Phylogeny of the Primates
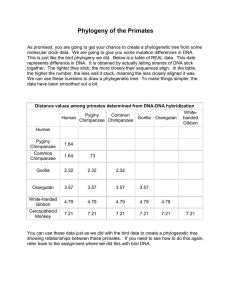
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
Using HIV Data Sets for Inquiry
... Split decomposition is one method for testing a tree. Under this procedure, we choose exactly four taxa (A, B, C, D) and examine the topologies of all possible unrooted trees. How many such trees are there? ...
... Split decomposition is one method for testing a tree. Under this procedure, we choose exactly four taxa (A, B, C, D) and examine the topologies of all possible unrooted trees. How many such trees are there? ...
Document
... Two brief categories of investigation Ethnographic Comparative Each one has two parts Present Recent past ...
... Two brief categories of investigation Ethnographic Comparative Each one has two parts Present Recent past ...
3000_2013_1e
... DNA-based characters work the same (idea is there may be more independence, and more of them) ...
... DNA-based characters work the same (idea is there may be more independence, and more of them) ...
Lecture5
... Bootstrapping phylogenies Characters are resampled with replacement to create many bootstrap replicate data sets Each bootstrap replicate data set is analysed (e.g. with parsimony, distance, ML etc.) Agreement among the resulting trees is summarized with a majority-rule consensus tree Frequen ...
... Bootstrapping phylogenies Characters are resampled with replacement to create many bootstrap replicate data sets Each bootstrap replicate data set is analysed (e.g. with parsimony, distance, ML etc.) Agreement among the resulting trees is summarized with a majority-rule consensus tree Frequen ...
A method for paralogy trees reconstruction
... Genes belonging to the same organism are called paralogs when they show a significant similarity in the sequences, even if they have a different biological function. It is an emergent biological paradigm that the families of paralogs derive from a mechanism of gene duplication with modification, rep ...
... Genes belonging to the same organism are called paralogs when they show a significant similarity in the sequences, even if they have a different biological function. It is an emergent biological paradigm that the families of paralogs derive from a mechanism of gene duplication with modification, rep ...
BlueJam Evolutionary Music Composition
... Genetic Programming (GP) and Evolutionary Algorithms (EA) have produced human-competitive results when applied to problems of all kinds. Their approach to problem solving can be described as a search through the space of possible solutions. In 1992, Koza brought Tree-based GP to prominence, and it h ...
... Genetic Programming (GP) and Evolutionary Algorithms (EA) have produced human-competitive results when applied to problems of all kinds. Their approach to problem solving can be described as a search through the space of possible solutions. In 1992, Koza brought Tree-based GP to prominence, and it h ...
Step 3. Construction of the phylogenetic tree Distance methods
... the probability increases that more than one mutation has occured at any one site. ...
... the probability increases that more than one mutation has occured at any one site. ...
A Large Margin Method for Semi
... labeled data. This imposes a great challenge in that the class probability given input can not be well estimated through labeled data alone. In this talk, I will present a large margin semisupervised method based on an efficient margin loss for unlabeled data. This loss seeks extracting the maximum ...
... labeled data. This imposes a great challenge in that the class probability given input can not be well estimated through labeled data alone. In this talk, I will present a large margin semisupervised method based on an efficient margin loss for unlabeled data. This loss seeks extracting the maximum ...
Language Trees
... Each edge represents an entry in our cognate-percentage matrix. They are color-coded by percentage similarity. ...
... Each edge represents an entry in our cognate-percentage matrix. They are color-coded by percentage similarity. ...
PHYLOGENETIC NETWORKS
... – UT CS: Tandy Warnow, Luay Nakhleh – UT BIO: Randy Linder – UNM CS: Bernard Moret ...
... – UT CS: Tandy Warnow, Luay Nakhleh – UT BIO: Randy Linder – UNM CS: Bernard Moret ...
Day6
... Pairwise distance and neighbor joining are distance methods. • There are two main categories of phylogeny methods, distance methods and character methods. In distance methods, the first step is to calculate a matrix of all pairwise differences between a set of sequences. Next, the tree is construct ...
... Pairwise distance and neighbor joining are distance methods. • There are two main categories of phylogeny methods, distance methods and character methods. In distance methods, the first step is to calculate a matrix of all pairwise differences between a set of sequences. Next, the tree is construct ...
