Lecture 5
... Hund’s rules (i) Of the terms arising from equivalent electrons, those with the highest multiplicity lie the lowest in energy. (ii) Of these, the lowest is that with the highest value of L. Lande’s interval rule For less than half-filled orbitals, smaller J has lower energy. For more than half-fill ...
... Hund’s rules (i) Of the terms arising from equivalent electrons, those with the highest multiplicity lie the lowest in energy. (ii) Of these, the lowest is that with the highest value of L. Lande’s interval rule For less than half-filled orbitals, smaller J has lower energy. For more than half-fill ...
Particle-Wave Duality
... While we use similar notation for particles and for true waves, various quantities are defined differently. Do not make the mistake of using optical definitions for particles. ...
... While we use similar notation for particles and for true waves, various quantities are defined differently. Do not make the mistake of using optical definitions for particles. ...
Bohr Model of the Atom
... Electrons from states with ni > 2 can return, initially, to the first-excited state (nf = 2), emitting one photon and then to the ground state emitting a second photon, with Eph = 10.2 eV, which is part of the Lyman series. Photons from transitions to the first-excited, (n = 2) state of the hydrogen ...
... Electrons from states with ni > 2 can return, initially, to the first-excited state (nf = 2), emitting one photon and then to the ground state emitting a second photon, with Eph = 10.2 eV, which is part of the Lyman series. Photons from transitions to the first-excited, (n = 2) state of the hydrogen ...
Structure of matter.
... The solution of the Schrödinger equation for the electron in the hydrogen atom leads to the values of the energies of the orbital electron. The solution of the Schrödinger equation often leads to numerical coefficients which determine the possible values of energy. These numerical coefficients a ...
... The solution of the Schrödinger equation for the electron in the hydrogen atom leads to the values of the energies of the orbital electron. The solution of the Schrödinger equation often leads to numerical coefficients which determine the possible values of energy. These numerical coefficients a ...
3.2 Bohr`s Model of the Atom
... The movement of an electron from one energy level to another is called a transition The ground state is the lowest energy state for an atom When an atom gains energy it moves into an excited state The transition from a lower energy level to a higher energy level requires a quantized amount of energy ...
... The movement of an electron from one energy level to another is called a transition The ground state is the lowest energy state for an atom When an atom gains energy it moves into an excited state The transition from a lower energy level to a higher energy level requires a quantized amount of energy ...
PPT - Tensors for Tots
... wavelength and frequency of the emissions of a black body for a certain temperature. According to Planck's law an oscillator with a frequency v can absorb only multiples of hº and it needs a minimal energy hº in order to be excited at all. ...
... wavelength and frequency of the emissions of a black body for a certain temperature. According to Planck's law an oscillator with a frequency v can absorb only multiples of hº and it needs a minimal energy hº in order to be excited at all. ...
File
... Bohr’s theory • the hydrogen atom’s electron exists only in certain definite energy levels • the electron changes energy levels when a photon is absorbed or emitted • the energy of the photon equals the difference between the two energy levels ...
... Bohr’s theory • the hydrogen atom’s electron exists only in certain definite energy levels • the electron changes energy levels when a photon is absorbed or emitted • the energy of the photon equals the difference between the two energy levels ...
Quantum theory or radiation
... Imagine being hit by 1020 marbles every second. This would be one of the consequences of life if the Planck constant was large – say 1. The electron volt is a useful unit when measuring the energy of a quantum of light emitted from atoms but sometimes we need to deal with larger quantities of energy ...
... Imagine being hit by 1020 marbles every second. This would be one of the consequences of life if the Planck constant was large – say 1. The electron volt is a useful unit when measuring the energy of a quantum of light emitted from atoms but sometimes we need to deal with larger quantities of energy ...
Steve Hansen`s second test - Kwantlen Polytechnic University
... The energy required to dissociate H2 molecules into H atoms is 432 kJ/mol. If the dissociation of an H2 molecule was accompolished by the absorption of a single photon with exactly the energy required, what would be its wavelength (in nanometers)? (4) ...
... The energy required to dissociate H2 molecules into H atoms is 432 kJ/mol. If the dissociation of an H2 molecule was accompolished by the absorption of a single photon with exactly the energy required, what would be its wavelength (in nanometers)? (4) ...
Handout
... wave function tells you the probability distribution of where you might find the particle, ψ ∗ (x)ψ(x) = |ψ(x)|2 R= P (x). Since the sum of all probabilities must be one, the amplitude of the wave is fixed, |ψ(x)|2 = 1. ...
