Honors Chemistry Midterm Review 2008
... symbols and numbers e. Newlands: -law of octaves 1864; He arranged all the elements known at the time into a table in order of relative atomic mass. When he did this, he found that each element was similar to the element eight places further on. For example, starting at Li, Be is the second element, ...
... symbols and numbers e. Newlands: -law of octaves 1864; He arranged all the elements known at the time into a table in order of relative atomic mass. When he did this, he found that each element was similar to the element eight places further on. For example, starting at Li, Be is the second element, ...
Laser and its applications
... In 1960, T.H.Maiman built the first laser device (ruby laser). Within months of the arrival of Maiman’s ruby laser, which emitted deep red light at a wavelength of 694.3 nm, A. Javan and associates developed the first gas laser (HeNe laser), which emitted light in both the infrared (at 1.15mm) and ...
... In 1960, T.H.Maiman built the first laser device (ruby laser). Within months of the arrival of Maiman’s ruby laser, which emitted deep red light at a wavelength of 694.3 nm, A. Javan and associates developed the first gas laser (HeNe laser), which emitted light in both the infrared (at 1.15mm) and ...
2011 University of Maryland SPESIF Revised
... availability. 5. A high-vacuum system able to evacuate the chamber from 10-6to 10–11Torr (nominally about 7.5 ×10-7Torr) is utilized. This is well within the state of the art, utilizing multi-stage pumping, and is a convenient choice. Utilized to essentially eliminate GB scattering. 6. A cooling sys ...
... availability. 5. A high-vacuum system able to evacuate the chamber from 10-6to 10–11Torr (nominally about 7.5 ×10-7Torr) is utilized. This is well within the state of the art, utilizing multi-stage pumping, and is a convenient choice. Utilized to essentially eliminate GB scattering. 6. A cooling sys ...
Name
... Fission splits a large nucleus into smaller nuclei. Fusion combines two small nuclei into one larger one. 41. Briefly describe what happens that allows you to see colors in the flame tests and the gas tubes. When energy is added to an atom, an electron jumps to a higher energy level (excited state). ...
... Fission splits a large nucleus into smaller nuclei. Fusion combines two small nuclei into one larger one. 41. Briefly describe what happens that allows you to see colors in the flame tests and the gas tubes. When energy is added to an atom, an electron jumps to a higher energy level (excited state). ...
Chapter 3
... The inverse square law: The irradiance from a point source is proportional to 1/r2. Total power I·4pr2 = constant, I E0 2 E01/r. ...
... The inverse square law: The irradiance from a point source is proportional to 1/r2. Total power I·4pr2 = constant, I E0 2 E01/r. ...
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
... Determine the wavelength of light emitted when a hydrogen atom makes a transition from the n = 6 to the n = 2 energy level according to the Bohr ...
... Determine the wavelength of light emitted when a hydrogen atom makes a transition from the n = 6 to the n = 2 energy level according to the Bohr ...
File
... element: a substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. compound: a substance made up of atoms of two ore more different elements joined by chemical bonds. atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. (The atomic number is the same f ...
... element: a substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. compound: a substance made up of atoms of two ore more different elements joined by chemical bonds. atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. (The atomic number is the same f ...
All That Matters - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... constant, but it can change from one form to another. During a chemical reaction, the amount of matter that is present at the beginning of the reaction should be that same as the amount found at the end of the reaction, and the amount of energy should remain constant throughout the reaction. ...
... constant, but it can change from one form to another. During a chemical reaction, the amount of matter that is present at the beginning of the reaction should be that same as the amount found at the end of the reaction, and the amount of energy should remain constant throughout the reaction. ...
At what intensity is the laser set?
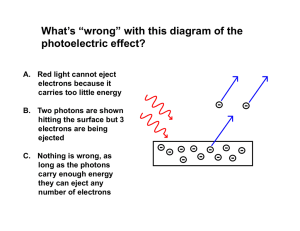
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
Atomic Theory (Or a quick Chemistry Review)
... Atomic Theory Q: What does science study? A: The natural world, the physical universe Q: What are the components of the P.U? A: matter, energy, forces ...
... Atomic Theory Q: What does science study? A: The natural world, the physical universe Q: What are the components of the P.U? A: matter, energy, forces ...
Electrons in Atoms
... Begin filling orbitals at the lowest energy level (Aufbau principle) Continue filling, applying Hund’s rule ...
... Begin filling orbitals at the lowest energy level (Aufbau principle) Continue filling, applying Hund’s rule ...
chapter 7: atomic structure and periodicity
... 4) The energy of the photons emitted or absorbed is equal to the difference between the 2 orbit energies. This explains why only certain lines of specific wavelengths appear on a line (or emission) spectrum. ...
... 4) The energy of the photons emitted or absorbed is equal to the difference between the 2 orbit energies. This explains why only certain lines of specific wavelengths appear on a line (or emission) spectrum. ...
Fall Exam 3 - Chemistry - University of Kentucky
... Print your name starting at the first space, LAST NAME first, then a space, followed by your FIRST NAME, then another space, followed by your MIDDLE INITIAL. Fill in the correct circles below your printed name corresponding to the letters of your name; for the spaces, fill in the top blank circle. ...
