Slide 1
... rarely in the course of human events have so many starting equations been given in so little time ...
... rarely in the course of human events have so many starting equations been given in so little time ...
CLASSICAL FIELD THEORY AND ELECTRODYNAMICS
... with the other components vanishing, t being the time since the origins of the frames K and K 0 overlapped and b referring to the closest distance of approach of the charge, assumed fixed on the x02 axis. 2. An alternative Lagrangian density for the electromagnetic field due to Enrico Fermi is ...
... with the other components vanishing, t being the time since the origins of the frames K and K 0 overlapped and b referring to the closest distance of approach of the charge, assumed fixed on the x02 axis. 2. An alternative Lagrangian density for the electromagnetic field due to Enrico Fermi is ...
EM Guided Notes KEY
... Another common tool that uses this concept is a credit card. The card has a magnetic strip incorporated in it. If the strip is not moving, there is no current. But when the strip moves through a reader, a particular current is formed which carries information about the cardholder. That is how the st ...
... Another common tool that uses this concept is a credit card. The card has a magnetic strip incorporated in it. If the strip is not moving, there is no current. But when the strip moves through a reader, a particular current is formed which carries information about the cardholder. That is how the st ...
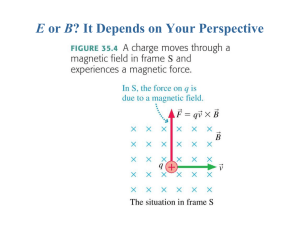
E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective
... Whether a field is seen as “electric” or “magnetic” depends on the motion of the reference frame relative to the sources of the field. ...
... Whether a field is seen as “electric” or “magnetic” depends on the motion of the reference frame relative to the sources of the field. ...
modello di descrizione delle singole attivita`formative
... conductors; electric potential and potential energy; capacitors; energy density of the electric field; D field. Electric current: electromotive force; Ohm, Joule, Kirchhoff’s laws. Magnetism: magnets and magnetic dipoles; Lorenz force; Ampère’s equivalence principle; 1st and 2nd Laplace formula; Amp ...
... conductors; electric potential and potential energy; capacitors; energy density of the electric field; D field. Electric current: electromotive force; Ohm, Joule, Kirchhoff’s laws. Magnetism: magnets and magnetic dipoles; Lorenz force; Ampère’s equivalence principle; 1st and 2nd Laplace formula; Amp ...
PHYS-2100 Introduction to Methods of Theoretical Physics Fall 1998 1) 2)
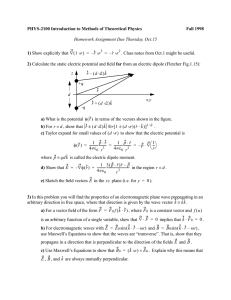
... 3) In this problem you will find the properties of an electromagnetic plane wave propagating in an arbitrary direction in free space, where that direction is given by the wave vector k ≡ kk̂ . a) For a vector field of the form F = F 0 f ( k ⋅ r ) , where F 0 is a constant vector and f ( u ) is an ar ...
... 3) In this problem you will find the properties of an electromagnetic plane wave propagating in an arbitrary direction in free space, where that direction is given by the wave vector k ≡ kk̂ . a) For a vector field of the form F = F 0 f ( k ⋅ r ) , where F 0 is a constant vector and f ( u ) is an ar ...
CHAPTER 3 QUIZ – ELECTROMAGNETISM
... An _______________ is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a _________________. _____________ found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a _________________. __________________ is t ...
... An _______________ is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a _________________. _____________ found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a _________________. __________________ is t ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.