
Walker3_Lecture_Ch30
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
Unit 2: Atoms and their Electrons
... in the same period, therefore they all have the same number of shielding electrons and the effective nuclear charge increases based on the number of protons in the nucleus, therefore the atomic radius decreases from left to right across the period. Potassium is larger than sodium because not only do ...
... in the same period, therefore they all have the same number of shielding electrons and the effective nuclear charge increases based on the number of protons in the nucleus, therefore the atomic radius decreases from left to right across the period. Potassium is larger than sodium because not only do ...
Matter: a Material World
... However, they do move in different “energy states” – some electrons in a given atom have more energy than others These energy states are “quantized”– there are only certain energies that the electrons are allowed to have. This is quantum physics. ...
... However, they do move in different “energy states” – some electrons in a given atom have more energy than others These energy states are “quantized”– there are only certain energies that the electrons are allowed to have. This is quantum physics. ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen Atom Line Spectra Produced when gases are placed under reduced pressure in a tube and a high voltage is applied - colored lines, separated by black regions are produced ...
... Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen Atom Line Spectra Produced when gases are placed under reduced pressure in a tube and a high voltage is applied - colored lines, separated by black regions are produced ...
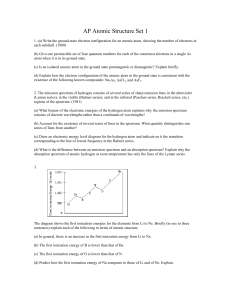
AP Atomic Structure Set 1
... 2. The emission spectrum of hydrogen consists of several series of sharp emission lines in the ultraviolet (Lyman series), in the visible (Balmer series), and in the infrared (Paschen series, Brackett series, etc,) regions of the spectrum. (1981) (a) What feature of the electronic energies of the hy ...
... 2. The emission spectrum of hydrogen consists of several series of sharp emission lines in the ultraviolet (Lyman series), in the visible (Balmer series), and in the infrared (Paschen series, Brackett series, etc,) regions of the spectrum. (1981) (a) What feature of the electronic energies of the hy ...
Arrangement of Electrons In Atoms
... 1. Explain relationship between speed, wavelength, frequency of electromagnetic radiation 2. Discuss the wave-particle duality of light 3. How the photoelectric effect and line-emission spectrum of hydrogen helped develop the atomic model 4. Describe the Bohr model of the atom ...
... 1. Explain relationship between speed, wavelength, frequency of electromagnetic radiation 2. Discuss the wave-particle duality of light 3. How the photoelectric effect and line-emission spectrum of hydrogen helped develop the atomic model 4. Describe the Bohr model of the atom ...
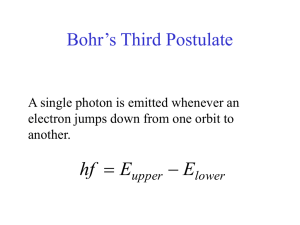
Bohr´s Third Postulate
... don’t all the photoelectrons have the same kinetic energy when they leave the metal’s surface? 4. What property of the emitted electrons depends on the intensity of incident light?What property of the emitted photoelectrons depends on the frequency of incident light? ...
... don’t all the photoelectrons have the same kinetic energy when they leave the metal’s surface? 4. What property of the emitted electrons depends on the intensity of incident light?What property of the emitted photoelectrons depends on the frequency of incident light? ...
e - Purdue Physics - Purdue University
... 3.40 eV - 1.51 eV=1.89 eV of energy, the energy of the red-color photon. •The 656 nm emission line from H has a frequency f=4.57×1014 Hz. A photon of this color has an energy of hf= 3.03×10−19 J (1.89 eV). ...
... 3.40 eV - 1.51 eV=1.89 eV of energy, the energy of the red-color photon. •The 656 nm emission line from H has a frequency f=4.57×1014 Hz. A photon of this color has an energy of hf= 3.03×10−19 J (1.89 eV). ...
Slide 1
... Experiments with "excited" atoms of H produced emission spectra - always a discrete set of lines at certain wavelengths White light dispersed by a prism or diffraction grating: - we see ROYGBIV – a continuous spectrum from 750 nm to 400 nm When a gas-filled tube is charged with current, only certai ...
... Experiments with "excited" atoms of H produced emission spectra - always a discrete set of lines at certain wavelengths White light dispersed by a prism or diffraction grating: - we see ROYGBIV – a continuous spectrum from 750 nm to 400 nm When a gas-filled tube is charged with current, only certai ...
File
... (b) Account for the existence of several series of lines in the spectrum. What quantity distinguishes one series of lines from another? (c) Draw an electronic energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom and indicate on it the transition corresponding to the line of lowest frequency in the Balmer seri ...
