Analysing genomic data with seeded Bayesian networks
... Include homologues of genes already in the network. Fitted network can be used to infer function of previously uncharacterized genes. ...
... Include homologues of genes already in the network. Fitted network can be used to infer function of previously uncharacterized genes. ...
C.Constance Biol 415 Hiram College
... 1904: Nuttall used immunological tests to deduce relationships between a variety of animals to place humans in their correct evolutionary position relative to other primates ...
... 1904: Nuttall used immunological tests to deduce relationships between a variety of animals to place humans in their correct evolutionary position relative to other primates ...
Evolution of HSV-1 and VZV.
... -A way to get “statistical significance” of a certain topology -Construct several new sequence sets (1000 st.) ...
... -A way to get “statistical significance” of a certain topology -Construct several new sequence sets (1000 st.) ...
Phylogenetic Trees - Elhanan Borenstein
... Enumerate and score all trees? How about the following algorithm: Enumerate every tree topology, fit least-squares best distances for each topology, keep best. Not used for distance trees - there is a much faster way to get very close to correct. ...
... Enumerate and score all trees? How about the following algorithm: Enumerate every tree topology, fit least-squares best distances for each topology, keep best. Not used for distance trees - there is a much faster way to get very close to correct. ...
Slides of Barbara`s talk - School of Mathematical Sciences
... 4. Move each gene into the class for which it has highest posterior probability 5. Go to step 2, when no genes change class STOP ...
... 4. Move each gene into the class for which it has highest posterior probability 5. Go to step 2, when no genes change class STOP ...
Generating Workflow Graphs Using Typed Genetic Programming
... In this paper we further develop our research line of chaining several preprocessing methods with classifiers [1], by generating the complete workflow schemes. These schemes, represented as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), contain computational intelligence methods together with preprocessing algorit ...
... In this paper we further develop our research line of chaining several preprocessing methods with classifiers [1], by generating the complete workflow schemes. These schemes, represented as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), contain computational intelligence methods together with preprocessing algorit ...
Talk in Powerpoint Format
... • Objective: determine probability estimates that a given sample belongs to a class Probability(x Class | attribute values) • Baysian network: – One node for each attribute – Nodes connected in an acyclic graph – Conditional independance ...
... • Objective: determine probability estimates that a given sample belongs to a class Probability(x Class | attribute values) • Baysian network: – One node for each attribute – Nodes connected in an acyclic graph – Conditional independance ...
Gene Set Analysis with Phenotypic Screening Data Results and Validation Purpose
... positive gene sets • The analysis was run on a viral infection cell proliferation assay then the significant sets were clustered (below). The themes are consistent with validated targets and pathways in viral infection. ...
... positive gene sets • The analysis was run on a viral infection cell proliferation assay then the significant sets were clustered (below). The themes are consistent with validated targets and pathways in viral infection. ...
CellCODE: a robust latent variable approach to differential
... Compared to the Coulter counter analysis ...
... Compared to the Coulter counter analysis ...
SK_DifficultProblems.
... For each pair of DNA sequences x and y, a 4 4 matrix with each possible pair of sites ...
... For each pair of DNA sequences x and y, a 4 4 matrix with each possible pair of sites ...
PPT - UT Computer Science
... • Much software exists, most of which attempt to solve one of two major optimization criteria: Maximum Parsimony and Maximum Likelihood. The most frequently used software package is PAUP*, which contains many different heuristics. • Methods for phylogeny reconstruction are evaluated primarily in sim ...
... • Much software exists, most of which attempt to solve one of two major optimization criteria: Maximum Parsimony and Maximum Likelihood. The most frequently used software package is PAUP*, which contains many different heuristics. • Methods for phylogeny reconstruction are evaluated primarily in sim ...
Classification and phylogeny – Chapter 2
... How can we tell which character state is derived and which is ancestral? ...
... How can we tell which character state is derived and which is ancestral? ...
slides
... classify the data sets using a maximum likelihood (MLHD) method. • Fitness = 200 – (E1 + E2) • E1 = cross validation error rate • E2 = independent test error rate. • The MLHD classifier involves a lot of math, but is based upon Bayes Rule • Used two previous rank-based methods on the same truncated ...
... classify the data sets using a maximum likelihood (MLHD) method. • Fitness = 200 – (E1 + E2) • E1 = cross validation error rate • E2 = independent test error rate. • The MLHD classifier involves a lot of math, but is based upon Bayes Rule • Used two previous rank-based methods on the same truncated ...
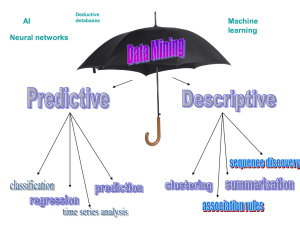
CSCE590/822 Data Mining Principles and Applications
... So what do the results mean? • 2 of 3 patients closer to dentist than to local controls. Statistical significance? More powerful analyses? • Do we have enough data to be confident in our conclusions? What additional data would help? • If we determine that the dentist’s virus is linked to those of p ...
