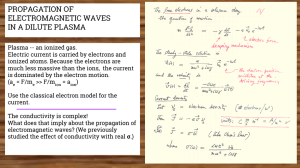
Topics covered in PH111 - Rose
... Electric Field and Coulomb’s Law: Electric charges, electric potential, equipotential lines, lines of force, force on a charge in a electric field. Magnetism: Magnetic field, lines of force and equipotential lines for a magnetic field, Earth as a magnet, force on a moving charge in a magnetic field. ...
... Electric Field and Coulomb’s Law: Electric charges, electric potential, equipotential lines, lines of force, force on a charge in a electric field. Magnetism: Magnetic field, lines of force and equipotential lines for a magnetic field, Earth as a magnet, force on a moving charge in a magnetic field. ...
Physics before the 20th century
... • Space & Time exists independent of matter. In fact, space is independent of time. They provide a rigid background for matter & force ...
... • Space & Time exists independent of matter. In fact, space is independent of time. They provide a rigid background for matter & force ...
EE4302 Fl04 Class Sy..
... EMAG 1 in Bold – EMAG 2 not bolded Section 1 Basic concepts and basic Mathematics History Maxwell’s equations in point and integral form Concept, Nature and sources of vector fields Proof of Divergence and stokes theorems Concept of vector and scalar potential Section II – Static electric and magnet ...
... EMAG 1 in Bold – EMAG 2 not bolded Section 1 Basic concepts and basic Mathematics History Maxwell’s equations in point and integral form Concept, Nature and sources of vector fields Proof of Divergence and stokes theorems Concept of vector and scalar potential Section II – Static electric and magnet ...
Homework Set 1 General homework instructions:
... E3. (a) Define “dielectric”. (b) List 5 examples of dielectric materials. ...
... E3. (a) Define “dielectric”. (b) List 5 examples of dielectric materials. ...
CHAPTER 3 QUIZ – ELECTROMAGNETISM
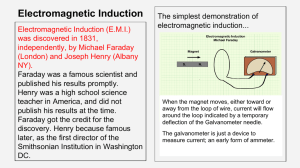
... An ELECTROMAGNET is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a GALVANOMETER. OERSTED found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a SOLENOID. ELECTROMAGNETISM is the relationship between ...
... An ELECTROMAGNET is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a GALVANOMETER. OERSTED found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a SOLENOID. ELECTROMAGNETISM is the relationship between ...
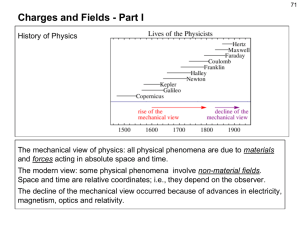
Charges and Fields - Part I
... The mechanical view of physics: all physical phenomena are due to materials and forces acting in absolute space and time. The modern view: some physical phenomena involve non-material fields. Space and time are relative coordinates; i.e., they depend on the observer. The decline of the mechanical vi ...
... The mechanical view of physics: all physical phenomena are due to materials and forces acting in absolute space and time. The modern view: some physical phenomena involve non-material fields. Space and time are relative coordinates; i.e., they depend on the observer. The decline of the mechanical vi ...
Unit 8: Electricity and Magnetism
... Unit Description This unit thoroughly examines the properties of static electricity, electric circuits, magnetic fields, and the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Enduring Understandings All particles of matter contain energy. Magnetic forces are very closely related to electric fo ...
... Unit Description This unit thoroughly examines the properties of static electricity, electric circuits, magnetic fields, and the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Enduring Understandings All particles of matter contain energy. Magnetic forces are very closely related to electric fo ...
Observations of Electrical Phenomena
... Electric Forces Electric field at point P due to single charge ...
... Electric Forces Electric field at point P due to single charge ...
The electromagnetic Spectrum
... • All electromagnetic waves travel at a speed of 3 X 108 m/s (c). • c=f.λ • Electromagnetic waves have a particle nature as well and the energy of the photons E = h. f ...
... • All electromagnetic waves travel at a speed of 3 X 108 m/s (c). • c=f.λ • Electromagnetic waves have a particle nature as well and the energy of the photons E = h. f ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.