Study Questions on Cardiovascular System
... 18. Blood pressure is measured as two numbers, which represent _____________ and ______________________ pressure in the _________. Blood pressure increases/decreases (circle one) as the vessels get further away from the heart. (sec 8.3) 19. Describe how blood pressure is measured using a sphygmomano ...
... 18. Blood pressure is measured as two numbers, which represent _____________ and ______________________ pressure in the _________. Blood pressure increases/decreases (circle one) as the vessels get further away from the heart. (sec 8.3) 19. Describe how blood pressure is measured using a sphygmomano ...
Heart and Circulation
... b. Very muscular walls, especially on the left – why? c. Inner walls have muscle folds called trabeculae carne. Some of the muscles are projections called papillary muscles that connect to the cords of the AV valves. ...
... b. Very muscular walls, especially on the left – why? c. Inner walls have muscle folds called trabeculae carne. Some of the muscles are projections called papillary muscles that connect to the cords of the AV valves. ...
Heart Sound Analysis: Theory, Techniques and Applications
... A feed-forward, back-propagation ANN with one hidden layer The significance of the features and the size of the network were evaluated Training was conducted using 2/3 of the data using errorminimization procedure The NN estimations were averaged for series of beats and compared to the measured PAP ...
... A feed-forward, back-propagation ANN with one hidden layer The significance of the features and the size of the network were evaluated Training was conducted using 2/3 of the data using errorminimization procedure The NN estimations were averaged for series of beats and compared to the measured PAP ...
SKELETAL SYSTEM
... *Avoid Tobacco products and exposure to second hand smoke *Avoid illegal drugs. Including stimulants,, marijuana, and ecstasy *Blood pressure ...
... *Avoid Tobacco products and exposure to second hand smoke *Avoid illegal drugs. Including stimulants,, marijuana, and ecstasy *Blood pressure ...
experiment 4 - heart rate and exercise
... expected? 4. Congestive heart failure is a condition in which the strength of contraction with each beat may be significantly reduced. For example, the ventricle may pump only half the usual volume of blood with each beat. Would you expect a person with congestive heart failure to have a faster or s ...
... expected? 4. Congestive heart failure is a condition in which the strength of contraction with each beat may be significantly reduced. For example, the ventricle may pump only half the usual volume of blood with each beat. Would you expect a person with congestive heart failure to have a faster or s ...
Slide 1
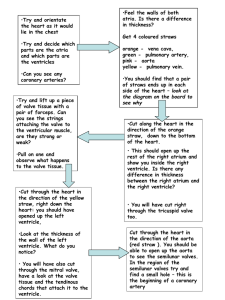
... •Cut along the heart in the direction of the orange straw, down to the bottom of the heart. • This should open up the rest of the right atrium and show you inside the right ventricle. Is there any difference in thickness between the right atrium and the right ventricle? • You will have cut right thr ...
... •Cut along the heart in the direction of the orange straw, down to the bottom of the heart. • This should open up the rest of the right atrium and show you inside the right ventricle. Is there any difference in thickness between the right atrium and the right ventricle? • You will have cut right thr ...
Cardiac Rhythm - WordPress.com
... • Calcium rushes in, causing muscle contraction • Na channels are closing now ...
... • Calcium rushes in, causing muscle contraction • Na channels are closing now ...
Name - Wilson`s Web Page
... What is meant by the phrase “the heartbeat is intrinsic”? What is the difference between systolic and diastolic? List the phases of the cardiac cycle and the length of time required by each phase. What causes the Lubb-Dub sound of a heart beat? List the proper name and common name for the nodal tiss ...
... What is meant by the phrase “the heartbeat is intrinsic”? What is the difference between systolic and diastolic? List the phases of the cardiac cycle and the length of time required by each phase. What causes the Lubb-Dub sound of a heart beat? List the proper name and common name for the nodal tiss ...
Weighing of the Heart Ceremony
... Weighing of the Heart Ceremony Ancient Egyptians believed that all of the good and bad deeds people did during their lifetimes were kept in their hearts. If they lived good lives their hearts would be as light as the “feather of truth” Ma’at wore on her head. Once the mummification process was compl ...
... Weighing of the Heart Ceremony Ancient Egyptians believed that all of the good and bad deeds people did during their lifetimes were kept in their hearts. If they lived good lives their hearts would be as light as the “feather of truth” Ma’at wore on her head. Once the mummification process was compl ...
anatomy and physiology of the cardiovascular system
... FENESTRATED- KIDNEY, SMALL INTESTINE,BRAIN SINUSOIDS- LIVER RED BONE MARROW, SPLEEN AND ...
