains the data. This method chooses the appropriate number of independent rate matrices using Bayes factors during the MCMC procedure. By default, BayesPhylogenies assigns uniform priors on a ...
Subtle Accents
... tree, compute tree, root node gives the final result. Perform random “evolutionary” operations on trees Combine parts of two tree into one(breeding) ...
... tree, compute tree, root node gives the final result. Perform random “evolutionary” operations on trees Combine parts of two tree into one(breeding) ...
Nuclear Gene Trees and the Phylogenetic Relationships of the
... Phylogenetic methods included maximum parsimony (MP) using PAUP version 3.1 (Swofford 1993) and maximum likelihood (ML) using the DNAML computer program within the PHYLIP Phylogeny Inference Package, version 3.572 (Felsenstein 1993). All MP analyses employed PAUP’s branch-and-bound search option. De ...
... Phylogenetic methods included maximum parsimony (MP) using PAUP version 3.1 (Swofford 1993) and maximum likelihood (ML) using the DNAML computer program within the PHYLIP Phylogeny Inference Package, version 3.572 (Felsenstein 1993). All MP analyses employed PAUP’s branch-and-bound search option. De ...
Align the DNA sequences
... Organism 1- A T G G G C T G T C A A Organism 2- A T G G G T G T C A A T At first glance, organism 1 and 2 appear to have dramatically different DNA sequences. In fact, they seem to share only 6 of the 12 bases being examined (50% sequence homology). Now examine these sequences properly aligned: Orga ...
... Organism 1- A T G G G C T G T C A A Organism 2- A T G G G T G T C A A T At first glance, organism 1 and 2 appear to have dramatically different DNA sequences. In fact, they seem to share only 6 of the 12 bases being examined (50% sequence homology). Now examine these sequences properly aligned: Orga ...
Week 9
... • Phylogenetic trees express the evolutionary relationships between a set of species • The relationship is inferred from the similarities and differences between homologue sequences • The inferred relationships are subject to influences from ...
... • Phylogenetic trees express the evolutionary relationships between a set of species • The relationship is inferred from the similarities and differences between homologue sequences • The inferred relationships are subject to influences from ...
L17 preview - Computer Science and Engineering
... points, not necessarily causing better convergence. ...
... points, not necessarily causing better convergence. ...
grappa - Department of Computer Science
... random events (based upon 120 genes and inversion only, but robust to errors in the model) . – Polynomial time, fastest of the three. ...
... random events (based upon 120 genes and inversion only, but robust to errors in the model) . – Polynomial time, fastest of the three. ...
STRAW: Species TRee Analysis Web server | Nucleic Acids
... MP-EST, STAR and NJst use gene trees estimated from DNA sequence data to infer species trees. Uncertainty of the estimated gene trees is incorporated in estimation of species trees using bootstrap techniques. In the MP-EST method, species trees are estimated from a collection of rooted gene trees by ...
... MP-EST, STAR and NJst use gene trees estimated from DNA sequence data to infer species trees. Uncertainty of the estimated gene trees is incorporated in estimation of species trees using bootstrap techniques. In the MP-EST method, species trees are estimated from a collection of rooted gene trees by ...
Is the Tiger a Copycat? A Phylogenetic Analysis Laboratory
... a problem with the data that was selected for this investigation. On the other hand, if the resulting tree indicated that the Lizard is the outgroup in comparison to the other cat species, this result would indicate that the selected data was probably reliable. ...
... a problem with the data that was selected for this investigation. On the other hand, if the resulting tree indicated that the Lizard is the outgroup in comparison to the other cat species, this result would indicate that the selected data was probably reliable. ...
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life (working
... Tabulate the molecular data for the species. The data represent a DNA sequence Consisting of just four nucleotide bases. Now focus on site 1 in the DNA sequence. In the tree on the left, a single base Change event, represented by the purple hatchmark on the branch leading to Species I and II is suff ...
... Tabulate the molecular data for the species. The data represent a DNA sequence Consisting of just four nucleotide bases. Now focus on site 1 in the DNA sequence. In the tree on the left, a single base Change event, represented by the purple hatchmark on the branch leading to Species I and II is suff ...
Horizontal gene transfer and microbial evolution: Is the Tree-of
... Phylogenetic reconstruction - How Parsimony analyses find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest proba ...
... Phylogenetic reconstruction - How Parsimony analyses find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest proba ...
DIVERSITY VERSUS DISPARITY: EXAMPLES FROM PRESENT
... 2. Exploration of morphospace in statoliths and beaks of cuttlefish and squid : evolutionary aspects of form disparity This work reports on a study using a Procrustes type analysis (Bookstein, 1991) of shape in exploring the morphospace of cephalopod statoliths and beaks. This method is based on the ...
... 2. Exploration of morphospace in statoliths and beaks of cuttlefish and squid : evolutionary aspects of form disparity This work reports on a study using a Procrustes type analysis (Bookstein, 1991) of shape in exploring the morphospace of cephalopod statoliths and beaks. This method is based on the ...
Investigating Polar Bear and Giant Panda Ancestry
... d. A new page will load that lets you follow the progress of your jobs. Click the “Refresh Tasks” tab near the top of the page, until the “View Status” button on the right turns into “View Results.” Click on the “View Results”: tab, and a page showing your results will appear. Click on the link “ou ...
