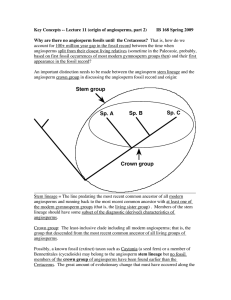
Sp. A Sp. B Sp. C Crown group Stem group
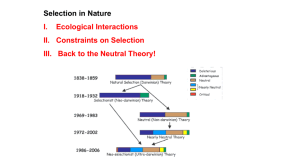
... of B. By the time that B arose (but possibly not before that time), all characteristics shared by modern angiosperms would have been in place. The above considerations are critical for understanding the arguments below about the four tree scenarios, Tree a through Tree d. Tree "a" = Upland hypothesi ...
... of B. By the time that B arose (but possibly not before that time), all characteristics shared by modern angiosperms would have been in place. The above considerations are critical for understanding the arguments below about the four tree scenarios, Tree a through Tree d. Tree "a" = Upland hypothesi ...
ANOVA and the Bootstrap - Computational Diagnostics Group
... Fit MHo to the observed data and calculate residuals and fitted values. Create a new data set by resampling with replacement from the residuals. Add the new residuals to the fitted values. Calculate t* by fitting Model MA to the new data set Repeat both steps many times (1000 times) Bootstrap p – va ...
... Fit MHo to the observed data and calculate residuals and fitted values. Create a new data set by resampling with replacement from the residuals. Add the new residuals to the fitted values. Calculate t* by fitting Model MA to the new data set Repeat both steps many times (1000 times) Bootstrap p – va ...
Concordance trees, concordance factors, and the exploration of
... has a known population history. At best one has molecular data for a number of loci for a set of individuals representative of the taxa under study. If we are prepared to make some assumptions about the nature of populations and genetic processes, these data contain information on the history of the ...
... has a known population history. At best one has molecular data for a number of loci for a set of individuals representative of the taxa under study. If we are prepared to make some assumptions about the nature of populations and genetic processes, these data contain information on the history of the ...
Metagenomic Analysis Using MEGAN4
... MEGANs analysis window compares multiple datasets. This enables creating distance matrices for a collection of datasets using different ecological indices. MEGAN supports a number of different methods for calculating a distance matrix, These can be visualized either using a split network calculated ...
... MEGANs analysis window compares multiple datasets. This enables creating distance matrices for a collection of datasets using different ecological indices. MEGAN supports a number of different methods for calculating a distance matrix, These can be visualized either using a split network calculated ...
Significance of bacterial identification by molecular
... primer sets can be used for at least three separate taxa (20). As you might expect there are some problems with this approach. The main problem is specificity for example, if a positive result occurs for a sample how do you know that it is actually an amplified product for the ...
... primer sets can be used for at least three separate taxa (20). As you might expect there are some problems with this approach. The main problem is specificity for example, if a positive result occurs for a sample how do you know that it is actually an amplified product for the ...
Yet viruses cannot be included in the tree of life - Université Paris-Sud
... approach implemented in PhyloBayes, using a mixture model (CAT) that was less sensitive to compositional bias and evolutionary rate heterogeneity between species18. Note that, in contrast to Claverie and Ogata’s 20-taxa tree4, there is not a single eukaryotic group but three distinct paralogues and ...
... approach implemented in PhyloBayes, using a mixture model (CAT) that was less sensitive to compositional bias and evolutionary rate heterogeneity between species18. Note that, in contrast to Claverie and Ogata’s 20-taxa tree4, there is not a single eukaryotic group but three distinct paralogues and ...
Homology - a persona..
... Gogarten has proposed a special term, synology, for those xenologs that arise, not by the transfer of a gene between two species, but by a hybridization of two species12. One might then question, given a successful hybrid, whether the two species are not effectively one and this is simply a case of ...
... Gogarten has proposed a special term, synology, for those xenologs that arise, not by the transfer of a gene between two species, but by a hybridization of two species12. One might then question, given a successful hybrid, whether the two species are not effectively one and this is simply a case of ...
Rapid radiation and cryptic speciation in squat lobsters of the genus
... underestimate of the familyÕs true diversity and there are numerous yet undescribed cryptic species (Macpherson and Machordom, 2001, and see below). Aside from their taxonomy, the phylogenetic affinities among the squat lobsters are poorly understood. The systematics of the group has not been fully re ...
