Comparison of Gene Co-expression Networks and Bayesian Networks
... and widely researched. Bilu and Linial’s [10] work proposes a hierarchical clustering through the metric “BLAST” which is a measure of similarity in genes. A functional prediction is then performed so as to validate the clustered genes. Yeast genes are studied using Bayesian Networks by Friedman, et ...
... and widely researched. Bilu and Linial’s [10] work proposes a hierarchical clustering through the metric “BLAST” which is a measure of similarity in genes. A functional prediction is then performed so as to validate the clustered genes. Yeast genes are studied using Bayesian Networks by Friedman, et ...
TKTL_luento3
... • Results from heuristics are analyzed using proposed Bayes model • Evaluation of the results using the artificial data – estimate how well the obtained model predicts the future data sets – compare the models with DJS that uses also prior information ...
... • Results from heuristics are analyzed using proposed Bayes model • Evaluation of the results using the artificial data – estimate how well the obtained model predicts the future data sets – compare the models with DJS that uses also prior information ...
slides2
... Idea: harness evolution/adaptation strategically for therapeutic/technological/scientific goals Model this as a 2-player 0-sum incomplete-information game between treater and opponent ...
... Idea: harness evolution/adaptation strategically for therapeutic/technological/scientific goals Model this as a 2-player 0-sum incomplete-information game between treater and opponent ...
Baylor /Waco Comments - Texas Water Resources Institute
... of water sampling sites that should be included in assessment and a method for how to select the minimum number of water sampling sites. Inadequate sample site selection and numbers can limit the significance of TMDL assessments or any watershed study. We want to ensure that future TMDL assessments ...
... of water sampling sites that should be included in assessment and a method for how to select the minimum number of water sampling sites. Inadequate sample site selection and numbers can limit the significance of TMDL assessments or any watershed study. We want to ensure that future TMDL assessments ...
Cytoscape: Network analysis and visualisation
... • Visual mapping of data to properties allows for representation of multiple dimensions of data • >10 visible properties of nodes (node shape, size, colour, opacity, line attributes, etc…) + more for edges • Examine different types of experimental results or analysis simultaneously on a networ ...
... • Visual mapping of data to properties allows for representation of multiple dimensions of data • >10 visible properties of nodes (node shape, size, colour, opacity, line attributes, etc…) + more for edges • Examine different types of experimental results or analysis simultaneously on a networ ...
Data Mining
... and potatoes together, he or she is likely to also buy beef. Such information can be used as the basis for decisions about marketing activities such as, e.g., promotional pricing or . In addition to the above example from market basket analysis association rules are employed today in many applicatio ...
... and potatoes together, he or she is likely to also buy beef. Such information can be used as the basis for decisions about marketing activities such as, e.g., promotional pricing or . In addition to the above example from market basket analysis association rules are employed today in many applicatio ...
1) of
... (matrix of traits) with the highest probability Prob(D|H). This quantity is also known as the likelihood of the hypothesis, given the data. However, to calculate Prob(D|H) we need to have some idea of how evolution occurred - for example, that some traits evolve faster than others. Bayesian methods ...
... (matrix of traits) with the highest probability Prob(D|H). This quantity is also known as the likelihood of the hypothesis, given the data. However, to calculate Prob(D|H) we need to have some idea of how evolution occurred - for example, that some traits evolve faster than others. Bayesian methods ...
2007GenomeInformaticsGMODPoster
... genome-scale biological databases. You can use it to create a small laboratory database of genome annotations, or a large webaccessible community database. GMOD includes a modular database schema called Chado that supports many common needs. ...
... genome-scale biological databases. You can use it to create a small laboratory database of genome annotations, or a large webaccessible community database. GMOD includes a modular database schema called Chado that supports many common needs. ...
CUSTOMER_CODE SMUDE DIVISION_CODE SMUDE
... infer a function from a set of samples. This technique provides a "learning approach"; it is driven by a test sample that is used for the initial inference and learning. With this kind of learning method, responses to new inputs may be able to be interpolated from the known samples. This interpolati ...
... infer a function from a set of samples. This technique provides a "learning approach"; it is driven by a test sample that is used for the initial inference and learning. With this kind of learning method, responses to new inputs may be able to be interpolated from the known samples. This interpolati ...
for networks - Vanderbilt Kennedy Center
... Genotype + Environment + DEVELOPMENT ==> Phenotype 1) Astounding Results Importance of Network thinking in development and physiology for data to explain phenotype (e.g. PAX6) ...
... Genotype + Environment + DEVELOPMENT ==> Phenotype 1) Astounding Results Importance of Network thinking in development and physiology for data to explain phenotype (e.g. PAX6) ...
A Novel Method to Detect Identities in tRNA Genes Using Sequence
... We applied the method to Class I tRNAs to detect characteristic sites. We found that about 40% of characteristic sites that we detected are identities that have been detected experimentally, and that the remaining characteristic sites are in T and D domains which are the elbow regions of tRNAs. This ...
... We applied the method to Class I tRNAs to detect characteristic sites. We found that about 40% of characteristic sites that we detected are identities that have been detected experimentally, and that the remaining characteristic sites are in T and D domains which are the elbow regions of tRNAs. This ...