... Print your name starting at the first space, LAST NAME first, then a space, followed by your FIRST NAME, then another space, followed by your MIDDLE INITIAL. Fill in the correct circles below your printed name corresponding to the letters of your name; for the spaces, fill in the top blank circle. ...
SOL PS3 Structure of the Atom by GA Tech
... in the Hydrogen Atom The atom will remain in the excited state for a short time before emitting a photon and returning to a lower stationary state. In equilibrium, all hydrogen atoms exist in n = 1. ...
... in the Hydrogen Atom The atom will remain in the excited state for a short time before emitting a photon and returning to a lower stationary state. In equilibrium, all hydrogen atoms exist in n = 1. ...
Periodic Table
... and can often be used to replace one another in compounds to produce new compounds with slightly different properties Horizontal rows are called periods ...
... and can often be used to replace one another in compounds to produce new compounds with slightly different properties Horizontal rows are called periods ...
Electromagnetically induced transparency
... The concept of EIT was first given by Harris et al in 1990. When a strong coupling laser field is used to drive a resonant transition in a three-level atomic system, the absorption of a weak probe laser field can be reduced or eliminated provided the two resonant transitions are coherently coupled t ...
... The concept of EIT was first given by Harris et al in 1990. When a strong coupling laser field is used to drive a resonant transition in a three-level atomic system, the absorption of a weak probe laser field can be reduced or eliminated provided the two resonant transitions are coherently coupled t ...
electron
... energies, quantization should be imperceptible. • When velocities are much smaller than the speed of light, relativistic effects are imperceptible. • The laws of quantum physics and relativity simply reduce to the classical theory at “everyday” speeds, energies, sizes, etc. • In other words, just ...
... energies, quantization should be imperceptible. • When velocities are much smaller than the speed of light, relativistic effects are imperceptible. • The laws of quantum physics and relativity simply reduce to the classical theory at “everyday” speeds, energies, sizes, etc. • In other words, just ...
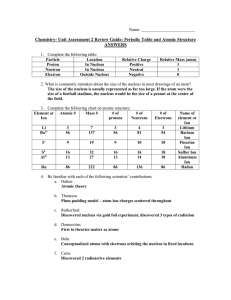
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what valence electrons are and how to know how many an element from the representative group has. Valence electrons are an a ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what valence electrons are and how to know how many an element from the representative group has. Valence electrons are an a ...
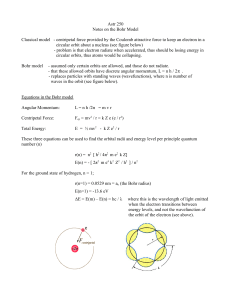
Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model
... r(n) = n2 [ h2 / 4π2 m e2 k Z] E(n) = - [ 2π2 m e4 k2 Z2 / h2 ] / n2 For the ground state of hydrogen, n = 1; r(n=1) = 0.0529 nm = ao (the Bohr radius) E(n=1) = -13.6 eV ΔE = E(m) – E(n) = hc / λ ...
... r(n) = n2 [ h2 / 4π2 m e2 k Z] E(n) = - [ 2π2 m e4 k2 Z2 / h2 ] / n2 For the ground state of hydrogen, n = 1; r(n=1) = 0.0529 nm = ao (the Bohr radius) E(n=1) = -13.6 eV ΔE = E(m) – E(n) = hc / λ ...
Review 2nd KEY
... c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. a px orbital. d. a combination of an s and a px orbital. ____ 3. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. energy must be released. b. energy must be absorbed. c. radiation must be emitted. d. the electron must make ...
... c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. a px orbital. d. a combination of an s and a px orbital. ____ 3. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. energy must be released. b. energy must be absorbed. c. radiation must be emitted. d. the electron must make ...
Discussion and Applications of Single and Entangled Photon Sources
... transmittance. In order to do this you would need to know the desired distance, power and wavelength of the light source to find how many photons per meter are produced. This is a good approximation for single photon sources, however this method does not produce true single, antibunched photons. ...
... transmittance. In order to do this you would need to know the desired distance, power and wavelength of the light source to find how many photons per meter are produced. This is a good approximation for single photon sources, however this method does not produce true single, antibunched photons. ...
Chapter 9a Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... We can say that light is wave when it is involved in its propagation only like interference and diffraction. This means that light interacts with itself. The light shows photon property when it interact with other materials. Let’s see another example of photon. ...
... We can say that light is wave when it is involved in its propagation only like interference and diffraction. This means that light interacts with itself. The light shows photon property when it interact with other materials. Let’s see another example of photon. ...
Quantum Imaging using Non-linear Optics 1 Introduction and Motivation December 15, 2011
... the source S enters the chamber opening and is scattered from the object, yielding a single sequence of photoevents from the integrating sphere C. The other beam is transmitted through a conventional optical system and detected using a single-photon-sensitive scanning (or array) detector D. The info ...
... the source S enters the chamber opening and is scattered from the object, yielding a single sequence of photoevents from the integrating sphere C. The other beam is transmitted through a conventional optical system and detected using a single-photon-sensitive scanning (or array) detector D. The info ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.