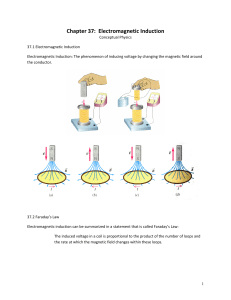
6 I – Rocket Science
... The magnetic force has been known for thousands of years, as long as people realized that needles made of certain metals always point into the same direction – the North Pole. The ancient Greeks also knew about the electric force. They observed that by rubbing amber on animal fur caused little crack ...
... The magnetic force has been known for thousands of years, as long as people realized that needles made of certain metals always point into the same direction – the North Pole. The ancient Greeks also knew about the electric force. They observed that by rubbing amber on animal fur caused little crack ...
Mathematics and waves
... uniform magnetic field B with direction into the page, as in fig. If the magnitude changes in time, describe the induced electric field for points inside the cylinder. ...
... uniform magnetic field B with direction into the page, as in fig. If the magnitude changes in time, describe the induced electric field for points inside the cylinder. ...
Introduction to Physics (in a nutshell) Based on the Physics Worktext
... W. Roentgen – X-rays Henri Berequel – radioactivity Max Planck – quantum theory (quantum mechanics) ...
... W. Roentgen – X-rays Henri Berequel – radioactivity Max Planck – quantum theory (quantum mechanics) ...
EE4301 sp06 Class Sy..
... *Homework and Notes handed in after the due date will not be counted! This rule will be strictly enforced! (This means that the homework/notes can be slid under my door that night. I usually arrive at ~8 AM.) ...
... *Homework and Notes handed in after the due date will not be counted! This rule will be strictly enforced! (This means that the homework/notes can be slid under my door that night. I usually arrive at ~8 AM.) ...
Fundamental nuclear symmetries meet classical electrodynamic
... • Maxwell’s equations – dynamics of the field – Source equations – charge (ρ,J) generates the E&M field – Force equations – nature of E&M force: conservation of (E,p) ...
... • Maxwell’s equations – dynamics of the field – Source equations – charge (ρ,J) generates the E&M field – Force equations – nature of E&M force: conservation of (E,p) ...
Electromagnetism Cloze - Science
... Electromagnetism Cloze Fill in the blanks with words from the box. cars fans magnetic ...
... Electromagnetism Cloze Fill in the blanks with words from the box. cars fans magnetic ...
Physics 3323 Intermediate Electricity and Magnetism
... o Purcell: “Electricity and Magnetism, Berkeley Physics Course – vol 2” o Lorrain, Corson & Lorrain: “Electromagnetic Fields and Waves” ...
... o Purcell: “Electricity and Magnetism, Berkeley Physics Course – vol 2” o Lorrain, Corson & Lorrain: “Electromagnetic Fields and Waves” ...
Magnetism
... By the end of the 2nd grade, students should know that Magnets can be used to make some things move without being touched. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that Without touching them, a magnet pulls on all things made of iron and either pushes or pulls on other magnets. Withou ...
... By the end of the 2nd grade, students should know that Magnets can be used to make some things move without being touched. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that Without touching them, a magnet pulls on all things made of iron and either pushes or pulls on other magnets. Withou ...
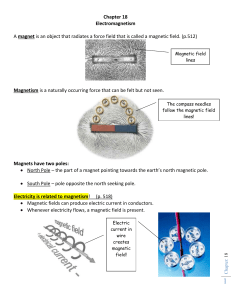
Chapter 18
... Magnetic fields can produce electric current in conductors. Whenever electricity flows, a magnetic field is present. ...
... Magnetic fields can produce electric current in conductors. Whenever electricity flows, a magnetic field is present. ...
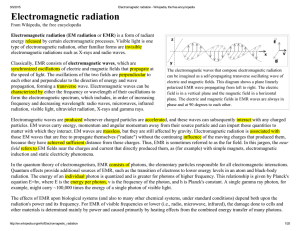
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.