... d. A new page will load that lets you follow the progress of your jobs. Click the “Refresh Tasks” tab near the top of the page, until the “View Status” button on the right turns into “View Results.” Click on the “View Results”: tab, and a page showing your results will appear. Click on the link “ou ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... To reconstruct the history of genes families, under the hypothesis that every family member derives from a duplication process of another member, means to put the set of members into a tree, that we call paralogy tree, in which the root represents the most ancient gene of the family, and each direct ...
... To reconstruct the history of genes families, under the hypothesis that every family member derives from a duplication process of another member, means to put the set of members into a tree, that we call paralogy tree, in which the root represents the most ancient gene of the family, and each direct ...
most - Salamander Genome Project
... Data from listed species were paired with data of the same type from the most closely related species. Used observed or expected heterozygosity If allozyme and microsatellite were available for the same taxon, the combined weighted average was used. ...
... Data from listed species were paired with data of the same type from the most closely related species. Used observed or expected heterozygosity If allozyme and microsatellite were available for the same taxon, the combined weighted average was used. ...
Teaching deep time through macroevolution and
... “tree” based on the similarity of characters--this is done by hand. [cladograms are visual representations of calculated relationships] 2. Students create character matrix and extract DNA/ sequence the 28s rRNA gene. [scaled up repetition, base pair differences are empirically determined] 3. Student ...
... “tree” based on the similarity of characters--this is done by hand. [cladograms are visual representations of calculated relationships] 2. Students create character matrix and extract DNA/ sequence the 28s rRNA gene. [scaled up repetition, base pair differences are empirically determined] 3. Student ...
Incomplete lineage sorting and other `rogue` data fell the tree of life
... evolutionary biology. The molecular genetics revolution has presented many contradictions for the TOL and the modern Darwinian synthesis. Incomplete lineage sorting (ILS) is a discordant and pervasive outcome produced when constructing phylogenetic trees using homologous biological sequence data acr ...
... evolutionary biology. The molecular genetics revolution has presented many contradictions for the TOL and the modern Darwinian synthesis. Incomplete lineage sorting (ILS) is a discordant and pervasive outcome produced when constructing phylogenetic trees using homologous biological sequence data acr ...
... Natural selection acts as a driving force at virtually all levels of biological organization. Phylogenetic analysis is a powerful methodology to investigate not only history but also selection mechanisms and function of biological networks at all levels [1]. Phylogenetic trees based on single loci s ...
Supporting Online Material for
... indicated with a different color. This tree does not depict descent relationships, just degree of chemical similarity. On the right, the evolution of these chemical types is reconstructed on a phylogeny of the plants (this does depict inferred evolutionary relationships). The colors correspond to th ...
... indicated with a different color. This tree does not depict descent relationships, just degree of chemical similarity. On the right, the evolution of these chemical types is reconstructed on a phylogeny of the plants (this does depict inferred evolutionary relationships). The colors correspond to th ...
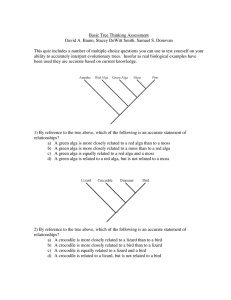
Basic Tree Thinking Assessment David A. Baum, Stacey DeWitt
... indicated with a different color. This tree does not depict descent relationships, just degree of chemical similarity. On the right, the evolution of these chemical types is reconstructed on a phylogeny of the plants (this does depict inferred evolutionary relationships). The colors correspond to th ...
... indicated with a different color. This tree does not depict descent relationships, just degree of chemical similarity. On the right, the evolution of these chemical types is reconstructed on a phylogeny of the plants (this does depict inferred evolutionary relationships). The colors correspond to th ...
PPT
... Reconstruction of the evolutionary history of a collection of organisms Takes the form of an evolutionary tree ...
... Reconstruction of the evolutionary history of a collection of organisms Takes the form of an evolutionary tree ...
Origin and evolution of the slime molds (Mycetozoa)
... as analyses of the large subunit (23S-like) rRNA (9) and 5S rRNA (10). In contrast, actin and b-tubulin trees place Physarum and Dictyostelium together with generally high confidence (11–14). Furthermore, these trees, along with trees of atubulin (11, 14), RNA polymerase largest subunit (15), and gl ...
... as analyses of the large subunit (23S-like) rRNA (9) and 5S rRNA (10). In contrast, actin and b-tubulin trees place Physarum and Dictyostelium together with generally high confidence (11–14). Furthermore, these trees, along with trees of atubulin (11, 14), RNA polymerase largest subunit (15), and gl ...
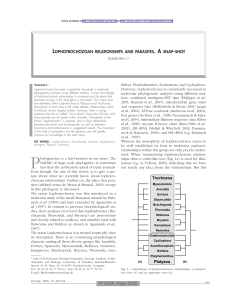
Lophotrochozoan relationships and parasites. A snap-shot
... There is a body of evidence (morphological and molecular) that Phoronida and Brachiopoda are closely related, and phoronids might be even a subtaxon of brachiopods (Cohen, 2000; Cohen & Weydmann, 2005). No parasitic forms are known for these two taxa. Still controversially discussed is the phylogene ...
... There is a body of evidence (morphological and molecular) that Phoronida and Brachiopoda are closely related, and phoronids might be even a subtaxon of brachiopods (Cohen, 2000; Cohen & Weydmann, 2005). No parasitic forms are known for these two taxa. Still controversially discussed is the phylogene ...