Plants and Pollinators
... returns to blood by way of lymphatic system • High blood pressure causes excessive ultrafiltration and results in edema ...
... returns to blood by way of lymphatic system • High blood pressure causes excessive ultrafiltration and results in edema ...
Chapter 39- The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... 12. List the two types of valves in the heart and their names. ...
... 12. List the two types of valves in the heart and their names. ...
Slide ()
... A. Left ventricular pressure–volume (P–V) loop, the segments of which correspond to events of the cardiac cycle: diastolic ventricular filling along the passive P–V curve (phase I), isovolumetric contraction (phase II), ventricular ejection (phase III), and isovolumetric relaxation (phase IV). B. Th ...
... A. Left ventricular pressure–volume (P–V) loop, the segments of which correspond to events of the cardiac cycle: diastolic ventricular filling along the passive P–V curve (phase I), isovolumetric contraction (phase II), ventricular ejection (phase III), and isovolumetric relaxation (phase IV). B. Th ...
Physiology of the Cardiovascular System
... repolarized and ventricular walls are completely depolarized ...
... repolarized and ventricular walls are completely depolarized ...
ASD ptient information leaflet - St Helens and Knowsley Teaching
... through the lungs than would normally. If left untreated, the ASD may cause problems in adulthood. These problems may include pulmonary hypertension (which is high blood pressure in the lungs), congestive heart failure (which is weakening of the heart muscle), atrial arrhythmias (abnormal rhythms or ...
... through the lungs than would normally. If left untreated, the ASD may cause problems in adulthood. These problems may include pulmonary hypertension (which is high blood pressure in the lungs), congestive heart failure (which is weakening of the heart muscle), atrial arrhythmias (abnormal rhythms or ...
atrioventricular septal defect (avsd)
... this small defect will often not cause many symptoms but may require closing later in childhood. If the defect involves the ventricles as well as the atria, this large hole in the middle of the heart allows oxygen rich blood from the left side of the heart to pass into the right side of the heart. T ...
... this small defect will often not cause many symptoms but may require closing later in childhood. If the defect involves the ventricles as well as the atria, this large hole in the middle of the heart allows oxygen rich blood from the left side of the heart to pass into the right side of the heart. T ...
Medicinea4
... Salvarsan and Prontosil Paul Ehrlich, the German bacteriologist, studied arsenic compounds for their anti-bacterial properties and invented Salvarsan in 1909 as a successful treatment for the fatal, sexually transmitted disease, syphilis. This strategy was followed by other researchers to find activ ...
... Salvarsan and Prontosil Paul Ehrlich, the German bacteriologist, studied arsenic compounds for their anti-bacterial properties and invented Salvarsan in 1909 as a successful treatment for the fatal, sexually transmitted disease, syphilis. This strategy was followed by other researchers to find activ ...
Heart Transplantation
... A heart transplant or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant method used on patients when they have heart failure or severe coronary artery disease. ...
... A heart transplant or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant method used on patients when they have heart failure or severe coronary artery disease. ...
Circulatory System
... • Also called the circulatory system • Consists of the heart, blood vessels & blood. • It carries needed substances to cells and carries waste products away. • Blood contains cells that fight disease. ...
... • Also called the circulatory system • Consists of the heart, blood vessels & blood. • It carries needed substances to cells and carries waste products away. • Blood contains cells that fight disease. ...
Chemistry
... You must answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper in complete sentences! 1. Describe the flow of blood through both the Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits. a. As you describe the blood flow, you must name each chamber, valve, artery and vein in the heart that blood travels through. 2. Explai ...
... You must answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper in complete sentences! 1. Describe the flow of blood through both the Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits. a. As you describe the blood flow, you must name each chamber, valve, artery and vein in the heart that blood travels through. 2. Explai ...
Blood Vessels
... Skeleton of Heart Fibrous rings around AV and semilunar valves Muscle of atria and ventricles attach to rings Prevent conduction of impulse from atria to ventricles ...
... Skeleton of Heart Fibrous rings around AV and semilunar valves Muscle of atria and ventricles attach to rings Prevent conduction of impulse from atria to ventricles ...
Click Here for Doc File
... Product Description : Verapamil is an L-type calcium channel blockerof the phenylalkylamine class. It has been used in the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, cardiac arrhythmia, and most recently, cluster headaches. It is also an effective preventive medication for migraine. Verapamil has a ...
... Product Description : Verapamil is an L-type calcium channel blockerof the phenylalkylamine class. It has been used in the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, cardiac arrhythmia, and most recently, cluster headaches. It is also an effective preventive medication for migraine. Verapamil has a ...
Laboratory Exercise 13: Cardiac Physiology
... The heart rate of a resting individual varies with body position, some postures place more stress on the cardiovascular system than others. A move from a horizontal (supine) to an upright position (sitting or standing) causes an immediate drop in the blood volume within vessels of the upper body due ...
... The heart rate of a resting individual varies with body position, some postures place more stress on the cardiovascular system than others. A move from a horizontal (supine) to an upright position (sitting or standing) causes an immediate drop in the blood volume within vessels of the upper body due ...