HPC
... Key challenge is mapping biomarkers into: biological context and understanding Requires an experimental model system ...
... Key challenge is mapping biomarkers into: biological context and understanding Requires an experimental model system ...
MultipleSequenceAlignment
... origin) have similar sequences. Orthologs are genes that are evolutionarily related, have a similar function, but now appear in different species. Paralogs are evolutionarily related (share an origin) but no longer have the same function. You can uncover either orthologs or paralogs through sequence ...
... origin) have similar sequences. Orthologs are genes that are evolutionarily related, have a similar function, but now appear in different species. Paralogs are evolutionarily related (share an origin) but no longer have the same function. You can uncover either orthologs or paralogs through sequence ...
The growing challenges of big data in the agricultural and ecological
... • Crops for the future will be based on advanced research and breeding using molecular methods • The genome sequencing and other ‘omics technologies are creating a data deluge • Distributed in centres around globe – particularly so for of agricultural species • Next data tsunami coming from image ba ...
... • Crops for the future will be based on advanced research and breeding using molecular methods • The genome sequencing and other ‘omics technologies are creating a data deluge • Distributed in centres around globe – particularly so for of agricultural species • Next data tsunami coming from image ba ...
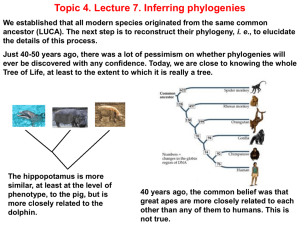
Chapter 26 Presentation-Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
... ancestral state; those that have changed more are excluded. A paraphyletic group contains only the conservative descendants from an ancestral species. ...
... ancestral state; those that have changed more are excluded. A paraphyletic group contains only the conservative descendants from an ancestral species. ...
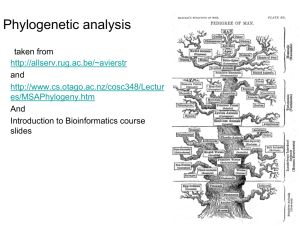
my_phylogeny1
... derive from a common ancestor. Phylip • Slower than distance methods. • Assumes molecular clock • Maximum Likelihood : Looks for the tree with the maximum likelihood: the most probable tree. • this is the slowest method of all but seems to give the best result and the most information about the tree ...
... derive from a common ancestor. Phylip • Slower than distance methods. • Assumes molecular clock • Maximum Likelihood : Looks for the tree with the maximum likelihood: the most probable tree. • this is the slowest method of all but seems to give the best result and the most information about the tree ...
ppt - r-evolution research server
... The analysed variables with the PCOP method can be independent because the method uses a hidden variable for ordering the data. PCOP is defined using the generalisation, at the local level, of the Principal-Components variance properties. The set of POPs obtained (PC at local level) makes up the PCO ...
... The analysed variables with the PCOP method can be independent because the method uses a hidden variable for ordering the data. PCOP is defined using the generalisation, at the local level, of the Principal-Components variance properties. The set of POPs obtained (PC at local level) makes up the PCO ...
temp_JSCS2016
... (Hapmap project) and simulated QTL data, and for the dominant model we performed a small size simulation study to compare the powers with QTLmarc. The results showed that our method was more effective for detecting the genotype-to-phenotype relationship than QTLmarc of Kamitsuji and Kamatani (2006) ...
... (Hapmap project) and simulated QTL data, and for the dominant model we performed a small size simulation study to compare the powers with QTLmarc. The results showed that our method was more effective for detecting the genotype-to-phenotype relationship than QTLmarc of Kamitsuji and Kamatani (2006) ...
GGSB Course Descriptions – Computational Track
... HGEN 46900 Human Variation and Disease. This course focuses on principles of population and evolutionary genetics and complex trait mapping as they apply to humans. It will include the discussion of genetic variation and disease mapping data. Spring. OR HGEN 47300 Genomics and Systems Biology. This ...
... HGEN 46900 Human Variation and Disease. This course focuses on principles of population and evolutionary genetics and complex trait mapping as they apply to humans. It will include the discussion of genetic variation and disease mapping data. Spring. OR HGEN 47300 Genomics and Systems Biology. This ...
Investigating Polar Bear and Giant Panda Ancestry
... distance of 0.00 indicates identical sequences and as the difference in gene sequences increases so does the number). 2. Provide a phylogenetic tree of the bears and the panda. Label the lines on the tree with the corresponding distances. 3. Explain and provide support for the conclusions made by th ...
... distance of 0.00 indicates identical sequences and as the difference in gene sequences increases so does the number). 2. Provide a phylogenetic tree of the bears and the panda. Label the lines on the tree with the corresponding distances. 3. Explain and provide support for the conclusions made by th ...
STRAW: Species TRee Analysis Web server | Nucleic Acids
... MP-EST, STAR and NJst use gene trees estimated from DNA sequence data to infer species trees. Uncertainty of the estimated gene trees is incorporated in estimation of species trees using bootstrap techniques. In the MP-EST method, species trees are estimated from a collection of rooted gene trees by ...
... MP-EST, STAR and NJst use gene trees estimated from DNA sequence data to infer species trees. Uncertainty of the estimated gene trees is incorporated in estimation of species trees using bootstrap techniques. In the MP-EST method, species trees are estimated from a collection of rooted gene trees by ...