... (b) Account for the existence of several series of lines in the spectrum. What quantity distinguishes one series of lines from another? (c) Draw an electronic energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom and indicate on it the transition corresponding to the line of lowest frequency in the Balmer seri ...
Chapter 5: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom I. The
... D. The Bohr Model of the Atom: 1. Bohr s major idea was that the energy states of the atom were _________, and that the amount of energy in the atom was related to the electron s position in the atom. 2. The electrons travel in orbits that are at a fixed distance from the nucleus. ...
... D. The Bohr Model of the Atom: 1. Bohr s major idea was that the energy states of the atom were _________, and that the amount of energy in the atom was related to the electron s position in the atom. 2. The electrons travel in orbits that are at a fixed distance from the nucleus. ...
7.4 The Wave Nature of Matter * 7.5 Quantum Mechanics and the Atom
... position and velocity at the same time. • Since we can not determine the exact location and velocity of an electron at the same time, experimentation has been done over time to identify the most likely places that the electrons exist in an atom. These locations are called orbitals. • Schrödinger's e ...
... position and velocity at the same time. • Since we can not determine the exact location and velocity of an electron at the same time, experimentation has been done over time to identify the most likely places that the electrons exist in an atom. These locations are called orbitals. • Schrödinger's e ...
Presentation
... momentum in terms of kinetic energy). 11. What would be the smallest diameter object you might expect to resolve with a microscope if the wavelength of light being used is 500 nm, the index of refraction is 1.4 and the total angle seen by the lens is 5°? 2 X 10-6 m = 2 µm ...
... momentum in terms of kinetic energy). 11. What would be the smallest diameter object you might expect to resolve with a microscope if the wavelength of light being used is 500 nm, the index of refraction is 1.4 and the total angle seen by the lens is 5°? 2 X 10-6 m = 2 µm ...
Part 1 Electron Arrangement
... • If an electron absorbs energy, it can go to a higher level. • If in a higher energy level, an electron can emit a certain amount of energy to move to a lower level. ...
... • If an electron absorbs energy, it can go to a higher level. • If in a higher energy level, an electron can emit a certain amount of energy to move to a lower level. ...
Chapter7 - FSU Chemistry
... (b) How many liters of CO2 (at 25 oC and 1 atm, R = 0.0821 atm.L/mol.K) are formed when 1 kg of octane is burned? How much work is done by the expanding CO2 as 1 kg of octane is burned (again, at 25 oC and 1 atm). (Hint, 1 J = 9.87.10-3 atm.L). What is !E for the reaction? (Hint, the definition of H ...
... (b) How many liters of CO2 (at 25 oC and 1 atm, R = 0.0821 atm.L/mol.K) are formed when 1 kg of octane is burned? How much work is done by the expanding CO2 as 1 kg of octane is burned (again, at 25 oC and 1 atm). (Hint, 1 J = 9.87.10-3 atm.L). What is !E for the reaction? (Hint, the definition of H ...
LASER IN Medicine
... to store energy, thereby allowing the production of great numbers of stimulated photons. To do this, we pump atoms into the metastable level at a rate that exceeds the rate at which they leave. A large number of atoms are therefore excited to and held in this level, leaving an almost empty level bel ...
... to store energy, thereby allowing the production of great numbers of stimulated photons. To do this, we pump atoms into the metastable level at a rate that exceeds the rate at which they leave. A large number of atoms are therefore excited to and held in this level, leaving an almost empty level bel ...
Chemistry 330 Chapter 11
... Energy of the H atom is quantized Electron is promoted from a low to high energy level by the absorption of a photon The amount of energy absorbed and emitted by the atom is quantized Only orbits of certain angular momenta are allowed ...
... Energy of the H atom is quantized Electron is promoted from a low to high energy level by the absorption of a photon The amount of energy absorbed and emitted by the atom is quantized Only orbits of certain angular momenta are allowed ...
The Spectrophotometer
... the left zero using the left knob. The needle may drift for 15 minutes or so, and minor adjustments will need to be made during this time. This is called "zeroing" the light output. Zeroing the light output is a means of maintaining equal operating conditions on a day-to-day basis. ...
... the left zero using the left knob. The needle may drift for 15 minutes or so, and minor adjustments will need to be made during this time. This is called "zeroing" the light output. Zeroing the light output is a means of maintaining equal operating conditions on a day-to-day basis. ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.





















![3 — Blackbody Radiation [Revision : 1.5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005908504_1-5005bdffc2e5f9c6e0687c31f49c7e9d-300x300.png)