TreeFam v9: a new website, more species and orthology-on-the
... predictions together with the evolutionary history of the genes. Here we describe an update of the TreeFam database. The TreeFam project was resurrected in 2012 and has seen two releases since. The latest release (TreeFam 9) was made available in March 2013. It has orthology predictions and gene tre ...
... predictions together with the evolutionary history of the genes. Here we describe an update of the TreeFam database. The TreeFam project was resurrected in 2012 and has seen two releases since. The latest release (TreeFam 9) was made available in March 2013. It has orthology predictions and gene tre ...
pplacer: linear time maximum-likelihood and Bayesian phylogenetic
... such situations [16]. The lack of signal problem is especially pronounced when using contemporary sequencing methods that produce a large number of short reads. Some methodologies, such as 454 [29], will soon be producing sequence in the 600-800 bp range, which is sufficient for classical phylogenet ...
... such situations [16]. The lack of signal problem is especially pronounced when using contemporary sequencing methods that produce a large number of short reads. Some methodologies, such as 454 [29], will soon be producing sequence in the 600-800 bp range, which is sufficient for classical phylogenet ...
Taxonomy of Bacteria and Archaea
... This diagram shows conserved and variable regions of the small subunit rRNA (16S in prokaryotes or 18S in eukaryotes). Each dot and triangle represents a position that holds a nucleotide in 95% of ...
... This diagram shows conserved and variable regions of the small subunit rRNA (16S in prokaryotes or 18S in eukaryotes). Each dot and triangle represents a position that holds a nucleotide in 95% of ...
Instructions for ICML-98 Authors
... gene j across all samples and xkj denotes the average level of gene j across samples belonging to class k. To give an explicit example here, assume we have four samples and two genes for each sample: the first gene’s expression level values for the four samples are (1, 2, 3, 4) and the second’s are ...
... gene j across all samples and xkj denotes the average level of gene j across samples belonging to class k. To give an explicit example here, assume we have four samples and two genes for each sample: the first gene’s expression level values for the four samples are (1, 2, 3, 4) and the second’s are ...
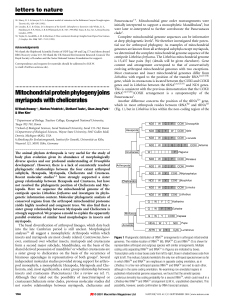
Mitochondrialproteinphylogenyjoins myriapods with chelicerates
... supported as a sister clade to insects, suggesting a paraphyletic Crustacea as recently noted11,12. Although the maximum-likelihood tree included a monophyletic Pancrustacea, branch-support analysis yielded little resolution with regard to the position of the Branchiopoda. The most striking result w ...
... supported as a sister clade to insects, suggesting a paraphyletic Crustacea as recently noted11,12. Although the maximum-likelihood tree included a monophyletic Pancrustacea, branch-support analysis yielded little resolution with regard to the position of the Branchiopoda. The most striking result w ...
doc - Lonely Joe Parker
... an analysis pipeline consisting of previously released software for phylogenetic tree manipulation, phylogenetic reconstruction and codon model analyses in a Maximum Likelihood (ML) framework, as well as of a set of utility classes (available on request) for data handling, parsing and model/hypothes ...
... an analysis pipeline consisting of previously released software for phylogenetic tree manipulation, phylogenetic reconstruction and codon model analyses in a Maximum Likelihood (ML) framework, as well as of a set of utility classes (available on request) for data handling, parsing and model/hypothes ...
Text S1.
... in [4], except that trees were inferred with RAXML [14] using a LG+F+ model. Briefly, this protocol evaluates whether every statistically supported branch in a single gene phylogeny is congruent with the concatenated phylogeny (Denis Baurain, unpublished). Since incomplete sequences may display ver ...
... in [4], except that trees were inferred with RAXML [14] using a LG+F+ model. Briefly, this protocol evaluates whether every statistically supported branch in a single gene phylogeny is congruent with the concatenated phylogeny (Denis Baurain, unpublished). Since incomplete sequences may display ver ...
