Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 076101 - APS Link Manager
... merges the computational lens and holographic approaches. Tuning to atomic absorption resonances is a widely used synchrotron radiation method to obtain element specificity, and this method has also been used in conjunction with coherent scattering to obtain nanoscale images [12–15]. Here we use x-r ...
... merges the computational lens and holographic approaches. Tuning to atomic absorption resonances is a widely used synchrotron radiation method to obtain element specificity, and this method has also been used in conjunction with coherent scattering to obtain nanoscale images [12–15]. Here we use x-r ...
Diffraction grating has periodic structure that splits and diffracts light
... be used to demonstrate the effect by reflecting sunlight off them onto a white wall. (see ). This is a side effect of their manufacture, as one surface of a CD has many small pits in the plastic, arranged in a spiral; that surface has a thin layer of metal applied to make the pits more visible. The ...
... be used to demonstrate the effect by reflecting sunlight off them onto a white wall. (see ). This is a side effect of their manufacture, as one surface of a CD has many small pits in the plastic, arranged in a spiral; that surface has a thin layer of metal applied to make the pits more visible. The ...
Ch 5 Electrons in Atoms
... a. Describe how isotopes of the same element differ from one another b. Do isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties? c. Explain how the number of neutrons affect the mass of an atom 8. Chemical properties of an atom are mostly determined by overall charge and total number of po ...
... a. Describe how isotopes of the same element differ from one another b. Do isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties? c. Explain how the number of neutrons affect the mass of an atom 8. Chemical properties of an atom are mostly determined by overall charge and total number of po ...
Introductory Experiments in the Physics Advanced Laboratory
... There are six introductory experiments in the physics advanced lab. These are: The Speed of Light This involves reflecting a beam of light off a rotating mirror to a distant mirror, which reflects the light back to the rotating mirror. Because this mirror has rotated, it reflects the returning light ...
... There are six introductory experiments in the physics advanced lab. These are: The Speed of Light This involves reflecting a beam of light off a rotating mirror to a distant mirror, which reflects the light back to the rotating mirror. Because this mirror has rotated, it reflects the returning light ...
3.3 Why do atoms radiate light?
... • This explains too, why atoms can be stable, although they have a rotational momentum (in the classical description they would always radiate light and thus be destroyed). This classical explanation results from the wrong picture, that the electron is moving through the orbital, leading to a steady ...
... • This explains too, why atoms can be stable, although they have a rotational momentum (in the classical description they would always radiate light and thus be destroyed). This classical explanation results from the wrong picture, that the electron is moving through the orbital, leading to a steady ...
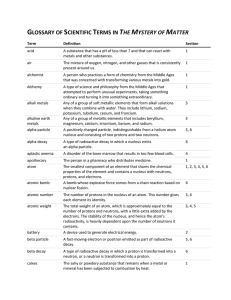
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... A table in which the chemical elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Elements with similar properties are arranged in the same column (called a group), and elements with the same number of electron shells are arranged in the same row (called a period). The substance thought by e ...
... A table in which the chemical elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Elements with similar properties are arranged in the same column (called a group), and elements with the same number of electron shells are arranged in the same row (called a period). The substance thought by e ...
Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Topic 6, Worksheet 2
... electrons but the current only depends on the number of electrons emitted per second not their speed. ...
... electrons but the current only depends on the number of electrons emitted per second not their speed. ...
two-slit interference,one photon at a time
... Recreate Young's two-slit measurement of the wavelength of laser light,and compare and contrast with single-slit interference.You can see obviously the interference pattern by eyes or in data. At the far end of the U-channel is a moveable single slit, the detector slit. It is attached to a translati ...
... Recreate Young's two-slit measurement of the wavelength of laser light,and compare and contrast with single-slit interference.You can see obviously the interference pattern by eyes or in data. At the far end of the U-channel is a moveable single slit, the detector slit. It is attached to a translati ...
Electrons in Atoms - Duplin County Schools
... Although the speed of all electromagnetic waves is the same, waves may have different wavelengths and frequencies ...
... Although the speed of all electromagnetic waves is the same, waves may have different wavelengths and frequencies ...
Energy levels and atomic structures lectures
... The Danish physicist Niels Bohr, who first presented this model of the atom, based it on ...
... The Danish physicist Niels Bohr, who first presented this model of the atom, based it on ...
Midterm Review.ppt - Chemistry R: 4(AE)
... Table have similar chemical properties. This similarity is most closely related to the atoms‘ 1. number of principal energy levels 2. number of valence electrons 3. atomic numbers 4. atomic masses ...
... Table have similar chemical properties. This similarity is most closely related to the atoms‘ 1. number of principal energy levels 2. number of valence electrons 3. atomic numbers 4. atomic masses ...
Atomic Physics - Moodle-Arquivo
... A gas at low pressure has a voltage applied to it A gas emits light characteristic of the gas When the emitted light is analyzed with a spectrometer, a series of discrete bright lines is observed ...
... A gas at low pressure has a voltage applied to it A gas emits light characteristic of the gas When the emitted light is analyzed with a spectrometer, a series of discrete bright lines is observed ...
1 pt
... is impossible to find both the speed and position of an electron simultaneously. Name the scientist and idea. ...
... is impossible to find both the speed and position of an electron simultaneously. Name the scientist and idea. ...
Chapter 1
... The effect of this notion? I very much fear ’Twill make doubtful all things that were formerly clear. Till soon the cat doctors will say in reports, “We’ve just flipped a coin and we’ve learned he’s a corpse.” ...
... The effect of this notion? I very much fear ’Twill make doubtful all things that were formerly clear. Till soon the cat doctors will say in reports, “We’ve just flipped a coin and we’ve learned he’s a corpse.” ...
Electron Configuration - Warren County Public Schools
... specific frequencies (and therefore wavelengths) that result when the light emitted from an element. • This spectra can be observed when the element is in gaseous form and has a current running through it or when it is being burned. ...
... specific frequencies (and therefore wavelengths) that result when the light emitted from an element. • This spectra can be observed when the element is in gaseous form and has a current running through it or when it is being burned. ...
Light and Quantized Energy
... Planck’s equation _________________, demonstrates mathematically that the energy of a quantum is related to the _______________ of the emitted radiation. Einstein went further by explaining that, in addition to its wavelike characteristics, a beam of light can be thought of as a stream of __________ ...
... Planck’s equation _________________, demonstrates mathematically that the energy of a quantum is related to the _______________ of the emitted radiation. Einstein went further by explaining that, in addition to its wavelike characteristics, a beam of light can be thought of as a stream of __________ ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.