... FENESTRATED- KIDNEY, SMALL INTESTINE,BRAIN SINUSOIDS- LIVER RED BONE MARROW, SPLEEN AND ...
Circulatory System
... b. Blood pressure (force of blood on walls) is felt in arteries 5. Capillaries – smallest vessels (walls are one cell thick) a. Bring nutrients and oxygen to cells and absorb carbon dioxide and wastes b. Blood cells are carried single file 6. Veins – blood vessels with thin walls and valves to preve ...
... b. Blood pressure (force of blood on walls) is felt in arteries 5. Capillaries – smallest vessels (walls are one cell thick) a. Bring nutrients and oxygen to cells and absorb carbon dioxide and wastes b. Blood cells are carried single file 6. Veins – blood vessels with thin walls and valves to preve ...
ECG NOTES
... • Atrial rate is too fast to count and individual P waves may be difficult to identify. Normal QRS complexes appear at irregular intervals. There will be many more P waves than QRS complexes. May cause blood clots to form and be sent to the brain, heart or lungs. ...
... • Atrial rate is too fast to count and individual P waves may be difficult to identify. Normal QRS complexes appear at irregular intervals. There will be many more P waves than QRS complexes. May cause blood clots to form and be sent to the brain, heart or lungs. ...
The Heart The cardiovascular system is divided into two circuits The
... more rapidly than other cells of the conducting system and thus begin the action potential • The stimulus spreads to the AV node where it is delayed briefly • The impulse then travels through ventricular conducting cells and is distributed by Purkinje fibers ...
... more rapidly than other cells of the conducting system and thus begin the action potential • The stimulus spreads to the AV node where it is delayed briefly • The impulse then travels through ventricular conducting cells and is distributed by Purkinje fibers ...
Introduction to the heart`s electrical conduction system
... The increase in volume of blood in the atria then starts to flow into both ventricles. This is facilitated by contraction of the atrial walls. Once the ventricles are full of blood, they in turn contract and eject their contents. Blood from the right ventricle travels to the lungs to pick up oxygen, ...
... The increase in volume of blood in the atria then starts to flow into both ventricles. This is facilitated by contraction of the atrial walls. Once the ventricles are full of blood, they in turn contract and eject their contents. Blood from the right ventricle travels to the lungs to pick up oxygen, ...
Cardiovascular System aka Circulatory System
... Cardio- means heart Vascular- means blood vessels Aka Circulatory System because its job is to circulate blood throughout the body. Blood carries many materials including: ...
... Cardio- means heart Vascular- means blood vessels Aka Circulatory System because its job is to circulate blood throughout the body. Blood carries many materials including: ...
PSE4U EXERCISE SCIENCE
... ii) Atrioventricular (AV) node – located in the right atrium along the lower part of the iii) Atrioventricular (AV) bundle (Bundle of His) iv) Purkinje fibres cardiac control centre located in the brain (medulla oblongata), the impulse for the heart contraction travels down to the sinoatrial (SA) ...
... ii) Atrioventricular (AV) node – located in the right atrium along the lower part of the iii) Atrioventricular (AV) bundle (Bundle of His) iv) Purkinje fibres cardiac control centre located in the brain (medulla oblongata), the impulse for the heart contraction travels down to the sinoatrial (SA) ...
Aging: Normal And Abnormal
... • Age dependent disease: direct consequence of physiologic senescence • Age related disease: occurs with increasing frequency with age. • The three leading causes of death in people 75 to 84 years of age are heart disease, cancer, and cerebrovascular disease. ...
... • Age dependent disease: direct consequence of physiologic senescence • Age related disease: occurs with increasing frequency with age. • The three leading causes of death in people 75 to 84 years of age are heart disease, cancer, and cerebrovascular disease. ...
Cardiology Notes
... Preoperatively, phenoxybenzamine preoperative adrenergic-blockade of a1 and a2 receptors with phenoxybenzamine (10-30 mg twice daily), or a1 receptors with prazosin (starting with 1 to 2 mg three times daily. Beta blockers can be useful for arrhythmias, but should not be commenced before alpha bloc ...
... Preoperatively, phenoxybenzamine preoperative adrenergic-blockade of a1 and a2 receptors with phenoxybenzamine (10-30 mg twice daily), or a1 receptors with prazosin (starting with 1 to 2 mg three times daily. Beta blockers can be useful for arrhythmias, but should not be commenced before alpha bloc ...
Cardiovascular system
... Blood flow is regulated to meet these demands through the control of heart rate and stroke volume under the influence of the autonomic nervous system and the hormone adrenaline. ...
... Blood flow is regulated to meet these demands through the control of heart rate and stroke volume under the influence of the autonomic nervous system and the hormone adrenaline. ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.