Document
... The function of many, typically 50%, of translated proteins can be inferred from sequence comparison with previously characterized sequences The assignment of function by homology gives only a partial understanding of a protein’s role within a cell A more complete understanding of a protein fu ...
... The function of many, typically 50%, of translated proteins can be inferred from sequence comparison with previously characterized sequences The assignment of function by homology gives only a partial understanding of a protein’s role within a cell A more complete understanding of a protein fu ...
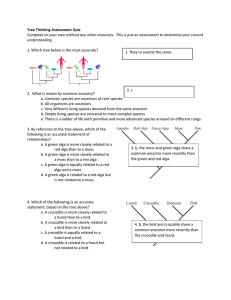
Tree Thinking Assessment Quiz
... on the left, and the gray branches indicate uncertainty in character reconstruction. What does a comparison of these two figures tell us about the evolution of plant secondary chemistry? a. The four groups of chemically similar species each constitutes a distinct evolutionary lineage b. The group co ...
... on the left, and the gray branches indicate uncertainty in character reconstruction. What does a comparison of these two figures tell us about the evolution of plant secondary chemistry? a. The four groups of chemically similar species each constitutes a distinct evolutionary lineage b. The group co ...
biol2007 - evolutionary trees and their uses
... Parsimony methods have been criticised for failing to use all of the information available – often only small proportions of datasets are used. Some researchers seek to exploit information more efficiently and (often using sophisticated statistical tests) seek to choose best tree among all possible ...
... Parsimony methods have been criticised for failing to use all of the information available – often only small proportions of datasets are used. Some researchers seek to exploit information more efficiently and (often using sophisticated statistical tests) seek to choose best tree among all possible ...
Phylogenetic analysis
... molecular sequences: reconstruct the evolutionary history of the species involved. A gene phylogeny only describes the evolution of that particular gene or encoded protein. This sequence may evolve more or less rapidly than other genes in the genome. The evolution of a particular sequence does not n ...
... molecular sequences: reconstruct the evolutionary history of the species involved. A gene phylogeny only describes the evolution of that particular gene or encoded protein. This sequence may evolve more or less rapidly than other genes in the genome. The evolution of a particular sequence does not n ...
Removing Unwanted Variation from High-Throughput Omic Data
... have been carried out, with the hope of understanding, predicting or discovering factors of interest such as prognosis or the subtypes of a cancer. The same applies to proteomic and metabolomic data, and to several other kinds of data. Large studies are often carried out over several years, and invo ...
... have been carried out, with the hope of understanding, predicting or discovering factors of interest such as prognosis or the subtypes of a cancer. The same applies to proteomic and metabolomic data, and to several other kinds of data. Large studies are often carried out over several years, and invo ...
NETWORK ANALYSIS COURSE
... Advanced topics in trait mapping, estimates of precision, estimates of power Exercise: Empirical precision of monogenic QTLs 2a. Network analysis seeded by single genes, transcripts, proteins... Review of mouse, rat, and human data sets Exercise: Cdc20 and the cell cycle Correlation to PC eigentrait ...
... Advanced topics in trait mapping, estimates of precision, estimates of power Exercise: Empirical precision of monogenic QTLs 2a. Network analysis seeded by single genes, transcripts, proteins... Review of mouse, rat, and human data sets Exercise: Cdc20 and the cell cycle Correlation to PC eigentrait ...
ODD-Genes - National e
... Researcher can reproduce this initial condition for repeated analyses Researcher need not perform each step manually and serially, or ask dedicated statistician to do so. ...
... Researcher can reproduce this initial condition for repeated analyses Researcher need not perform each step manually and serially, or ask dedicated statistician to do so. ...
Molecular evolution and phylogenetic implications in clinical research
... to making errors during DNA replication, which means that duplicates are not always identical to the original. If DNA replication is accurate, there would be no variation on which natural selection could act. Errors are thus the key to evolution. In many cases, the classification of the species was ...
... to making errors during DNA replication, which means that duplicates are not always identical to the original. If DNA replication is accurate, there would be no variation on which natural selection could act. Errors are thus the key to evolution. In many cases, the classification of the species was ...
here - CMBI
... sequence changes to other character states • BLOck SUbstitution Matrix (BLOSUM) is based on observed substitutions between proteins with e.g. >62% sequence identity ...
... sequence changes to other character states • BLOck SUbstitution Matrix (BLOSUM) is based on observed substitutions between proteins with e.g. >62% sequence identity ...
Molecular Phylogeny
... • A phylogenetic tree is characterised by its topology (form) and its length (sum of its branch lengths) ; • Each node of a tree is an estimation of the ancestor of the elements included in this node; • There are 3 main classes of phylogenetic methods for constructing phylogenies from sequence data ...
... • A phylogenetic tree is characterised by its topology (form) and its length (sum of its branch lengths) ; • Each node of a tree is an estimation of the ancestor of the elements included in this node; • There are 3 main classes of phylogenetic methods for constructing phylogenies from sequence data ...
Glycemia and Wt Mngt. Olz
... there is less than a 5% chance of obtaining a difference this large or larger. c) There is a 95% chance that if the study is repeated, the result will be replicated. d) There is a 95% chance that there is a real difference between the two population means. Adapted from: Wulff HR, Andersen B, Branden ...