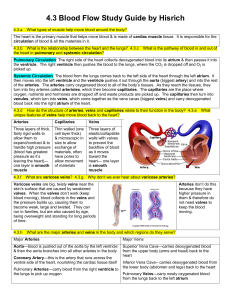
4.3 Blood Flow Study Guide by Hisrich
... listens to the pulse in that region. Arteriosclerosis (“abnormal condition of hard arteries”) & atherosclerosis (“hard arteries due to fat deposits”) can both impede blood flow by making the arteries more narrow (that’s atherosclerosis) and less flexible (that’s arteriosclerosis). That can lead to p ...
... listens to the pulse in that region. Arteriosclerosis (“abnormal condition of hard arteries”) & atherosclerosis (“hard arteries due to fat deposits”) can both impede blood flow by making the arteries more narrow (that’s atherosclerosis) and less flexible (that’s arteriosclerosis). That can lead to p ...
D Prabhakaran DM, FRCP, FNASc Discussant: Low
... • Benefit unlikely in very low risk population ( <1% events per year) • Role in special groups, younger populations not evaluated well ( eg: LMIC/LIC; ethnicities with high risk for CHD ) • Risk scores needed for LMIC for identification of high risk subjects • Await results of other studies in prima ...
... • Benefit unlikely in very low risk population ( <1% events per year) • Role in special groups, younger populations not evaluated well ( eg: LMIC/LIC; ethnicities with high risk for CHD ) • Risk scores needed for LMIC for identification of high risk subjects • Await results of other studies in prima ...
4.3 Blood Flow Study Guide by Hisrich
... listens to the pulse in that region. Arteriosclerosis (“abnormal condition of hard arteries”) & atherosclerosis (“hard arteries due to fat deposits”) can both impede blood flow by making the arteries more narrow (that’s atherosclerosis) and less flexible (that’s arteriosclerosis). That can lead to p ...
... listens to the pulse in that region. Arteriosclerosis (“abnormal condition of hard arteries”) & atherosclerosis (“hard arteries due to fat deposits”) can both impede blood flow by making the arteries more narrow (that’s atherosclerosis) and less flexible (that’s arteriosclerosis). That can lead to p ...
The Division of Cardiology of the Children`s Hospital of Philadelphia
... It is estimated that sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) claims the life of up to 7,000 children and adolescents each year in the US, accounting for 5-10% of childhood deaths annually. The most common causes of SCA in children are hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) (33-50%), other cardiomyopathies (10-20%), ...
... It is estimated that sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) claims the life of up to 7,000 children and adolescents each year in the US, accounting for 5-10% of childhood deaths annually. The most common causes of SCA in children are hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) (33-50%), other cardiomyopathies (10-20%), ...
Name Circulation Web Quest Date______ Part I: Parts of the Heart
... system to give oxygen to all of your cells?___________________________ Now click on “Heart Main Page” and go to the “Interactive Labels” Link 2. Roll your cursor over the heart to IDENTIFY the parts of the human heart! In addition, circle the part with a BLUE pen or pencil to represent DEOXYGENATED ...
... system to give oxygen to all of your cells?___________________________ Now click on “Heart Main Page” and go to the “Interactive Labels” Link 2. Roll your cursor over the heart to IDENTIFY the parts of the human heart! In addition, circle the part with a BLUE pen or pencil to represent DEOXYGENATED ...
Curing Cancer and Caring for the Heart: Advancing
... She has no past medical history and is not taking any medications. Her family history is significant for cardiac disease in her father. Her social history is unremarkable. Her baseline and post-doxorubicin echocardiograms demonstrate a normal heart function, as assessed by left ventricular eje ...
... She has no past medical history and is not taking any medications. Her family history is significant for cardiac disease in her father. Her social history is unremarkable. Her baseline and post-doxorubicin echocardiograms demonstrate a normal heart function, as assessed by left ventricular eje ...
Atrial Fibrilation And Whole Body Vibration1
... Atrial Fibrillation and Whole Body Vibration Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a type of arrhythmia that involves abnormal electrical signals arising from the atrium of the heart. These signals are sent to the ventricles of the heart at irregular intervals resulting in an irregular, fast heart rate. It is ...
... Atrial Fibrillation and Whole Body Vibration Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a type of arrhythmia that involves abnormal electrical signals arising from the atrium of the heart. These signals are sent to the ventricles of the heart at irregular intervals resulting in an irregular, fast heart rate. It is ...
File
... - The heart muscle depolarises (loses electrical charge) when it contracts, and repolarises (regains charge) when it relaxes. - Patches with wires are placed on the patients chest and wires are connected to a monitor. - Electric charges are recorded by an electrocardiograph, as a electrocardiogram/E ...
... - The heart muscle depolarises (loses electrical charge) when it contracts, and repolarises (regains charge) when it relaxes. - Patches with wires are placed on the patients chest and wires are connected to a monitor. - Electric charges are recorded by an electrocardiograph, as a electrocardiogram/E ...
Guide to Transthoracic Echocardiography
... A transthoracic echocardiogram (also called an "echo") is an ultrasound examination of the heart. Ultrasound (high frequency sound waves-‐not heard by the human ear) is sent into the body to outline tissu ...
... A transthoracic echocardiogram (also called an "echo") is an ultrasound examination of the heart. Ultrasound (high frequency sound waves-‐not heard by the human ear) is sent into the body to outline tissu ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.