Phylogenomics: improving functional predictions for uncharacterized
... alignment is assumed to include amino acids or nucleotides that have a common evolutionary history, and each column is treated separately in the phylogenetic analysis. Therefore, regions in which the assignment of positional homology is ambiguous should be excluded (Gatesy et al. 1993). The exclusio ...
... alignment is assumed to include amino acids or nucleotides that have a common evolutionary history, and each column is treated separately in the phylogenetic analysis. Therefore, regions in which the assignment of positional homology is ambiguous should be excluded (Gatesy et al. 1993). The exclusio ...
Phylogenetic analysis of the insect order Odonata using 28S and
... suggested that it is actually a relict of the early branching of the Anisozygoptera from the other two suborders. A phylogenetic analysis of the entire Insecta using 18S rDNA supports the viewpoint of Nel et al. (Kjer 2004); however, Kjer noted that the sequence diversity of this gene was very low i ...
... suggested that it is actually a relict of the early branching of the Anisozygoptera from the other two suborders. A phylogenetic analysis of the entire Insecta using 18S rDNA supports the viewpoint of Nel et al. (Kjer 2004); however, Kjer noted that the sequence diversity of this gene was very low i ...
Species
... • A rooted tree includes a branch to represent the last common ancestor of all taxa in the tree • A basal taxon diverges early in the history of a group and originates near the common ancestor of the group • A polytomy is a branch from which more than two ...
... • A rooted tree includes a branch to represent the last common ancestor of all taxa in the tree • A basal taxon diverges early in the history of a group and originates near the common ancestor of the group • A polytomy is a branch from which more than two ...
Document
... The VCHERRY trees and outputs (figures to the left) compare the predicted tree architectures, crop loads, and LA:F ratios for 4-yearold ‘Bing’ / Gisela®5 trees trained to 3 different systems. VCHERRY can remove and replace leaves at any time to reveal where the crop is being borne in the canopy. The ...
... The VCHERRY trees and outputs (figures to the left) compare the predicted tree architectures, crop loads, and LA:F ratios for 4-yearold ‘Bing’ / Gisela®5 trees trained to 3 different systems. VCHERRY can remove and replace leaves at any time to reveal where the crop is being borne in the canopy. The ...
seq.
... Phylogenetic reconstruction - How Parsimony analyses find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest proba ...
... Phylogenetic reconstruction - How Parsimony analyses find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest proba ...
seq.
... Phylogenetic reconstruction - How Parsimony analyses find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest proba ...
... Phylogenetic reconstruction - How Parsimony analyses find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest proba ...
OUTLINE
... then constructed for this marker. For example, if n=7, then the 7 covariates take values (0,0,0,1,0,1,0) for a genotype of 4/6 and (0,0,0,0,0,0,2) for a genotype of 7/7. The covariates include gender, the parental ...
... then constructed for this marker. For example, if n=7, then the 7 covariates take values (0,0,0,1,0,1,0) for a genotype of 4/6 and (0,0,0,0,0,0,2) for a genotype of 7/7. The covariates include gender, the parental ...
Are 100 enough? Inferring acanthomorph teleost phylogeny using
... taxonomic sampling than what was used for the original UCE design, increasing capture efficiency for a wider taxonomic range relative to those markers. This facilitates the capture of homologous loci that are useful for both old and more recent divergences, a property shared with UCEs [22, 27]. One ...
... taxonomic sampling than what was used for the original UCE design, increasing capture efficiency for a wider taxonomic range relative to those markers. This facilitates the capture of homologous loci that are useful for both old and more recent divergences, a property shared with UCEs [22, 27]. One ...
Tài liệu PDF
... random genomic segments from one species of prokaryote to another. GTAs have been shown to be responsible for genetic changes, sometimes at a very high frequency compared to other evolutionary processes. The first GTA was characterized in 1974 using purple, non-sulfur bacteria. These GTAs, which are ...