... underestimate of the familyÕs true diversity and there are numerous yet undescribed cryptic species (Macpherson and Machordom, 2001, and see below). Aside from their taxonomy, the phylogenetic affinities among the squat lobsters are poorly understood. The systematics of the group has not been fully re ...
Sequence Heterogeneities Among 16s
... reaction (PCR) products. Direct sequencing of PCR products produces a mean sequence in which mutations present in the most variable domains become hidden. Cloning a single operon results in a sequence that differs from that of the other operons and of the mean sequence by several point mutations. Fo ...
... reaction (PCR) products. Direct sequencing of PCR products produces a mean sequence in which mutations present in the most variable domains become hidden. Cloning a single operon results in a sequence that differs from that of the other operons and of the mean sequence by several point mutations. Fo ...
09ConsensusGene
... Greedy consensus trees are constructed by sequentially is the only 2-taxon clade which satisfies rule 2 and no adding one clade at a time, the most frequently occurr- 3-taxon clade satisfies rule 3. For these input trees, the ing clade that is compatible with clades already included majority-rule co ...
... Greedy consensus trees are constructed by sequentially is the only 2-taxon clade which satisfies rule 2 and no adding one clade at a time, the most frequently occurr- 3-taxon clade satisfies rule 3. For these input trees, the ing clade that is compatible with clades already included majority-rule co ...
pdf
... understand an organism’s ancestral pathway and determine the degree of relatedness of one organism to another. As part of the discovery and cataloguing process of a new species, a thorough phylogenetic analysis must be performed in order to determine where on the tree the species is to be placed. Th ...
... understand an organism’s ancestral pathway and determine the degree of relatedness of one organism to another. As part of the discovery and cataloguing process of a new species, a thorough phylogenetic analysis must be performed in order to determine where on the tree the species is to be placed. Th ...
Comparative In silico Study of Sex
... Downloaded from rbmb.net at 0:52 +0430 on Monday June 19th 2017 ...
... Downloaded from rbmb.net at 0:52 +0430 on Monday June 19th 2017 ...
20071217161016301
... Xenoturbella, hemichordate and starfish. This lead Bourlat et al. to conclude that Delsuc et al’s inference was an artifact of sparse taxonsampling / model mis-specification. (They used a concatenated analysis WAG+F+) ...
... Xenoturbella, hemichordate and starfish. This lead Bourlat et al. to conclude that Delsuc et al’s inference was an artifact of sparse taxonsampling / model mis-specification. (They used a concatenated analysis WAG+F+) ...
neutphylo
... Chamary and Hurst (2009) 'The price of silent mutations', Scientific American, June 2009, pp34-41. It appears that bases in protein coding exons can be also intron splicing recognition sites, and that a synonymous mutation can prevent intron splicing, resulting in mutated proteins ...
... Chamary and Hurst (2009) 'The price of silent mutations', Scientific American, June 2009, pp34-41. It appears that bases in protein coding exons can be also intron splicing recognition sites, and that a synonymous mutation can prevent intron splicing, resulting in mutated proteins ...
Computational Biology
... Drawbacks of breakpoint analysis: costly + ambiguous Let us consider a simple example: Suppose that the genomes G1, G2, and G3, evolved from the ancestral genome A = 1 2 3 4 5 6 by one reversal each such that G1 = 1 2 -4 -3 5 6 G2 = 1 -4 -3 -2 5 6 G3 = 1 2 3 4 -5 6 Searching for the breakpoint medi ...
... Drawbacks of breakpoint analysis: costly + ambiguous Let us consider a simple example: Suppose that the genomes G1, G2, and G3, evolved from the ancestral genome A = 1 2 3 4 5 6 by one reversal each such that G1 = 1 2 -4 -3 5 6 G2 = 1 -4 -3 -2 5 6 G3 = 1 2 3 4 -5 6 Searching for the breakpoint medi ...
Document
... p9: "In the present study, we could not locate the leucine zipper in the GSA dehydrogenase domain " p9: " ...it appears that leucine zippers may not be involved in the tetrameric organization of P5CS. p9: "The P5CS enzyme can be feed back regulated ..." -> feedback = one word p9: "They also found th ...