... So what do the results mean? • 2 of 3 patients closer to dentist than to local controls. Statistical significance? More powerful analyses? • Do we have enough data to be confident in our conclusions? What additional data would help? • If we determine that the dentist’s virus is linked to those of p ...
Mine Microarray Gene Expression Data, Predict Cancers
... • Single gene (zyxin), single branch tree 38/38 correct on training cases 31/34 correct on test cases, 3 errors X*5735_at <=(8+1)38: ALL • Tree size up to 3 genes 1 decision tree with 1 error 7 decision trees with 2 errors 7 decision trees with 3 errors ...
... • Single gene (zyxin), single branch tree 38/38 correct on training cases 31/34 correct on test cases, 3 errors X*5735_at <=(8+1)38: ALL • Tree size up to 3 genes 1 decision tree with 1 error 7 decision trees with 2 errors 7 decision trees with 3 errors ...
Chuanlong (Ben) Du
... Invented non-statistical methods to filter genes/variables/features; alleviated the problem of large number of variables (genes) and small number of observations (samples). Integrated the lasso method with the logistic regression model to further select genes; identified a small list of biologic ...
... Invented non-statistical methods to filter genes/variables/features; alleviated the problem of large number of variables (genes) and small number of observations (samples). Integrated the lasso method with the logistic regression model to further select genes; identified a small list of biologic ...
Our material on phylogenetics in bioinformatics was roughly divided
... * what is the likelihood ratio test and how is it used to test a wide variety of possible hypotheses about sequence evolution, such as: rates of evolution, monophyly of group or sequences, similarity of branching history of two trees, etc. ...
... * what is the likelihood ratio test and how is it used to test a wide variety of possible hypotheses about sequence evolution, such as: rates of evolution, monophyly of group or sequences, similarity of branching history of two trees, etc. ...
An Introduction to Phylogenetics
... What can I do with phylogenetics? • Deduce relationships among species or genes • Deduce the origin of pathogens • Identify biological processes that affect how your sequence has evolved e.g. identify genes or residues ...
... What can I do with phylogenetics? • Deduce relationships among species or genes • Deduce the origin of pathogens • Identify biological processes that affect how your sequence has evolved e.g. identify genes or residues ...
click here and type title
... that when the individual studies are large, two-stage methods produce nearly unbiased exposure estimates and standard errors of the exposure estimates from a generalized linear mixed model (GLMM). Based on these considerations, several existing cancer epidemiology consortia suggested in their protoc ...
... that when the individual studies are large, two-stage methods produce nearly unbiased exposure estimates and standard errors of the exposure estimates from a generalized linear mixed model (GLMM). Based on these considerations, several existing cancer epidemiology consortia suggested in their protoc ...
Diapositiva 1
... Distance trees were constructed using Neighbor-Joining with a maximum likelihood distance matrix using the model selected by MODELTEST. The standard errors of branch lengths were estimated using PAUP . Divergence dates with low and high confidence intervals and associated evolutionary rates were est ...
... Distance trees were constructed using Neighbor-Joining with a maximum likelihood distance matrix using the model selected by MODELTEST. The standard errors of branch lengths were estimated using PAUP . Divergence dates with low and high confidence intervals and associated evolutionary rates were est ...
Agenda - UCLA Human Genetics
... Systems Biology Analysis Methods for Genomic Data 9:30am-5:15pm, Tuesday, 7 October 2014 13-105 CHS (Center for Health Sciences), UCLA Description We will describe network analysis methods widely used in systems biologic and systems genetic applications. The goal is to familiarize researchers with n ...
... Systems Biology Analysis Methods for Genomic Data 9:30am-5:15pm, Tuesday, 7 October 2014 13-105 CHS (Center for Health Sciences), UCLA Description We will describe network analysis methods widely used in systems biologic and systems genetic applications. The goal is to familiarize researchers with n ...
Lecture 8-9 The word as a unit of analysis Alphabetic writing was
... The word as a unit of analysis Alphabetic writing was particularly important for the identification of the word as a basic unit of analysis in linguistics. Although linguists have been searching for writing-independent criteria for establishing the boundaries of words in different languages around t ...
... The word as a unit of analysis Alphabetic writing was particularly important for the identification of the word as a basic unit of analysis in linguistics. Although linguists have been searching for writing-independent criteria for establishing the boundaries of words in different languages around t ...
Marked Patterns of Lexical Borrowing in Southeast Asia Uri Tadmor
... Some features of Southeast Asian languages are shared among many languages of the region, regardless of genetic affiliation. When taken together, such areal features permit us to consider Southeast Asia as a linguistic area. The more universally marked these features, the stronger evidence they cons ...
... Some features of Southeast Asian languages are shared among many languages of the region, regardless of genetic affiliation. When taken together, such areal features permit us to consider Southeast Asia as a linguistic area. The more universally marked these features, the stronger evidence they cons ...