Clover Park School District Physics Curriculum Guide 2013
... spectrum differ regarding wavelength, frequency, and energy, and how they are used (e.g., infrared in heat lamps, microwaves for heating food, X-rays for medical imagining.) ...
... spectrum differ regarding wavelength, frequency, and energy, and how they are used (e.g., infrared in heat lamps, microwaves for heating food, X-rays for medical imagining.) ...
Classical electromagnetism
... emission of radiation; then the radiation is calculated from the trajectory as a given source distribution. It is evident that this manner of handling problems in electrodynamics can be of only approximative validity.« As a consequence, we do not yet have physical understanding of those electromecha ...
... emission of radiation; then the radiation is calculated from the trajectory as a given source distribution. It is evident that this manner of handling problems in electrodynamics can be of only approximative validity.« As a consequence, we do not yet have physical understanding of those electromecha ...
Fundamental Interaction www.AssignmentPoint.com Fundamental I
... Einstein abolished action at a distance by theorizing a gravitational field—4D spacetime— that waves while transmitting motion across the universe at light speed. All objects always travel at light speed in 4D spacetime. At zero relative speed, an object is observed to travel none through space, but ...
... Einstein abolished action at a distance by theorizing a gravitational field—4D spacetime— that waves while transmitting motion across the universe at light speed. All objects always travel at light speed in 4D spacetime. At zero relative speed, an object is observed to travel none through space, but ...
Syllabus - The University of Texas at Dallas
... • Students will use Coulomb’s law to describe the effects of static charge on nearby materials • Given a diagram of a “slide wire” generator, students will use Faraday’s and Lenz laws to find the electromotive force generated. Course Description: This brief high-level description is intended to give ...
... • Students will use Coulomb’s law to describe the effects of static charge on nearby materials • Given a diagram of a “slide wire” generator, students will use Faraday’s and Lenz laws to find the electromotive force generated. Course Description: This brief high-level description is intended to give ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
... • A transformer is a device that can change one alternating-current voltage to a different alternating-current voltage. • The voltage across the secondary coil is greater than the voltage across the primary coil in a step-up transformer. • In a step-down transformer, the secondary coil has fewer loo ...
... • A transformer is a device that can change one alternating-current voltage to a different alternating-current voltage. • The voltage across the secondary coil is greater than the voltage across the primary coil in a step-up transformer. • In a step-down transformer, the secondary coil has fewer loo ...
D. Gravitational, Electric, and Magnetic Fields
... energies, potential, and exchange particles • analyse, and solve problems relating to, Newton’s law of universal gravitation and circular motion (e.g., with respect to satellite orbits, black holes, dark matter) • analyse, and solve problems involving, electric force, field strength, potential ener ...
... energies, potential, and exchange particles • analyse, and solve problems relating to, Newton’s law of universal gravitation and circular motion (e.g., with respect to satellite orbits, black holes, dark matter) • analyse, and solve problems involving, electric force, field strength, potential ener ...
Slide 1
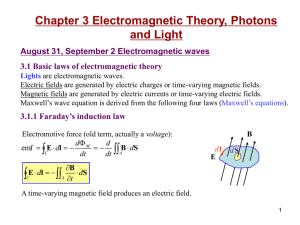
... “The energy in electromagnetic phenomena is the same as mechanical energy. The only question is, ‘Where does it reside?’ In the old theories, it resides in electrified bodies. In our theory, it resides in the electromagnetic field, in the space surrounding the electrified bodies.”—James Maxwell ...
... “The energy in electromagnetic phenomena is the same as mechanical energy. The only question is, ‘Where does it reside?’ In the old theories, it resides in electrified bodies. In our theory, it resides in the electromagnetic field, in the space surrounding the electrified bodies.”—James Maxwell ...
Electromagnetic Radiation and Global Climate change
... are helpful, his theories are only as good as the next round of evidence. • Now we have electromagnetic fields and energy without tiny solid particles. • The Newtonian Universe is most popular and helpful for the everyday understanding of how the world works, but our popular view is a few centuries ...
... are helpful, his theories are only as good as the next round of evidence. • Now we have electromagnetic fields and energy without tiny solid particles. • The Newtonian Universe is most popular and helpful for the everyday understanding of how the world works, but our popular view is a few centuries ...
Week8-figs-ppt
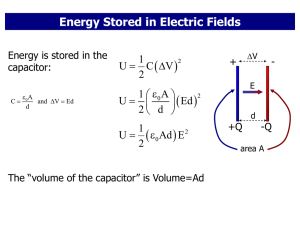
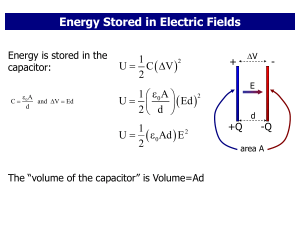
... Parallel plate capacitor Note: it is ASSUMED that charge is equal and opposite on the two plates ...
... Parallel plate capacitor Note: it is ASSUMED that charge is equal and opposite on the two plates ...
LIGHT - University of Virginia
... sphere nearby. Then connect the two spheres by a wire. Now remove the wire, then remove the positive sphere. Question: Do the two original spheres have any charge on them? If so, what sign? ...
... sphere nearby. Then connect the two spheres by a wire. Now remove the wire, then remove the positive sphere. Question: Do the two original spheres have any charge on them? If so, what sign? ...
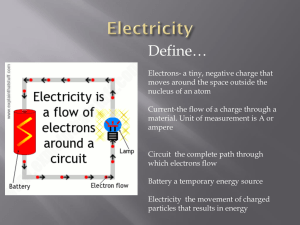
Electricity - WordPress.com
... Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and the flow of electrical current. In addition, electricity permits the cre ...
... Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and the flow of electrical current. In addition, electricity permits the cre ...
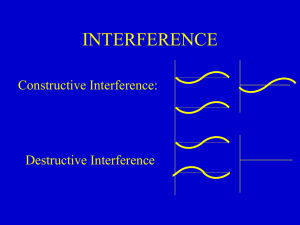
Electromagnetic Waves Test Review
... 2. A(n) (mechanical or electromagnetic) wave can travel through space and matter. 3. Electromagnetic Waves are (longitudinal or transverse) waves. 4. Light is a type of ______________________________ wave. 5. Electromagnetic waves transmit a. charges b. fields c. matter ...
... 2. A(n) (mechanical or electromagnetic) wave can travel through space and matter. 3. Electromagnetic Waves are (longitudinal or transverse) waves. 4. Light is a type of ______________________________ wave. 5. Electromagnetic waves transmit a. charges b. fields c. matter ...
TAP410-0: Preparation for electromagnetic topic
... have to be measured both for permanent magnets and with simple geometries of wires and coils. A Hall probe, especially one that is calibrated, is helpful but search coils can also be used; the latter will need a mains supply that can produce a current of a few amperes and/or a signal generator. Some ...
... have to be measured both for permanent magnets and with simple geometries of wires and coils. A Hall probe, especially one that is calibrated, is helpful but search coils can also be used; the latter will need a mains supply that can produce a current of a few amperes and/or a signal generator. Some ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.