Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
Chem 1151
... Many emission lines were observed when the hydrogen atom was excited. Which equation corresponds to the process in which n = 1 = quantum number of the initial state and m = ∞ = quantum number of the final state? equation **A H H+ + eB H+ + e- H C H (1s1) H(3s1) D H+ H2+ + eWhen you go from l ...
... Many emission lines were observed when the hydrogen atom was excited. Which equation corresponds to the process in which n = 1 = quantum number of the initial state and m = ∞ = quantum number of the final state? equation **A H H+ + eB H+ + e- H C H (1s1) H(3s1) D H+ H2+ + eWhen you go from l ...
Chapter 7_01042016
... several exceptions to this rule in each period, which consider the change in electron repulsions as a function of electron configuration. • When we go down a group, electron affinity should become more positive (less energy released) since the electron is added at increasing distances from the nucle ...
... several exceptions to this rule in each period, which consider the change in electron repulsions as a function of electron configuration. • When we go down a group, electron affinity should become more positive (less energy released) since the electron is added at increasing distances from the nucle ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum Web Quest
... Directions: Use the following web sites to answer the questions below. Make sure your responses are in complete sentences. 1) Use the following web site http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hframe.html to choose a specific wavelength of visible light, a radio wave, and an x-ray to fill in the ...
... Directions: Use the following web sites to answer the questions below. Make sure your responses are in complete sentences. 1) Use the following web site http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hframe.html to choose a specific wavelength of visible light, a radio wave, and an x-ray to fill in the ...
Sep 2
... will have the same proportions of elements Two different samples of CO2: Sample 1: 25.6 g O; 9.6 g C Sample 2: 21.6 g O; 8.10 g C ...
... will have the same proportions of elements Two different samples of CO2: Sample 1: 25.6 g O; 9.6 g C Sample 2: 21.6 g O; 8.10 g C ...
28_lecture_acl
... §28.1 Wave-Particle Duality Light is both wave-like (interference & diffraction) and particle-like (photoelectric effect). Double slit experiment: allow only 1 photon at a time, but: • still makes interference pattern! • can’t determine which slit it will pass thru • can’t determine where it will h ...
... §28.1 Wave-Particle Duality Light is both wave-like (interference & diffraction) and particle-like (photoelectric effect). Double slit experiment: allow only 1 photon at a time, but: • still makes interference pattern! • can’t determine which slit it will pass thru • can’t determine where it will h ...
Lecture 5: Spectroscopy and Photochemistry I
... • Spectroscopy of atmospheric molecules is used to detect them in situ – OH is detected via its electronic transition at 310 nm – NH3 is detected via its fundamental vibrational transition at ...
... • Spectroscopy of atmospheric molecules is used to detect them in situ – OH is detected via its electronic transition at 310 nm – NH3 is detected via its fundamental vibrational transition at ...
CHAPTER 5
... What is the energy of a photon of green light with wavelength 5200 Å? What is the energy of 1.00 mol of these photons? ...
... What is the energy of a photon of green light with wavelength 5200 Å? What is the energy of 1.00 mol of these photons? ...
Chemistry Electrons in Atoms Outline
... 5. diffraction patterns produced by electrons passing through a substance are similar to diffraction patterns of light passing through a small hole B. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle 1. we cannot tell the position and the momentum of an electron simultaneously (at the same time) 2. by observing an ...
... 5. diffraction patterns produced by electrons passing through a substance are similar to diffraction patterns of light passing through a small hole B. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle 1. we cannot tell the position and the momentum of an electron simultaneously (at the same time) 2. by observing an ...
Lect 23 Presentation
... If the electron in the hydrogen atom was 207 times heavier (a muon), the Bohr radius would be 1) 207 Times Larger h 2 1 Bohr Radius ( ) 2 mke2 2) Same Size 3) 207 Times Smaller This “m” is electron mass, not proton mass! ...
... If the electron in the hydrogen atom was 207 times heavier (a muon), the Bohr radius would be 1) 207 Times Larger h 2 1 Bohr Radius ( ) 2 mke2 2) Same Size 3) 207 Times Smaller This “m” is electron mass, not proton mass! ...