... p9: "In the present study, we could not locate the leucine zipper in the GSA dehydrogenase domain " p9: " ...it appears that leucine zippers may not be involved in the tetrameric organization of P5CS. p9: "The P5CS enzyme can be feed back regulated ..." -> feedback = one word p9: "They also found th ...
Evaluation of the phylogenetic position of the planctomycete
... In recent years, it has become apparent that the extent of LGT is so great that it must be regarded as one of the major driving forces of evolution. The view that all genetic information in a given lineage traces back to one common ancestor simply does not apply in the world of prokaryotes, where ea ...
... In recent years, it has become apparent that the extent of LGT is so great that it must be regarded as one of the major driving forces of evolution. The view that all genetic information in a given lineage traces back to one common ancestor simply does not apply in the world of prokaryotes, where ea ...
video slide
... • The rate of evolution of DNA sequences varies from one part of the genome to another; therefore, comparing these different sequences helps us to investigate relationships between groups of organisms’ that diverged a long time ago. – DNA that codes for rRNA changes relatively slowly and is useful f ...
... • The rate of evolution of DNA sequences varies from one part of the genome to another; therefore, comparing these different sequences helps us to investigate relationships between groups of organisms’ that diverged a long time ago. – DNA that codes for rRNA changes relatively slowly and is useful f ...
A Step-by-Step Tutorial: Divergence Time Estimation with
... An advantage of the approximate likelihood method is that arbitrary data sets could be combined and analyzed together. For example, one partition could be amino acid data and another partition could be nucleotide data. Once the branch lengths, g and H have been calculated, there is no way MCMCTREE c ...
... An advantage of the approximate likelihood method is that arbitrary data sets could be combined and analyzed together. For example, one partition could be amino acid data and another partition could be nucleotide data. Once the branch lengths, g and H have been calculated, there is no way MCMCTREE c ...
(ARG) as Compatible Networks of SNP Patterns
... Mutation creates alternating states at particular genome positions known as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs); a genome sequence can be reduced to a set of SNPs, and recombination will shuffle these sequences to produce new haplotypes. The coalescence time of a SNP is a direct function of its a ...
... Mutation creates alternating states at particular genome positions known as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs); a genome sequence can be reduced to a set of SNPs, and recombination will shuffle these sequences to produce new haplotypes. The coalescence time of a SNP is a direct function of its a ...
Compressed suffix tree—a basis for genome
... extensively studied by other people. In addition to these navigational operations, suffix trees have several other useful operations such as suffix links, constant time lowest common ancestor (lca) queries, possibility to attach additional information to each node/edge and pattern search capabilitie ...
... extensively studied by other people. In addition to these navigational operations, suffix trees have several other useful operations such as suffix links, constant time lowest common ancestor (lca) queries, possibility to attach additional information to each node/edge and pattern search capabilitie ...
The emergence of individual species
... Analogy between evolution of organisms and physical annealing In the communal ancestor, HGT could happen almost without “friction”. It is because cellular design of organisms was simple and modular. In other words, cellular components were not connected or loosely connected so that each component w ...
... Analogy between evolution of organisms and physical annealing In the communal ancestor, HGT could happen almost without “friction”. It is because cellular design of organisms was simple and modular. In other words, cellular components were not connected or loosely connected so that each component w ...
Visualization of Mappings between the Gene Ontology
... We have to address similar problems with respect to the Cluster Tree visualization as we had to do with the GO representation. The tree is usually huge and any traditional type of visualization would not scale. The application of conventional tree drawing algorithms would produce rather high tree dr ...
... We have to address similar problems with respect to the Cluster Tree visualization as we had to do with the GO representation. The tree is usually huge and any traditional type of visualization would not scale. The application of conventional tree drawing algorithms would produce rather high tree dr ...
The use of Minimum spanning Trees in microarray expression data
... Feature selection counts the gene’s support to a partition Feature selection used here is t-statistic with pooled variance. T-statistic is heuristic measure Genes with absolute t-statistic greater than a threshold are selected University of Crete ...
... Feature selection counts the gene’s support to a partition Feature selection used here is t-statistic with pooled variance. T-statistic is heuristic measure Genes with absolute t-statistic greater than a threshold are selected University of Crete ...