... wave function tells you the probability distribution of where you might find the particle, ψ ∗ (x)ψ(x) = |ψ(x)|2 R= P (x). Since the sum of all probabilities must be one, the amplitude of the wave is fixed, |ψ(x)|2 = 1. ...
NicholasBarbutoPoster - Physics
... for the precise control of light both within and outside of the photonic crystal. In particular the emission direction, spectrum, and intensity can be affected by the band structure. We will study photoluminescence properties in one-dimensional polymeric photonic crystals containing photoluminescent ...
... for the precise control of light both within and outside of the photonic crystal. In particular the emission direction, spectrum, and intensity can be affected by the band structure. We will study photoluminescence properties in one-dimensional polymeric photonic crystals containing photoluminescent ...
綜合化學 - 中原大學
... 14. There are five resonance structures of phenanthrene, one of which is shown. Draw the other four and predict which of its carbon-carbon bonds is shortest. ...
... 14. There are five resonance structures of phenanthrene, one of which is shown. Draw the other four and predict which of its carbon-carbon bonds is shortest. ...
Photosynthesis Pt 1 Light
... When Light Interacts with matter • 1. Light passes through the matter (transparent) • 2. Light is reflected (resulting in the colors you see) • 3. Light is absorbed (energy is released as heat or used to excite electrons to make chemical bonds!) ...
... When Light Interacts with matter • 1. Light passes through the matter (transparent) • 2. Light is reflected (resulting in the colors you see) • 3. Light is absorbed (energy is released as heat or used to excite electrons to make chemical bonds!) ...
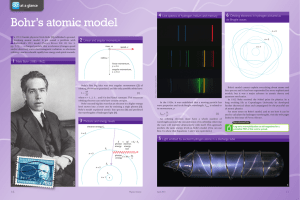
Bohr`s atomic model
... wavelengths around the circumference of its orbit (6), otherwise the wave will interfere destructively with itself. This approach predicts the same energy levels as Bohr’s model. (You can use Box 2 to show that Equations 1 and 2 are equivalent.) ...
... wavelengths around the circumference of its orbit (6), otherwise the wave will interfere destructively with itself. This approach predicts the same energy levels as Bohr’s model. (You can use Box 2 to show that Equations 1 and 2 are equivalent.) ...
Spectra of Atoms
... How to explain these numerical series? Before we tackle that mystery, consider another: Mystery #5: Why don’t the electrons in an atom spiral into the nucleus? In classical electrodynamics, an accelerated charged particle ...
... How to explain these numerical series? Before we tackle that mystery, consider another: Mystery #5: Why don’t the electrons in an atom spiral into the nucleus? In classical electrodynamics, an accelerated charged particle ...
EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES
... K-lines for elements with atomic number (Z) between 9 and 35, L-lines for elements with Z less than 83 and all M lines. This technique is highly sensitive to the detection of low elements such as Be, B, C, N, O and F, but the measurement error is high. Quantitative analysis requires making correctio ...
... K-lines for elements with atomic number (Z) between 9 and 35, L-lines for elements with Z less than 83 and all M lines. This technique is highly sensitive to the detection of low elements such as Be, B, C, N, O and F, but the measurement error is high. Quantitative analysis requires making correctio ...
Skill Assessment Sheet Modern Atomic Theory (Quantum Mechanics)
... I am approaching proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I could finish with some help) I can consistently demonstrate proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I can do this and will be able to do it later) I can consistently exceed key concepts, processes & skills. Exceeds the standard ( I can do more ...
... I am approaching proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I could finish with some help) I can consistently demonstrate proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I can do this and will be able to do it later) I can consistently exceed key concepts, processes & skills. Exceeds the standard ( I can do more ...
4/10/2006 Chapter 37 Lasers, a Model Atom and Zero Point Energy
... Chapter 37 Lasers, a Model Atom and Zero Point Energy We have discussed de Broglie’s (correct) hypothesis that objects have a wave nature when they are traveling. In the 1920’s this wave model for objects in motion was put onto a solid theoretical foundation with the development of the Schrodinger W ...
... Chapter 37 Lasers, a Model Atom and Zero Point Energy We have discussed de Broglie’s (correct) hypothesis that objects have a wave nature when they are traveling. In the 1920’s this wave model for objects in motion was put onto a solid theoretical foundation with the development of the Schrodinger W ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.