Physics 200 Class #1 Outline
... Light rays reflecting off the different faces of the crystal can interfere with each other. This is similar to thin film interference we spoke about. In the diagram below, we're looking at the path length difference between rays bouncing off the top layer of a crystal and the second layer. The impor ...
... Light rays reflecting off the different faces of the crystal can interfere with each other. This is similar to thin film interference we spoke about. In the diagram below, we're looking at the path length difference between rays bouncing off the top layer of a crystal and the second layer. The impor ...
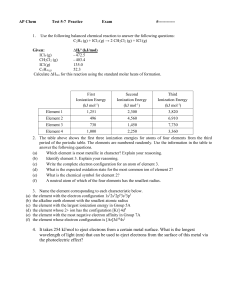
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A the element whose electron configuration is [Ar]3d104s2 ...
... the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A the element whose electron configuration is [Ar]3d104s2 ...
T1_The_Origins_Of_Quantum_Mechanics
... known from solar spectrum lines: (1) all hydrogen atoms must be identical, and (2) they absorb and emit light only at specific frequencies (corresponding to specific energies, Eg = hf). His major insight was that different electron orbits correspond to different electron total energy. The atom would ...
... known from solar spectrum lines: (1) all hydrogen atoms must be identical, and (2) they absorb and emit light only at specific frequencies (corresponding to specific energies, Eg = hf). His major insight was that different electron orbits correspond to different electron total energy. The atom would ...
Physics 11 Laboratory
... where Planck’s constant h = 6.626x10-34Js and the speed of light c = 2.998x108m/s. These two equations taken together imply that excited atoms should emit light only at discrete wavelengths given by ...
... where Planck’s constant h = 6.626x10-34Js and the speed of light c = 2.998x108m/s. These two equations taken together imply that excited atoms should emit light only at discrete wavelengths given by ...
PHYS-201 LAB-03 Bohr`s Model and Emission Spectra of Hydrogen
... mechanics, will lose energy by radiation and would spiral down and eventually fall into the nucleus. Bohr knew this but, since atoms are stable, he also recognized that it was ...
... mechanics, will lose energy by radiation and would spiral down and eventually fall into the nucleus. Bohr knew this but, since atoms are stable, he also recognized that it was ...
Chem20u2(5.2) - Mr. Searcy Chemistry 20
... Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the modern view of electrons in atoms. 5. Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom’s energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orbitals. II. The following questions will help to cover these objectives as you read through the section. Briefly answer each questio ...
... Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the modern view of electrons in atoms. 5. Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom’s energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orbitals. II. The following questions will help to cover these objectives as you read through the section. Briefly answer each questio ...
Problems and Questions on Lecture 2 Useful equations and
... What is the frequency of the emitted photon if an electron makes a transition from the n = 3 level to the n = 2 level? What is the wavelength of the photon for the same transition? Would the emitted photon be visible? ...
... What is the frequency of the emitted photon if an electron makes a transition from the n = 3 level to the n = 2 level? What is the wavelength of the photon for the same transition? Would the emitted photon be visible? ...
File
... • Homogenous Mixture-a mixture with a composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or ...
... • Homogenous Mixture-a mixture with a composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or ...
worksheet 7b answers - Iowa State University
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
Science Olympiad
... (A) The outermost two electrons are paired in the same atomic orbital. (B) The 4f shell is completely full. (C) Only one of the 55 electrons is involved in most interactions of Cs with other atoms. (D) The 4f shell is only partially filled. (E) Cesium will react to share one electron to fill the 6s ...
... (A) The outermost two electrons are paired in the same atomic orbital. (B) The 4f shell is completely full. (C) Only one of the 55 electrons is involved in most interactions of Cs with other atoms. (D) The 4f shell is only partially filled. (E) Cesium will react to share one electron to fill the 6s ...
Answer
... values from 0 to n − 1. In this case n = 2, so the allowed values of the angular momentum quantum number are 0 and 1. Each allowed value of the angular momentum quantum number labels a subshell. Within a given subshell (label l) there are 2l + 1 allowed energy states (orbitals) each labeled by a dif ...
... values from 0 to n − 1. In this case n = 2, so the allowed values of the angular momentum quantum number are 0 and 1. Each allowed value of the angular momentum quantum number labels a subshell. Within a given subshell (label l) there are 2l + 1 allowed energy states (orbitals) each labeled by a dif ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.