“Statistical Dissection of Gene-environment Interactions: A Semi-Parametric Perspective” Yuehua Cui
... Michigan State University ...
... Michigan State University ...
Creating Phylogenetic Trees with MEGA
... – At each site, the likelihood is determined by evaluating the probability that a certain evolutionary model (eg. BLOSSUM or PAM matrices) has generated the observed data. – The likelihood’s for each site are then multiplied to provide likelihood for each tree – Choose the tree with maximum like ...
... – At each site, the likelihood is determined by evaluating the probability that a certain evolutionary model (eg. BLOSSUM or PAM matrices) has generated the observed data. – The likelihood’s for each site are then multiplied to provide likelihood for each tree – Choose the tree with maximum like ...
AbstractSEE
... involves two different data types (for instance, GWAS and expression data, as in eQTL analyses). The availability of more than 2 omics data types derived from the same set of individuals is rare. And when these exist, several technical and statistical hurdles need to be taken to ensure optimal power ...
... involves two different data types (for instance, GWAS and expression data, as in eQTL analyses). The availability of more than 2 omics data types derived from the same set of individuals is rare. And when these exist, several technical and statistical hurdles need to be taken to ensure optimal power ...
A Phase Transition in Molecular Evolution with Applications to the Assembly of the Tree of Life
... of the massive data sets produced in current evolutionary studies. In particular, the estimation of evolutionary trees on increasingly large scales has prompted the development of novel reconstruction methods. An important issue in this context is the fundamental trade-off between statistical accura ...
... of the massive data sets produced in current evolutionary studies. In particular, the estimation of evolutionary trees on increasingly large scales has prompted the development of novel reconstruction methods. An important issue in this context is the fundamental trade-off between statistical accura ...
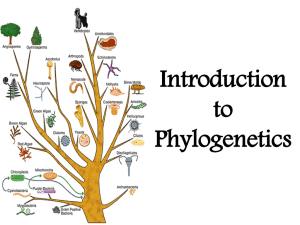
Introduction to Phylogenetics - Lectures For UG-5
... Making trees using character-based methods The main idea of character based methods is to search for a tree that requires the smallest number of evolutionary changes to explain the differences among the OTUs under study. ...
... Making trees using character-based methods The main idea of character based methods is to search for a tree that requires the smallest number of evolutionary changes to explain the differences among the OTUs under study. ...
Phylogenetic - Nematode bioinformatics. Analysis tools and data
... Mitochondrial DNA, most nuclear DNAencoded genes, and DNA/DNA hybridization all show that bonobos and chimpanzees are related more closely to humans than either are to gorillas. ...
... Mitochondrial DNA, most nuclear DNAencoded genes, and DNA/DNA hybridization all show that bonobos and chimpanzees are related more closely to humans than either are to gorillas. ...
CIPRES.2006.algorthms_sr
... • Breakthrough: Optimal logarithmic sequence length tree reconstruction (Daskalakis, Mossel, Roch 05). Simplified version (Mihaescu et al. 06). Preliminary Implementation [Adkins et al.]. ...
... • Breakthrough: Optimal logarithmic sequence length tree reconstruction (Daskalakis, Mossel, Roch 05). Simplified version (Mihaescu et al. 06). Preliminary Implementation [Adkins et al.]. ...
m12-comparative_genomics
... Organize a collection of modern-day sequences according to their evolutionary history Distance-based methods operate on a table of pairwise distances between sequences o UPGMA: ~agglomerative clustering; naïve method for tree-building; assumes a molecular clock (all branches changing at the same ...
... Organize a collection of modern-day sequences according to their evolutionary history Distance-based methods operate on a table of pairwise distances between sequences o UPGMA: ~agglomerative clustering; naïve method for tree-building; assumes a molecular clock (all branches changing at the same ...
tree
... A tree is a connected, acyclic 2D graph Leaf: Taxon Node: Vertex Branch: Edge Tree length = sum of all branch lengths Phylogenetic trees are binary trees ...
... A tree is a connected, acyclic 2D graph Leaf: Taxon Node: Vertex Branch: Edge Tree length = sum of all branch lengths Phylogenetic trees are binary trees ...
Genealogical Trees,Coalescent Theory and the Analysis of Genetic
... N. Rosenberg and M. Nordborg ...
... N. Rosenberg and M. Nordborg ...