... random genomic segments from one species of prokaryote to another. GTAs have been shown to be responsible for genetic changes, sometimes at a very high frequency compared to other evolutionary processes. The first GTA was characterized in 1974 using purple, non-sulfur bacteria. These GTAs, which are ...
Species Tree Estimation using Maximum Likelihood Version 1.1
... solution) and values closer to 1 result in more rapid cooling (shorter search time but trees found are more likely to be only locally optimal). The default value given in the settings file should be adequate for most problems, and thus the user will not generally need to change this setting. The alg ...
... solution) and values closer to 1 result in more rapid cooling (shorter search time but trees found are more likely to be only locally optimal). The default value given in the settings file should be adequate for most problems, and thus the user will not generally need to change this setting. The alg ...
Basic Phylogenetics and Tree Building
... duplications are too common, specially in plants, and in some cases almost impossible to resolve. But when possible we should try to pick genes that are syntenic (in the same order) as other genes so we are sure it is an ortholog. ...
... duplications are too common, specially in plants, and in some cases almost impossible to resolve. But when possible we should try to pick genes that are syntenic (in the same order) as other genes so we are sure it is an ortholog. ...
Evolutionary Biology Today
... relatedness (a recent common ancestor). Conversely, some traits may differ among closely related taxa due to chance factors like random genetic drift, or because selection in different environments has caused divergence in those traits. One key here is to choose traits according to the level of taxo ...
... relatedness (a recent common ancestor). Conversely, some traits may differ among closely related taxa due to chance factors like random genetic drift, or because selection in different environments has caused divergence in those traits. One key here is to choose traits according to the level of taxo ...
Molecualr Biology and Evolution
... to the gram-positive/cyanobacterial clade, although the confounding effects of paralogous comparisons made interpretation of the data difficult. An additional test of nifgene horizontal transfer using nzjD was made, but the NifD phylogeny lacked resolution. Here nifgene phylogeny is addressed with a ...
... to the gram-positive/cyanobacterial clade, although the confounding effects of paralogous comparisons made interpretation of the data difficult. An additional test of nifgene horizontal transfer using nzjD was made, but the NifD phylogeny lacked resolution. Here nifgene phylogeny is addressed with a ...
Causes, consequences and solutions of
... Phylogenetic analysis is used to recover the evolutionary history of species, genes or proteins. Understanding phylogenetic relationships between organisms is a prerequisite of almost any evolutionary study, as contemporary species all share a common history through their ancestry. Moreover, it is i ...
... Phylogenetic analysis is used to recover the evolutionary history of species, genes or proteins. Understanding phylogenetic relationships between organisms is a prerequisite of almost any evolutionary study, as contemporary species all share a common history through their ancestry. Moreover, it is i ...
Slide 1
... growth, form, wood quality or other desired characteristics and appears to be adaptable. ...
... growth, form, wood quality or other desired characteristics and appears to be adaptable. ...
CHAPTER 24 Molecular Evolution
... 1. When DNA sequences diverge, they begin to collect mutations. The number of substitutions (K) found in an alignment is widely used in molecular evolution analysis. a. If the alignment shows few substitutions, a simple count is used. b. If many substitutions have occurred, it is likely that a simpl ...
... 1. When DNA sequences diverge, they begin to collect mutations. The number of substitutions (K) found in an alignment is widely used in molecular evolution analysis. a. If the alignment shows few substitutions, a simple count is used. b. If many substitutions have occurred, it is likely that a simpl ...
https://liberles.cst.temple.edu/public/BPO/Hermansen_et_al_2016_additional_file_1.pdf
... Check for instances where 4R event is not called due to possible phylogenetic error If (sequences are on different chromosomes){ Assign node as 4R ...
... Check for instances where 4R event is not called due to possible phylogenetic error If (sequences are on different chromosomes){ Assign node as 4R ...