... there is less than a 5% chance of obtaining a difference this large or larger. c) There is a 95% chance that if the study is repeated, the result will be replicated. d) There is a 95% chance that there is a real difference between the two population means. Adapted from: Wulff HR, Andersen B, Branden ...
introduction to molecular phylogeny
... tree (that whose total branch length is minimum). In that sense, the NJ method is very similar to parsimony because branch lengths represent substitutions. NJ produces always unrooted trees, that need to be rooted by the outgroup method. NJ always finds the correct tree if distances are tree-like. N ...
... tree (that whose total branch length is minimum). In that sense, the NJ method is very similar to parsimony because branch lengths represent substitutions. NJ produces always unrooted trees, that need to be rooted by the outgroup method. NJ always finds the correct tree if distances are tree-like. N ...
lecture 03 - phylogenetics - Cal State LA
... Since we can’t travel back in time to identify common ancestors, relationships of existing species must be estimated or inferred from data – therefore, a phylogeny is always a hypothesis ...
... Since we can’t travel back in time to identify common ancestors, relationships of existing species must be estimated or inferred from data – therefore, a phylogeny is always a hypothesis ...
RidgeRace: ridge regression for continuous ancestral character
... Such reconstructions can reach into the distant past and can provide insights into the history of a population or a set of species when fossil data are not available, or they can be used to test evolutionary hypotheses, e.g. on the co-evolution of traits. Typical methods for ancestral character stat ...
... Such reconstructions can reach into the distant past and can provide insights into the history of a population or a set of species when fossil data are not available, or they can be used to test evolutionary hypotheses, e.g. on the co-evolution of traits. Typical methods for ancestral character stat ...
A common ancestor
... Pairwise Sequence Alignment • Methods – Global alignment • Closely related sequences • Similar length ...
... Pairwise Sequence Alignment • Methods – Global alignment • Closely related sequences • Similar length ...
reduce
... • reduces experimental noise and is well suited for uncovering groups of genes • a quantitative expression of the widespread notion18 that transcription initiation occurs through the recruitment of the polymerase by reversible binding to transcription factors and hence to the regulatory sequences • ...
... • reduces experimental noise and is well suited for uncovering groups of genes • a quantitative expression of the widespread notion18 that transcription initiation occurs through the recruitment of the polymerase by reversible binding to transcription factors and hence to the regulatory sequences • ...
download PDF program in pamphlet form
... Linguists have for a century suggested a common linguistic heritage for NaDene and Yeniseian, but only recently has a case been made using traditional methods of historical reconstruction (Vajda 2010). Our work responds to challenges to use alternative methodologies to evaluate this hypothesis (Camp ...
... Linguists have for a century suggested a common linguistic heritage for NaDene and Yeniseian, but only recently has a case been made using traditional methods of historical reconstruction (Vajda 2010). Our work responds to challenges to use alternative methodologies to evaluate this hypothesis (Camp ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Lee Lab
... • They can be DNA nucleotides or other heritable traits • They are used to group taxa that are more closely related to one another ...
... • They can be DNA nucleotides or other heritable traits • They are used to group taxa that are more closely related to one another ...
manual
... -l LSCALE, --length scale=LSCALE Sequence lengths scaling for alignments. Each alignment in each simulation can be scaled with the same number. -v THETA, --theta=THETA θ parameter for generating gene trees from the species trees before generating alignments along the species tree. For the definition ...
... -l LSCALE, --length scale=LSCALE Sequence lengths scaling for alignments. Each alignment in each simulation can be scaled with the same number. -v THETA, --theta=THETA θ parameter for generating gene trees from the species trees before generating alignments along the species tree. For the definition ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Lee Lab
... • They can be DNA nucleotides or other heritable traits • They are used to group taxa that are more closely related to one another ...
... • They can be DNA nucleotides or other heritable traits • They are used to group taxa that are more closely related to one another ...
Practical theory (15-20 min) A phylogeny is the representation of the
... Phylogram: tree that shows the relations and distances among sequences. The length of the branches are proportional to the distance between two sequences. ...
... Phylogram: tree that shows the relations and distances among sequences. The length of the branches are proportional to the distance between two sequences. ...
Lectures 21, 22, and 23: Phylogenic Trees and Evolution Steven
... Because the various algorithms and heuristics give different trees on the same data, more evidence is needed than a single tree to define the history. For this reason, there are suites of programs (e.g. Phylip) which contain implementations of many different tree construction algorithms and heuristi ...
... Because the various algorithms and heuristics give different trees on the same data, more evidence is needed than a single tree to define the history. For this reason, there are suites of programs (e.g. Phylip) which contain implementations of many different tree construction algorithms and heuristi ...
Document
... Likelihood • Calculate the Likelihood for each base position in the sequence and summarizes across all base positions. • The ML tree is the tree that produces the highest likelihood. • Evaluates the branching structure of the tree, and also the branch length, using similar tree-searching strategies ...
... Likelihood • Calculate the Likelihood for each base position in the sequence and summarizes across all base positions. • The ML tree is the tree that produces the highest likelihood. • Evaluates the branching structure of the tree, and also the branch length, using similar tree-searching strategies ...